The menstrual cycle is the time interval between the first day of menstruation and the last day before the next menstruation.
The menstrual cycle lasts an average of 28 days and is divided into 3 phases, according to the hormonal changes that occur in the woman’s body. Menstruation represents the fertile years of a woman’s life, which begin in adolescence and last until menopause.
It is normal for cycle length to vary between 21 and 35 days, but cycles with shorter or longer intervals may be a sign of a health problem, such as polycystic ovary syndrome. Therefore, in case of doubt or changes in the cycle, it is important to consult a gynecologist.
Menstrual cycle calculator
To find out when your next period will be, fill in the data in the calculator:
If you want to know when your most fertile period will be, please use the fertile period calculator.
How long does the menstrual cycle last?
The normal menstrual cycle lasts an average of 28 days, starting on the first day of menstruation and ending when the following month’s menstruation begins.
Still, some women may have shorter or longer cycles, which tend to vary between 21 and 35 days. Cycles with durations outside this range should be evaluated by a gynecologist.
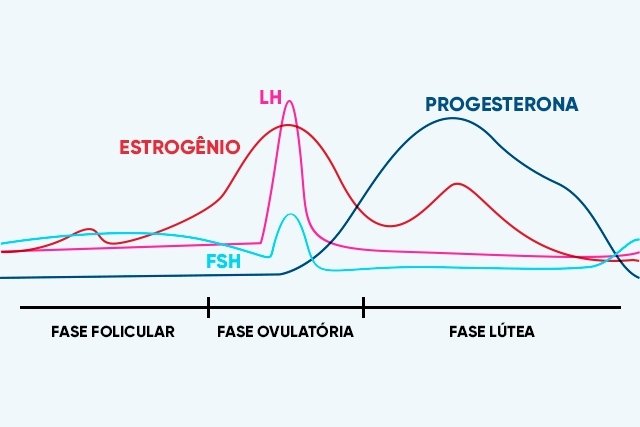
Menstrual cycle hormones
The menstrual cycle is regulated by the increase and decrease in the production of hormones, such as FSH, LH, estrogens and progesterone:
- FSH: this hormone, also known as follicle-stimulating hormone, is produced by the pituitary gland and its function is to regulate the maturation of the ovaries;
- LH: this hormone, also called luteinizing hormone, is responsible for the maturation of follicles, ovulation and production of progesterone, being fundamental for a woman’s reproductive capacity;
- Estrogens: These hormones are responsible for regulating the hormonal cycle during childbearing age. During puberty, estrogens stimulate breast development and the maturation and development of the reproductive system;
- Progesterone: This hormone is produced by the ovaries and is important for regulating a woman’s menstrual cycle and preparing the uterus to receive the fertilized egg. Levels of this hormone increase shortly after ovulation and remain high during pregnancy. However, if there is no pregnancy, there is a decrease in the concentration of progesterone, leading to the elimination of the lining of the uterus, characterizing menstruation.
Furthermore, androgenic hormones are also part of the menstrual cycle, are produced in the ovary and serve to form estrogen hormones and promote muscle and bone growth. Testosterone is the main androgenic hormone in women, being found in lower quantities.
Phases of the menstrual cycle
Each menstrual cycle is divided into 3 phases:
1. Follicular phase
This is the first phase of the cycle, which begins on the first day of menstruation and lasts between 5 and 12 days. At this stage, the brain increases the production of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which causes the ovaries to mature their eggs.
With this maturation, the ovary also begins to release greater amounts of estrogen, which is another hormone, responsible for making the lining of the uterus ready for a possible pregnancy.
2. Ovulatory phase
At this stage, estrogen levels continue to increase and lead the body to produce luteinizing hormone (LH) in greater quantities, which is responsible for selecting the most mature egg and making it leave the ovary, which is when ovulation occurs, generally , around day 14 of the cycle.
Once released, the egg travels through the tubes until it reaches the uterus. Normally, the egg survives for 24 hours outside the ovary and, therefore, if it comes into contact with sperm, it can be fertilized. Since sperm can last up to 5 days inside a woman’s body, it is possible that if a woman has had unprotected sex up to 5 days before ovulation, she could become pregnant.
3. Luteal phase
This phase occurs, on average, in the last 12 days of the cycle and, during these days, the follicle, left by the egg inside the ovary, begins to produce progesterone in greater quantities, to continue preparing the lining of the uterus in the event of a possible pregnancy. In addition, there is also an increase in estrogen production and, as a result, some women may experience breast tenderness, mood changes and even swelling.
When fertilization does not occur, the follicle shrinks inside the ovary and, therefore, estrogen and progesterone levels decrease until the lining of the uterus is eliminated, starting menstruation and the next menstrual cycle.
If fertilization occurs, the egg becomes attached to the walls of the uterus and the body begins to produce hCG, a hormone that keeps the follicle producing estrogen and progesterone at high levels to maintain the lining of the uterus until the placenta is formed.
How to count the cycle
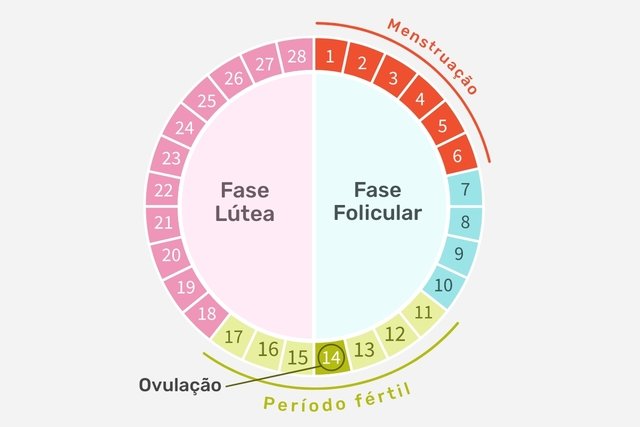
To count how many days the menstrual cycle lasts, you must consider the time interval between the first day of menstruation and the day before the next menstruation.
For example: If a woman menstruated on day 5, the first day of menstruation should be considered day 5. If the next menstruation occurs on day 30, the cycle should end on day 29. In this case, the menstrual cycle is 25 days (including the 5th and the 29th).
This type of calculation works best for women who have a regular menstrual cycle. Anyone who has an irregular cycle should take an average of the number of days in each cycle over a given period of time. For example, for 3 or 6 months you should write down the duration of each cycle and, at the end, add up the total number of days and divide by the number of cycles you had. See how to calculate the fertile period in an irregular cycle.
Fertile period symptoms
The signs and symptoms that may indicate that a woman is in her fertile period are: transparent discharge similar to egg white; increased sensitivity of the breasts and slight pain in the uterine region, similar to a mild cramp.
In addition to these signs, it is also possible to identify ovulation through the ovulation pharmacy test. See how to use the ovulation test.
Irregular menstrual cycle
An irregular menstrual cycle is one in which you don’t know when your period will come. The most common causes of irregular cycle are:
- Beginning of fertile life in adolescence, up to 2 years after the first menstruation;
- Post-pregnancy period;
- Pre-menopause, due to intense hormonal changes;
- Eating disorders that cause excess weight loss, such as anorexia nervosa;
- Excessive intense physical activity, especially in female athletes;
- Hyperthyroidism;
- Polycystic ovary;
- Change of contraceptive;
- Stress or emotional disturbances;
- Presence of inflammation, polyps or tumors in the female reproductive system.
In the presence of an irregular menstrual cycle or when the menstrual cycle does not occur for more than 3 months, you should consult a gynecologist to investigate the cause of the problem. See 10 myths and truths about Menstruation.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13