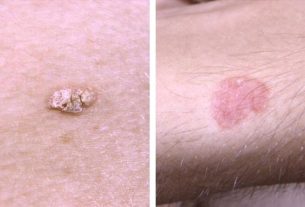
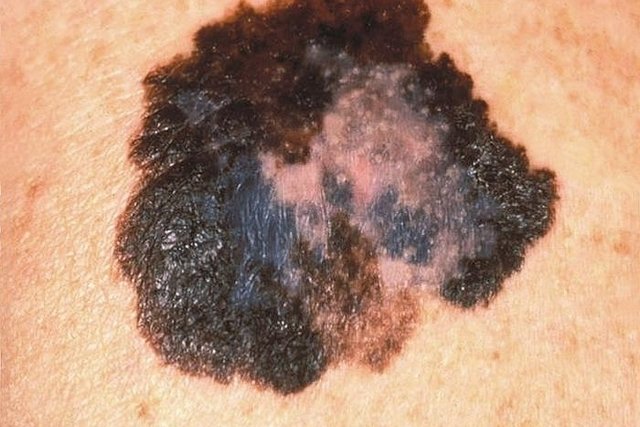
Melanoma is a malignant skin cancer that develops in melanocytes, which are the skin cells responsible for producing melanin, the substance that gives color to the skin, and can be identified through symptoms such as moles, spots or asymmetrical signs on the skin, with irregular edges and different colors, for example.
This type of skin cancer is more common in adults with lighter skin, and in areas of the skin more exposed to UV radiation from the sun or artificial tanning. However, despite being rarer, melanoma can also appear in the eyes, nails, mucous membranes of the mouth, nose, throat, anus, vagina or gastrointestinal tract.
Melanoma is an aggressive cancer that can spread to other organs and, therefore, at the first sign of a change in the skin, spots or growth appear. spots, you should consult a dermatologist to identify melanoma early, facilitating treatment and increasing the chances of a cure.
Melanoma symptoms
The main symptoms of melanoma are spots, spots or moles on the skin with the following characteristics:
- Asymmetry, in which half of the stain is different from the other;
- Irregular edges or contours;
- Different colors, such as red, blue, brown, black or white;
- Diameter greater than 6 mm;
- Raised surface;
- Increase in size, change in color or shape;
- Itching or easy bleeding;
- Wounds that take a long time to heal or ulcers.
These symptoms may appear in a mole or spot on new or existing skin, or on mucous membranes or nails.
Furthermore, other symptoms may also appear in the case of metastases, which vary according to the affected organ, such as lungs, brain, liver, bones or intestine, for example. Check out the main symptoms of metastatic melanoma.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of melanoma is made by a dermatologist or oncologist through the evaluation of the characteristics of the mole, mole or spot on the skin using the ABCDE method and the use of a dermatoscope, in addition to an evaluation of the health history and physical examination of the lymph nodes.
If you have signs and symptoms of melanoma, make an appointment with the dermatologist in the nearest region:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor must perform a skin biopsy, removing a sample or the entire mole, lesion or patch of skin, to be analyzed in the laboratory and check for the presence of malignant cells. Find out how a skin biopsy is performed.
Possible causes
Melanoma is caused by damage to melanocytes, which are skin cells responsible for producing the melanin that gives color to the skin, which begin to multiply quickly, abnormally and out of control.
This damage is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, mainly exposure to UV rays from the sun or tanning beds.
Melanoma can appear anywhere on the body, even in places that are not exposed to UV radiation, such as the eyes or mucous membranes such as the mouth, nose, throat, anus, vagina or gastrointestinal tract, for example.
Who is most at risk of getting melanoma
Some factors that can increase the risk of developing melanoma are:
- Family history of melanoma;
- Fair skin, blonde or red hair and blue eyes;
- Easy sunburn or history of sunburn;
- Freckles or benign and/or dysplastic melanocytic nevi;
- Having many unusual spots or blemishes on your skin;
- People who have had a transplant or have blood cancer.
People with 1 or more of these factors should make regular appointments with a dermatologist to have a complete skin assessment in order to identify possible changes that could be an early sign of cancer.
Main types
The types of melanoma vary according to the place of emergence and the way in which it develops, the main types being:
1. Extensive superficial melanoma
Superficial extensive melanoma is the most common type of melanoma and initially develops in the most superficial cells of the skin, and can spread to deeper regions of the skin.
This type of melanoma begins as brown or light brown areas on the skin or as small red, white, black, or blue dots.
2. Melanoma nodular
Nodular melanoma is the second most common type of melanoma and the most aggressive as it grows quickly and can affect other parts of the body from the beginning.
This type of cancer begins as a hard, raised spot or lump that is black, bluish, or bluish-red in color and causes no symptoms. However, it is an easy tumor to identify due to the rapid increase in size of the lesion.
3. Lentigo maligna melanoma
Lentigo maligna melanoma generally occurs in areas that are most exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, scalp and back of the hands, and is more common in elderly people with skin that is very damaged by the sun.
This type of melanoma can invade deeper layers of the skin and begins with a flat spot on the skin, brown or black, with irregular margins and different colors such as dark brown or black dots on its surface.
4. Acral lentiginous melanoma
Acral lentiginous melanoma is rarer and initially affects the most superficial layers of the skin, especially the palms of the hands, soles of the feet and nails, with melanoma being more common in blacks, Asians and Hispanics.
5. Melanoma subungueal
Subungual melanoma is a rare type of melanoma that appears under the nail and can be initially identified by the presence of a dark vertical spot on the nail that increases over time. See how to identify subungual melanoma.
6. Melanoma ocular
Ocular melanoma that develops in the iris of the eye, which is the colored part of the eye, or in the uvea which is tissue under the white part of the eye.
This type of melanoma can cause symptoms such as blurred vision, flashing lights, visual field defects, irritation, redness, pain, or a feeling of pressure in the eye.
How the treatment is carried out
The treatment of melanoma depends on the size, stage of the cancer, and the person’s health status. It should be guided by an oncologist or dermatologist, and may be recommended:
- Surgery for melanoma removal;
- Immunotherapy to help the immune system fight cancer;
- Target therapy which acts directly on melanoma cells;
- Radiotherapy which can be done if it is not possible to remove the melanoma completely by surgery or to treat the lymph nodes affected by the melanoma;
- Chemotherapy to kill melanoma cells and can be administered directly into a vein or taken orally as tablets.
If metastases exist, chemotherapy and radiotherapy should be started as soon as possible. However, success rates are relatively low, as metastases appear in more advanced stages of cancer. See more about skin cancer treatment.
Is melanoma curable?
Melanoma has a high cure rate when it has not yet spread to other parts of the body and when the diagnosis is made as soon as the first sign appears. Therefore, it is very important to frequently observe skin signs and blemishes, looking for changes.
Furthermore, people who have already had some type of skin cancer or who have cases in their family should see a dermatologist regularly, as they have a higher risk of developing melanoma.
How to prevent melanoma
Some measures can help prevent or reduce the risk of developing melanoma, such as:
- Avoid the sun during peak hours between 10 am and 4 pm;
- Use sunscreen dailywith at least SPF 30, even on cloudy days;
- Wear a hat with brims if it is unavoidable to expose yourself to the sun;
- Avoid artificial tanning.
In addition, the skin of the entire body should be frequently examined, especially the areas most exposed to the sun such as the face, neck, ears and scalp, looking for changes such as the appearance of blemishes, moles, freckles, swelling or changes in skin marks. existing births. Find out how to prevent skin cancer.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13