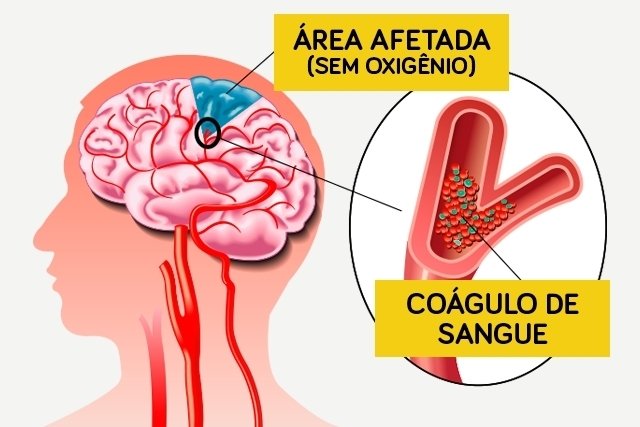
Ischemic stroke occurs when one of the brain vessels becomes obstructed by a clot, preventing the passage of oxygen to the brain cells, causing symptoms such as difficulty speaking, crooked mouth, loss of strength on one side of the body and changes in vision.
Typically, ischemic stroke is more common in the elderly or people who have some type of cardiovascular disorder, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol or diabetes, but it can happen to any person and age.
Since brain cells begin to die a few minutes after blood circulation is interrupted, stroke is always considered a medical emergency, which must be treated as quickly as possible in the hospital, in order to avoid serious sequelae, such as paralysis, changes brain damage and even death.
Main symptoms
The most characteristic symptoms of ischemic stroke include:
- Difficulty speaking or smiling;
- Crooked mouth and asymmetrical face;
- Loss of strength on one side of the body;
- Difficulty raising your arms;
- Difficulty walking.
In addition, other symptoms may also appear, such as tingling, vision changes, fainting, headache and even vomiting, depending on the affected region of the brain.
See how to identify a stroke and the first aid that should be given.
What is a transient ischemic attack?
A transient ischemic attack, or TIA, occurs when the stroke is caused by a very small clot that, however, was pushed through the blood circulation and stopped obstructing the vessel. In these episodes, in addition to symptoms improving within a few minutes, it is common for exams carried out in the hospital to not show any type of change in the brain.
Understand better what a transient ischemic attack is.
How to confirm the diagnosis
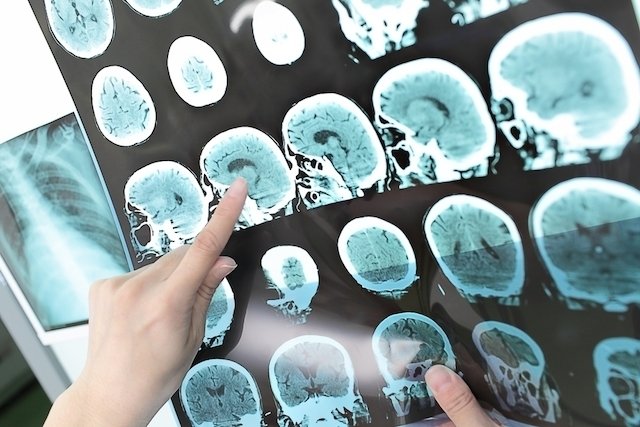
Whenever a stroke is suspected, it is very important to go to the hospital to confirm the diagnosis. Generally, the doctor uses imaging tests, such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, to identify the blockage that is causing the stroke and thus begin the most appropriate treatment.
What causes ischemic stroke
Ischemic stroke occurs when one of the brain’s vessels becomes obstructed and, as a result, blood cannot pass through and feed the brain cells with oxygen and nutrients. This obstruction can happen in two different ways:
- Blockage by a clot: it is more common in the elderly or people with heart problems, especially atrial fibrillation;
- Vessel narrowing: It generally happens in people with uncontrolled high blood pressure or atherosclerosis, as the vessels become less flexible and narrower, reducing or preventing the passage of blood.
Furthermore, there are many other situations that increase the risk of developing a clot and suffering an ischemic stroke, such as having a history of stroke in the family, smoking, being overweight, not exercising or taking contraceptive pills, for example.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for ischemic stroke is carried out in the hospital and is normally started with the injection of thrombolytic medicines directly into the vein, which are medicines that thin the blood and help eliminate the clot that is causing the blockage in the vessel.
However, when the clot is very large and cannot be eliminated with the use of thrombolytics alone, it may be necessary to perform a mechanical thrombectomy, which consists of inserting a catheter, which is a thin, flexible tube, into one of the arteries in the groin or neck. neck, and guide it to the vessel in the brain where the clot is located. Then, with the help of this catheter, the doctor removes the clot.
In cases where the stroke is not being caused by a clot, but by the narrowing of the vessel, the doctor may also use a catheter to place a stent in place, which is a small metal mesh that helps keep the vessel open, allowing the passage of blood.
After treatment, the person must always be under observation in the hospital and, therefore, it is necessary to stay hospitalized for a few days. During hospitalization, the doctor will assess the presence of sequelae and may recommend the use of medication to reduce these sequelae, as well as physiotherapy and speech therapy sessions. See the 6 most common consequences after a stroke and what recovery is like.
Is ischemic stroke curable?
Ischemic stroke can be cured when the person is referred to the hospital as soon as the first symptoms are noticed and treatment is carried out to dissolve the clots. This way, it is possible to combat symptoms and prevent sequelae.
Difference between ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke?
Unlike ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke is rarer and happens when a vessel in the brain ruptures and, therefore, blood cannot pass correctly. Hemorrhagic stroke is more common in people with uncontrolled high blood pressure, who are taking blood thinners or have an aneurysm. Learn more about the two types of stroke and how to differentiate.
Bibliography
- CDC. Types of Stroke. Available at: <https://www.cdc.gov/stroke/types_of_stroke.htm>. Accessed on 03 Jul 2020
- AMERICAN STROKE ASSOCIATION. Acute Ischemic Stroke: what you need to know about acute ischemic stroke treatment. 2018. Disponível em: <https://www.stroke.org/-/media/stroke-files/ais-patient-resources/patient-education-presentation-currently-experiencing-ischemic-stroke-ucm_498771.pdf?la=en>. Acesso em 03 jul 2020
- STROKE ASSOCIATION UK. Ischaemic stroke. 2012. Disponível em: <http://www.stroke.org.uk/sites/default/files/Ischaemic%20stroke.pdf>. Acesso em 03 jul 2020
- AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CLINICAL PHARMACY. Acute Ischemic Stroke. 2020. Available at: <https://www.accp.com/docs/bookstore/psap/p2020b1_sample.pdf>. Accessed on 03 Jul 2020
- AMERICAN STROKE ASSOCIATION. Let’s Talk About Ischemic Stroke. 2020. Disponível em: <https://www.stroke.org/-/media/stroke-files/help-and-support/ds15794_ltas_ischemicstroke_12_20.pdf?la=en>. Acesso em 03 jul 2020

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13