The Mirena IUD is a contraceptive considered very safe and long-lasting. Find out more about this hormonal contraceptive, its advantages and disadvantages.
Have you ever heard of the so-called Mirena IUD? There are currently a considerable number of contraceptive methods, and this type of IUD is one of the most famous. Although they all have the same purpose, each of them acts in a different way.
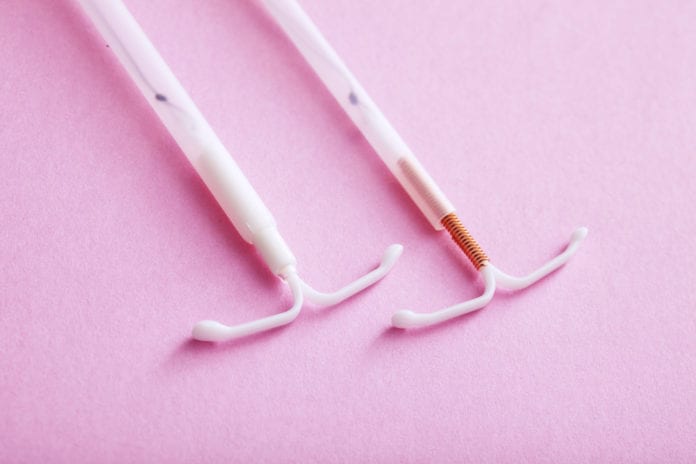
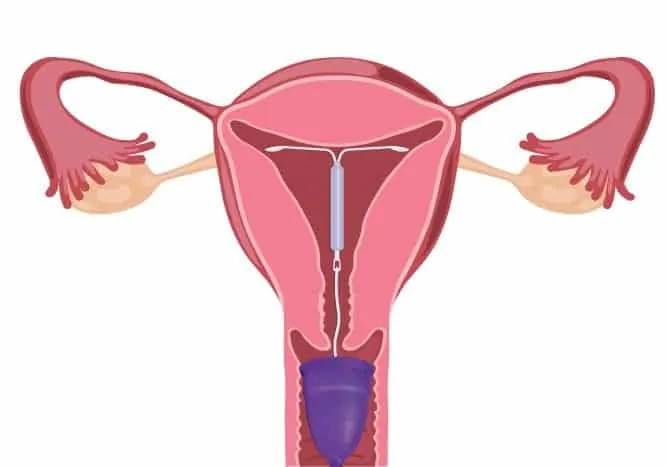
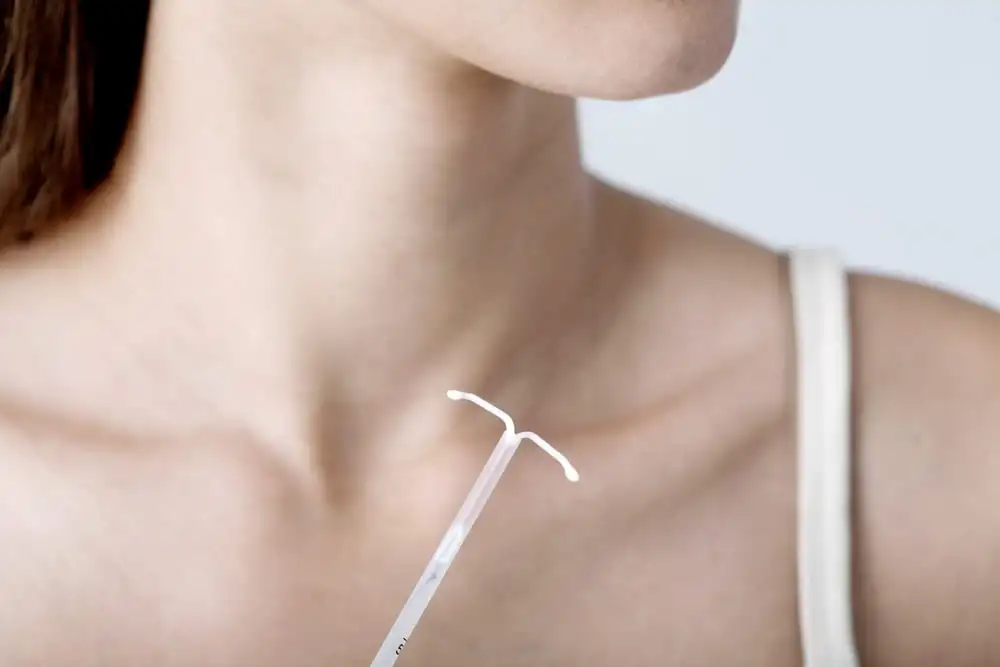
In the case of the IUD, for example, it is a small T-shaped plastic object inserted inside the uterus. As it is an Intrauterine Device, much is said about the effectiveness of the IUD.
