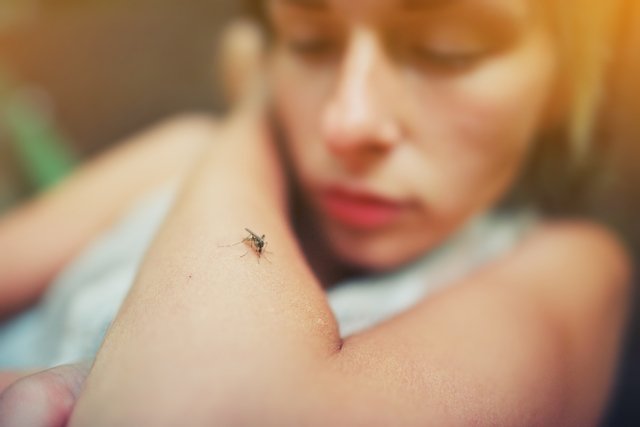
Kala-azar is a disease caused by protozoa Leishmania chagasi e Leishmania donovani and it happens when a small insect of the species Lutzomyia longipalpis, popularly known as straw mosquito or birigui, infected by one of the protozoa, bites the person and releases this parasite into the bloodstream, resulting in illness.
The symptoms of this disease, also called visceral leishmaniasis or tropical splenomegaly, can take days to years to appear, including chills, weakness, excessive tiredness, weight loss, paleness and enlargement of the abdomen due to the enlargement of the spleen and liver.
It is important that treatment for kala-azar is started as soon as signs and symptoms suggestive of the disease are observed, and the doctor recommends the use of specific medications to combat the parasite. In some cases, it may be necessary for the person to stay in the hospital to be properly monitored and thus prevent complications.

Kala-azar symptoms
The main symptoms of visceral leishmaniasis are:
- High fever, which comes and goes, of long duration;
- Chills;
- Enlargement of the abdomen, due to the enlargement of the spleen and liver;
- Weakness and excessive tiredness;
- Weight loss;
- Paleness, due to anemia caused by the disease;
- Easier bleeding, from the gums, nose or feces, for example;
- Frequent infections, caused by viruses and bacteria, due to a drop in immunity;
- Diarrhea.
After the bite of the infected mosquito that transmits the disease, the protozoa spread through the bloodstream and organs responsible for the formation of blood cells and the body’s immunity, such as the spleen, liver, lymph nodes and bone marrow, causing symptoms.
Visceral leishmaniasis has an incubation period of between 10 days and two years, and as it is not a common disease and its symptoms appear gradually, they can be confused with other diseases such as malaria, typhoid fever, dengue fever or Zika, for example. Therefore, in the presence of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention so that a diagnosis can be made and appropriate treatment can be initiated.
Don’t ignore the signs your body is giving you!
Diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis
The diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis is made through a parasitological examination, in which a culture of bone marrow, spleen or liver is taken with the aim of observing one of the evolutionary forms of the protozoan. Furthermore, the diagnosis can be made using immunological tests, such as ELISA, or immunochromatography, which are popularly known as rapid tests.
How transmission happens
The main reservoir of the protozoa responsible for kala-azar are dogs and, therefore, they are also considered the main source of infection for the insect. In other words, when the insect bites the infected dog, it acquires the protozoan, which develops in its body and can be transmitted to the person through the bite. Not all dogs carry the disease Leishmania chagasi or Leishmania donovanithis being more common in dogs that are not dewormed regularly or do not receive ideal care.
When the parasite is in the insect’s body, it can easily develop and then travel to the salivary glands. When the infected insect bites a person, it passes the parasite present in their salivary glands into the person’s bloodstream, being easily spread throughout the organs.
Kala-azar occurs more frequently in children over 10 years of age and adults who have some nutritional deficiency, such as a lack of iron, vitamins and proteins, and live in places with poor sanitation and hygiene.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for kala-azar must begin as soon as possible and can be done with the use of specific medications, such as Pentavalent Antimonial Compounds, Amphotericin B and Pentamidine, which must be indicated by the doctor and used according to his guidance.
When starting treatment, it is also important to take some precautions, such as evaluating and stabilizing clinical conditions, such as malnutrition and bleeding, in addition to treating other accompanying infections. It may be necessary to remain hospitalized for intravenous medication, but in cases where the infection is stable and there is easy access to the hospital, the doctor may recommend treatment at home and go to the hospital for follow-up.
This disease must be treated quickly, as it worsens within a few days and therefore the affected person may be at risk of death due to complications such as lung infection, respiratory failure, digestive hemorrhage, circulatory failure or opportunistic infections, viruses and bacteria. See more details on the treatment for visceral leishmaniasis.
Bibliography
- MINISTRY OF HEALTH. Visceral Leishmaniasis: what it is, causes, symptoms, treatment, diagnosis and prevention. Available at: <http://portalms.saude.gov.br/saude-de-az/leishmaniose-visceral>. Accessed on May 29, 2019
- NEVES, David P. Human Parasitology. 12 ed. Athenaeus, 69-88.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13