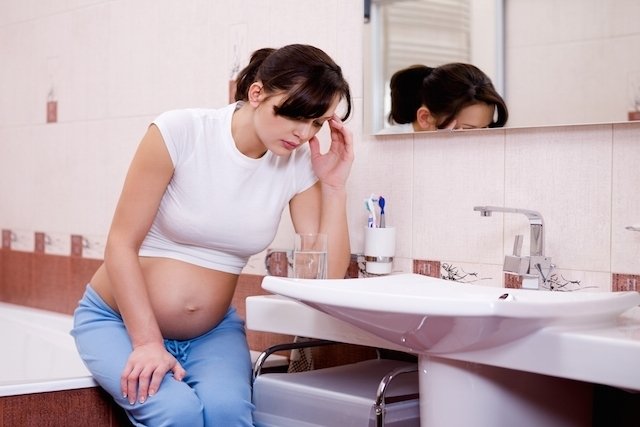
Low blood pressure during pregnancy is a very common change, especially at the beginning of pregnancy, due to hormonal changes that cause blood vessels to relax, causing the pressure to decrease.
Although it is not serious, like having high blood pressure during pregnancy, the sharp decrease in blood pressure can cause great discomfort for the pregnant woman during the day and even cause symptoms such as fainting and falls, which can put the baby and the pregnant woman at risk. .
To try to keep your blood pressure more regulated, you should avoid sudden changes in position, drinks such as alcohol, soft drinks and coffee, as well as eating at regular intervals and avoiding very hot environments, for example.

Symptoms of low blood pressure in pregnancy
The main symptoms of low blood pressure during pregnancy are:
- Weakness;
- Blurred, double or darkened vision;
- Feeling of fainting;
- Dizziness;
- Nausea.
Furthermore, in more serious cases, a feeling of fainting may appear, and it is important to consult an obstetrician if these symptoms occur frequently. Check out a great home remedy for low blood pressure, which can be used during pregnancy.
What to do if you feel faint
In case of low blood pressure during pregnancy, the pregnant woman should:
- Drop what you are doing;
- Sit, take a deep breath and lean your body forwardbringing the head towards the knees for a few minutes;
- Drink 2 glasses of water;
- Lie in a comfortable position and elevate your legs, to help normalize blood flow. If the pregnant woman is in the third trimester of pregnancy, she should lie on the left side of her body.
If low blood pressure symptoms persist for more than 15 minutes or appear very frequently, it is recommended to go to the hospital or contact your obstetrician.
Why pressure drops during pregnancy
During the first and second trimesters of pregnancy, there is an increase in blood flow, necessary to supply the blood circulation of the mother, the placenta and the small embryo. At this stage, the woman’s body adapts and creates the necessary conditions for the development of the fetus, so the blood must circulate faster to meet the body’s needs.
To circulate faster, hormones produced during pregnancy cause blood vessels to relax much more, causing blood to reach the placenta faster, which can lower blood pressure.
Another cause of low blood pressure is the pressure exerted by the uterus on the aorta and the abdominal vena cava. This occurs mainly in the third trimester of pregnancy, where the weight of the uterus is greater, and is known as supine hypotension syndrome.
Furthermore, it is also possible for pregnant women to suffer from orthostatic hypotension, in which dizziness and vertigo occur when getting up from a sitting or lying position, or when making any sudden movement. The ideal in these cases is to get up more slowly, sit for a few minutes and only then get up, preferably with help or some support.
Possible risks of low blood pressure
The main risk of low blood pressure during pregnancy is fainting, which can result in a fall and can cause trauma to the pregnant woman. Normally, this trauma is mild and does not cause more than a small scare, but if the fainting occurs in a place where the fall could be more serious, such as on a staircase, for example, it can put the lives of the pregnant woman and the baby at risk. See how to control blood pressure during pregnancy.
Low blood pressure during pregnancy stops being common when the blood volume increases and the pregnant woman’s body begins to adapt, producing a greater quantity of blood. Only at this stage does the pressure tend to return to normal, therefore requiring all care and attention, especially when the woman goes out alone.
How to avoid low blood pressure during pregnancy
To try to keep the pressure well regulated and avoid a sharp decrease in pressure, some measures can be taken, such as:
- Always have something salty in your bagsuch as crackers or dried fruits, so as not to go too long without eating;
- Drink around 2 liters of water throughout the day and in small quantities, in order to avoid dehydration and lowering of pressure;
- Wear light and comfortable clothingsuitable for pregnancy;
- Avoid staying for long periods in very hot and humid environments, as well as avoiding taking very hot baths;
- Avoid consuming alcoholic beverages and soft drinksto reduce the chances of dehydration;
- Practice light to moderate physical exercise regularlyas they have beneficial effects on blood circulation and blood pressure;
- Avoid sudden changes in position how to get up very quickly, for example;
- No medication caseconfirm with the obstetrician whether it has any secondary effect on blood pressure.
If low blood pressure attacks are frequent, the pregnant woman should see a doctor for clinical evaluation, as although it is not common, low blood pressure may be a sign of a disease that needs to be investigated and treated, before it puts the pregnancy at risk.
Bibliography
- SECRETARY OF HEALTH OF THE STATE OF JALISCO. Recommended SJS sleeping position during pregnancy. Available at: <https://ssj.jalisco.gob.mx/prensa/noticia/6106>. Accessed on Aug 23, 2022
- MUTIPLE SYSTEM ATROPHY TRUST. Postural Hypotension. Disponível em: <https://www.msatrust.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/FS102-Postural-Hypotension_v1.5-1.pdf>. Acesso em 23 ago 2022

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13