However, several doubts arise about it, ranging from the correct way to introduce it to its specific characteristics, which change according to the type. Today we have three types available: the Copper IUD, the Mirena IUD and the new favorite, the Kyleena IUD.
Firstly, the non-hormonal IUD (the copper one) acts exclusively as a mechanical barrier that prevents male genetic material from accessing the egg. The Mirena IUD, in addition to providing this contraceptive barrier, can also be used to treat some diseases. This is because it is a method that uses hormones. The Kyleena IUD, like the Mirena, also uses hormones.
Anyway, today we are going to talk about this second method. We will tell you how it works, what its advantages and disadvantages are. In fact, we will also explore some myths and curiosities about the Mirena IUD.
What is a Mirena IUD?
First of all, the hormonal IUD, popularly known as the Mirena IUD or SIU, is a contraceptive method considered very safe. This is because the device produces inflammatory reactions in the uterus, due to its structure containing the hormone progesterone. Approximately, the product contains about 52 mg of this hormone.
This hormone, in turn, is released little by little during use. As a result, a small amount of the substance is absorbed into the bloodstream, on average 20 mcg per day. However, like the copper IUD, its purpose is to prevent pregnancy.
As safe as this method is, it is not free from side effects. According to the Mirena IUD leaflet itself, around two-thirds of women who use the device experience blocked menstruation.
The positive point is that the chances of getting pregnant using the Mirena IUD drop to 0.2%. But, in addition, it can also be indicated as a treatment in cases of uterine fibroids, endometriosis and adenomyosis.
In the case of excessive idiopathic menstrual bleeding, levonorgestrel works to reduce bleeding. And, more than that, hormonal contraceptives also relieve menstrual cramps.
In other words, the Mirena IUD works through the action of hormones, making ovulation difficult. In other words, it prevents eggs from attaching to the uterus, thickening the mucus in the cervix, forming a kind of barrier that prevents sperm from reaching there.
Furthermore, the Mirena IUD has a protective effect of up to 5 years. In other words, it is one of the most suitable methods for those looking for a safe and long-term form of hormonal contraception.
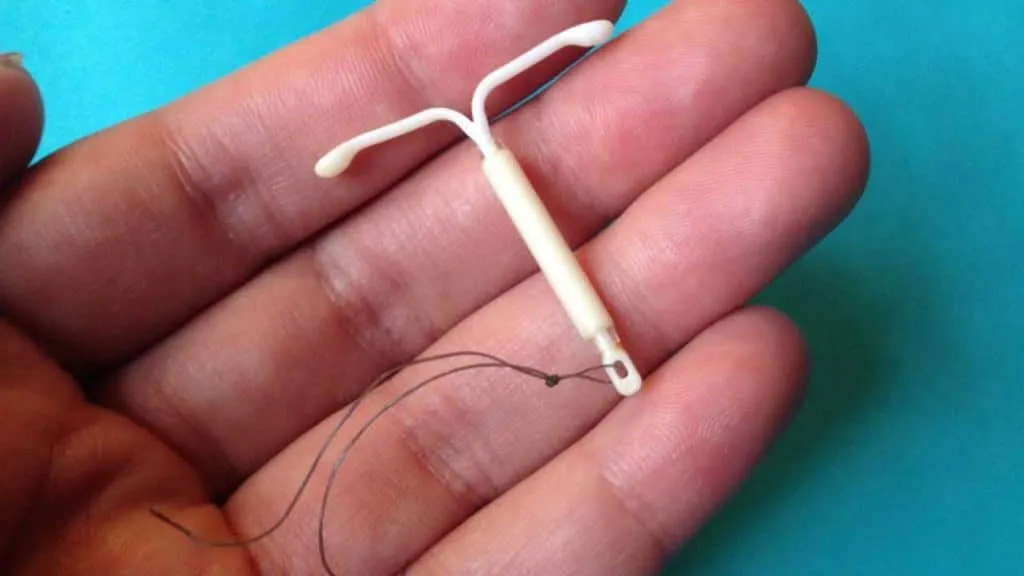
How is the Mirena IUD inserted?
