Liver elastography, also known as Fibroscan, is a test used to assess the presence of fibrosis in the liver, which allows the identification of damage caused by chronic diseases in this organ, such as hepatitis, cirrhosis or the presence of fat.
This is a quick exam, which can be done in a few minutes and does not cause pain, as it is performed using ultrasound, and does not require needles or cuts. Liver elastography can also, in some cases, be used to diagnose diseases, replacing the classic biopsy, where it is necessary to collect liver cells.
Although this type of procedure is not yet present throughout the SUS network, it can be carried out in several private clinics.
What is it for
Liver elastography is used to assess the degree of liver fibrosis in people with chronic liver disease, such as:
- Hepatitis;
- Fat in the liver;
- Alcoholic liver disease;
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis;
- Hemochromatosis;
- Wilson’s disease.
In addition to being used to diagnose and identify the severity of these diseases, this exam can also be used to evaluate the success of treatment, as it can assess the improvement or worsening of liver tissue.
Check out 11 symptoms that may indicate liver problems.
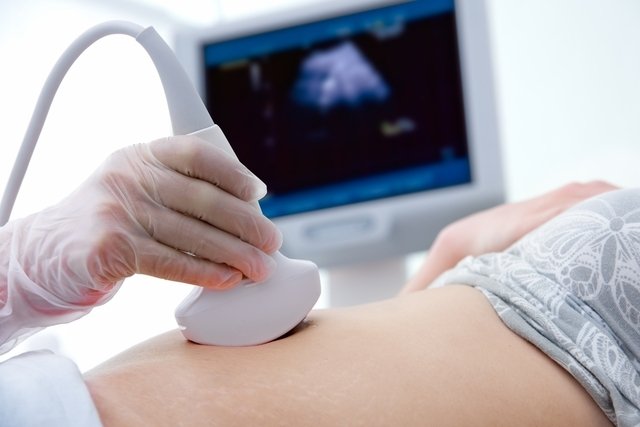
How the exam is carried out
Liver elastography is similar to an ultrasound exam, in which the person lies on their back with their shirt raised to expose the abdomen. Then, the doctor, or technician, applies a lubricating gel and passes a probe through the skin, applying slight pressure. This probe emits small ultrasound waves that pass through the liver and record a score, which is then evaluated by the doctor.
The exam lasts an average of 5 to 10 minutes and normally does not require any preparation, although, in some cases, the doctor may recommend a period of 4 hours of fasting. Depending on the device used to perform liver elastography, it may be called transient ultrasonic or ARFI.
Advantages over biopsy
As it is a painless exam that does not require preparation, elastography does not pose any risks to the patient, unlike what can occur during a liver biopsy, in which the patient has to be hospitalized so that a small piece of the organ can be removed for analysis.
The biopsy usually causes pain at the site of the procedure and bruising in the abdomen, and in rarer cases it can also cause complications such as hemorrhage and pneumothorax. Therefore, the ideal is to talk to the doctor to evaluate the best test to identify and monitor the liver disease in question.
How to understand the result
The result of liver elastography is presented in the form of a score, which can vary from 2.5 kPa to 75 kPa. People who obtain levels below 7 kPa generally mean that they do not have any problems with the organ. The higher the result obtained, the greater the degree of fibrosis in the liver.
Could the result go wrong?
Only a small portion of elastography test results may be unreliable, a problem that occurs mainly in cases of overweight, obesity and advanced age of the patient.
Furthermore, the exam may also fail when performed on people with a BMI lower than 19 kg/m2 or when the evaluator has no experience in performing the exam.
Who should not take the exam?
The liver elastography test is normally not recommended for pregnant women, patients with a pacemaker and people with acute hepatitis, heart problems and acute hepatitis.
Bibliography
- NHS. Having a fibroscan. 2012. Disponível em: <http://www.swbh.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/Having-a-fibroscan-ML3958.pdf>. Acesso em 20 jan 2021
- UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN. Liver Elastography. Disponível em: <https://www.uofmhealth.org/conditions-treatments/digestive-and-liver-health/liver-elastography>. Acesso em 20 jan 2021

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13