Lupus is an autoimmune disease that causes defense cells to attack healthy cells in the body, which can cause inflammation in various parts of the body, especially joints, skin, kidneys, bone marrow, heart, lungs, eyes and brain.
Lupus is more common in young women, between 14 and 45 years old, but its symptoms can appear from birth until very old ages. However, in milder cases it is common for the disease to take a while to be diagnosed, but due to an infection, the use of some medications or even excessive exposure to the sun, more intense crises can occur.
Although lupus has no cure, there are some treatments, recommended by a rheumatologist, that help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life, and the use of anti-inflammatory medications, corticosteroids or immunosuppressants may be recommended.
Main symptoms
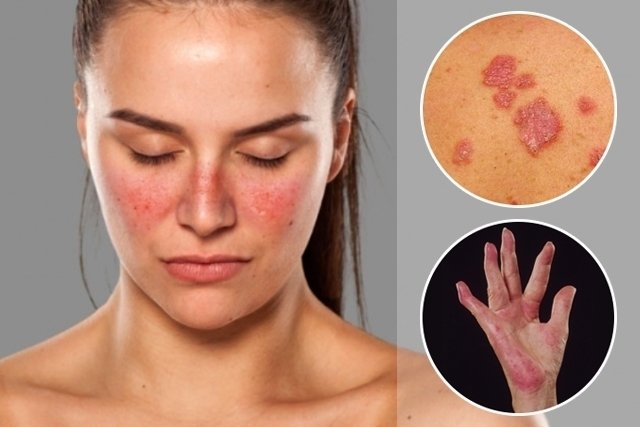
The most common symptoms of lupus include:
- Red spots on the skin, especially on the butterfly-shaped face and other places exposed to the sun;
- Greater sensitivity to light;
- Fever and generalized malaise;
- Weight loss and abdominal pain;
- Loss of hair;
- Blurry vision;
- Ulcers in the mouth or throat;
- Joint pain or inflammation;
- Mental changes, such as depression or psychosis;
- Kidney changes, such as glomerulonephritis, also called lupus nephritis.
These symptoms normally appear in crises, that is, they appear intensely for a few days or weeks and then reduce in intensity again, and may even disappear, but there are also cases in which the symptoms remain constant. Learn more about the symptoms of lupus.
Don’t ignore the signs your body is giving you!
Online symptom test
To find out your risk of having lupus, select the symptoms presented in the following test:
The symptom test is only a guidance tool and does not replace consultation with a dermatologist, rheumatologist or general practitioner.
Types of lupus
Depending on the characteristics of the symptoms and cause, the main types of lupus are:
1. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is characterized by inflammation in various parts and organs of the body, especially the skin, joints, heart, kidneys and lungs, causing spots on the skin exposed to the sun, joint symptoms such as arthritis, anemia, decreased blood cells. defense and platelets, and changes in the central nervous system, mainly.
Read too: Types of lupus: main symptoms (and treatment)
2. Discoid or cutaneous lupus
Discoid or cutaneous lupus causes lesions to appear only on the skin, not affecting other organs. This type of lupus causes red plaques to appear on the skin, especially on the scalp and face. However, some people with discoid lupus may develop systemic lupus over time. Learn more about discoid lupus.
3. Drug-induced lupus
Drug-induced lupus can generate manifestations throughout the body, such as systemic lupus, or just in the skin, such as discoid lupus, and occurs due to the use of certain medications, for example: hydralazine, procainamide or isoniazid. There is usually temporary inflammation and the symptoms disappear a few months after stopping the medication.
4. Neonatal lupus
Neonatal lupus is one of the rarest types of lupus, but it can happen in babies born to women with lupus.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of lupus must be made by a rheumatologist or dermatologist initially based on the signs and symptoms presented by the person and a physical examination.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor must recommend carrying out common laboratory tests, such as blood count and urine tests, as well as more specific tests that allow evaluating the presence of antibodies that can be produced in this disease, such as the antinuclear antibody test (ANA). ), anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies, anti-Smith (SM) antibodies and antiphospholipid antibodies, for example.
Read too: FAN exam: what it is, what it is for and results
Possible causes
Lupus is an autoimmune disease and its exact cause is not known, however, it is believed that it is normally caused by external stimuli (such as sunlight, medications or infections) in people with a certain genetic profile, therefore, it is not It is a contagious disease that can be transmitted.
Furthermore, other factors have been related to the development of lupus, such as female gender, age, which is more common between the ages of 20 and 30, and African-American descent.
In the vast majority of cases, the person is born without any symptoms and only develops them during adulthood, due to factors that can stimulate the appearance of these symptoms, such as prolonged exposure to the sun, viral infections or the use of some medications.
How the treatment is carried out
Lupus treatment must be guided by a rheumatologist according to the type of disease, symptoms presented and frequency with which they occur.
Although there is no treatment capable of curing lupus, the doctor may recommend the use of some medications that help alleviate symptoms during periods of crisis, which may be recommended:
- Anti-inflammatoriessuch as naproxen or ibuprofen, to relieve fever and joint pain or swelling;
- Antimalarialssuch as hydroxychloroquine, help treat sensitivity to light, hair loss, skin blemishes and joint pain;
- Corticosteroidssuch as prednisone or betamethasone, are indicated in severe cases of lupus to prevent central nervous system disorders, hemolytic anemia and other symptoms that have not improved with other treatments;
- Immunosuppressantssuch as azathioprine or methotrexate, are indicated in the most serious cases, where the symptoms can put the person’s life at risk, such as serious changes in the central nervous system, glomerulonephritis or, in cases where treatment with corticosteroids was not effective.
It is important that medications are used according to the doctor’s recommendation, as this can promote symptom control and quality of life.
Is lupus curable?
There is no cure for lupus, however its symptoms can be controlled and prevented, as long as the doctor’s instructions are followed, such as applying sunscreen and taking medications recommended by the doctor. See more about treatment to control lupus symptoms.
Care during treatment
Some precautions may be recommended by the rheumatologist during lupus treatment, to help alleviate symptoms, such as sleeping the number of hours recommended for the person’s age, avoiding exposure to the sun, in addition to using sunscreen, protective clothing, such as a hat , long-sleeved clothes or clothes that have a sun protection factor of SPF 40. See the recommended amount of sleep hours by age.
Furthermore, it is also important to eat a healthy diet and exercise regularly. See an example of a lupus menu.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13