Before choosing to use the Mirena IUD, a doctor’s evaluation is necessary. He is the one who will tell you whether this method is suitable for you, based on your medical history and needs.
Once this is done, the Mirena IUD is inserted, in the office, by a gynecologist. The process is carried out by the female organ, and lasts from 15 to 30 minutes, maximum. There is no need for anesthesia, and the woman will only feel slight discomfort during the procedure.
Regarding its effectiveness, as we have already mentioned, the effect of Mirena lasts up to 5 years. However, if the woman changes her mind, it can be removed at any time. Again, with the help of a medical professional.
After removing the IUD, its contraceptive effect soon wears off. Therefore, the woman is able to get pregnant normally, like those who did not use contraceptives.
Although it is a very effective method, the Mirena IUD is not suitable for all women. Therefore, a medical evaluation is essential before using it, to know exactly whether this is the correct contraceptive method for the patient.
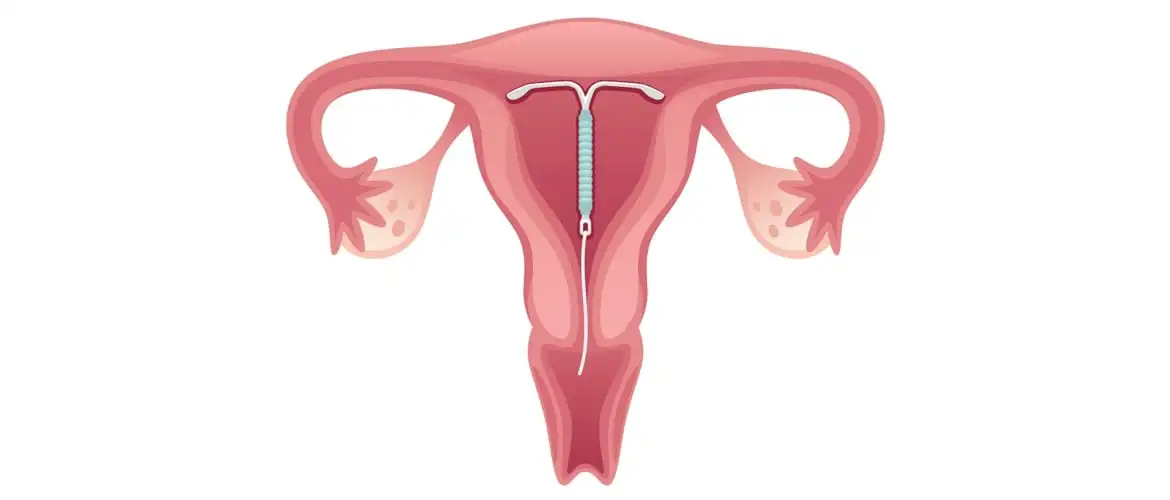
When to insert the Mirena IUD?
Before placing the device, you must make sure that the patient is not pregnant. After confirmation, the hormonal IUD can be inserted at any time during the menstrual cycle.
However, it is generally placed during menstruation. This is because, during this period, the cervix becomes more dilated, which facilitates its insertion. And, regardless of the phase of the menstrual cycle, its effectiveness is immediate.
Mirena IUD x Birth Control Pill
Although both are contraceptive methods, each of them acts in a different way in the body. Therefore, it is difficult to compare them. This is because each of them has different concentrations of hormones.
However, the hormonal IUD releases 20 mcg of levonorgestrel per day, and the common pill usually has only 0.1 mg of this hormone. In this case, the IUD has a much greater load of female hormones. Therefore, each case must be studied so that recommendations for use of either the IUD or contraceptive are appropriate.
When should the Mirena IUD not be used?
In general, this device can be used by women over 14 years old and who have an active intimate life. However, as we have already said here, it is not recommended for all cases, with some exceptions. Therefore, the Mirena IUD is not indicated if the woman:
- You are pregnant or suspect that you may be pregnant;
- Have current or recurrent pelvic inflammatory disease;
- Have a lower genital tract infection;
- Have a uterus infection;
- Have a cervical infection;
- Notice cellular abnormalities in your cervix;
- You have or are suspected of having cervical cancer;
- Have hormone-dependent tumors;
- Have undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding;
- You have an abnormality of the cervix or uterus, including fibroids, if these cause deformation of the uterine cavity;
- Have conditions associated with increased susceptibility to infections;
- Have liver disease or tumor;
- Know that you are allergic to levonorgestrel or any component of the product.
Possible side effects of the Mirena IUD
Like most contraceptive methods, the Mirena IUD can also have side effects. These include:
- Uterine pain or contractions, more common in women who have never had children;
- Small bleeding shortly after insertion of the IUD;
- Fainting;
- Vaginal discharge.
However, the hormonal IUD can also cause a reduction in menstrual flow or even the absence of menstruation. In some cases, only small amounts of menstrual blood appear.
Other effects can be noticed with an increase in pimples, headaches, pain and breast tension, fluid retention, ovarian cysts and even weight gain. However, it is not certain that you will have these effects if you use an IUD, as they are just common effects that vary depending on each woman’s body.
Advantages and disadvantages of the Mirena IUD
Not unlike other contraceptive methods, the Mirena IUD also has advantages and disadvantages. So, before choosing to use it, it is important to know what the positive and negative points are.
Advantages of the Mirena IUD
- Reduction or even suspension of menstruation;
- Benefit for women with endometriosis or who are in the transition phase after menopause;
- Protection against endometrial cancer.
Disadvantages of the Mirena IUD
- Causes changes in mood and libido, due to hormones;
- It is more expensive compared to the Copper IUD;
- Its effectiveness may be affected by antiepileptics (phenobarbital, phenytoin, carbamazepine), antituberculostatics (rifampicin), antiretrovirals (ritonavir or nevirapine) and antibiotics (e.g. rifampicin, rifabutin, nevirapine, efavirenz).
4 Facts about the Mirena IUD you need to know
1. Mirena IUD placement is not painful
A concern for almost all women, after all, is the placement of the device, whether there is any discomfort or pain. However, its placement is well accepted by most of them, with not many complaints. In fact, what may occur is discomfort and dizziness after placement, which is normal.
2. The Mirena IUD does not harm intimate relationships
Another important point is about interference in the relationship. Generally, the device does not interfere at all, as it is not even felt. However, if there is any discomfort or pain during the act, or even if you feel its presence, the ideal is to see a gynecologist to check if the device is positioned correctly.
3. Tampons or menstrual cups do not affect the Mirena IUD
As the IUD is positioned inside the uterus, and the tampon and collector do not reach this depth, there is therefore no contact between them. This is because the cervix sits between the two, separating them. However, care must still be taken to ensure that the absorbent or collector does not pull the IUD removal threads.
4. The Mirena IUD does not protect against STIs
Just like any other contraceptive or hormonal contraceptive method, the Mirena IUD does not protect against sexually transmitted infections. Therefore, you should not be careless when it comes to sexual intercourse and always use condoms, both male and female, to maintain safe sex.
Myths related to the IUD
- They rarely lead to Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID);
- They do not increase the risk of contracting STIs, including HIV;
- They do not increase the risk of miscarriage when a woman becomes pregnant after the IUD is removed;
- The IUD does not make a woman sterile;
- They do not cause birth defects or malformations;
- Contraceptives do not cause cancer;
- They do not travel to the heart or brain;
- They do not cause discomfort or pain to the woman during intercourse;
- They substantially reduce the risk of ectopic pregnancy (a complication in which the embryo forms outside the uterus).
Anyway, now that you are familiar with the Mirena IUD, it might be interesting to know more about the morning-after pill.
Sources: ABC Med, Minha Vida, Tua Saúde
Featured Image Source: Women’s Health

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13