An inverted uterus is when the uterus is backwards, that is, facing the back and not forwards, over the bladder, as happens in most women. In these cases, it is also common for the ovaries and fallopian tubes to also face backwards.
Despite being an anatomical change, the inverted uterus, also called retroverted uterus, does not interfere with a woman’s fertility or prevent pregnancy. Furthermore, in most cases there are no signs or symptoms, which are identified by the gynecologist during routine examinations, such as ultrasound and Pap smears, for example.
Although in most cases there are no signs or symptoms, some women may report pain when urinating, evacuating and after intimate contact, and in this situation it is recommended to perform a surgical procedure so that the uterus is turned forward, thus reducing symptoms. .
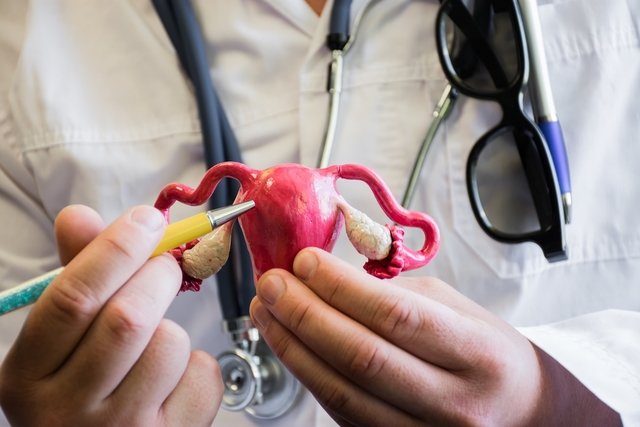
Inverted Uterus Symptoms
The main symptoms of an inverted uterus are:
- Pain in the hip region;
- Severe cramps before and during menstruation;
- Pain during and after intimate contact;
- Pain when urinating and evacuating;
- Difficulty using tampons;
- Sensation of pressure in the bladder.
However, the majority of women with an inverted uterus do not present symptoms and, therefore, this condition is normally diagnosed during routine examinations, and treatment is not necessary in these cases.
How the diagnosis is made
The diagnosis of a retroverted uterus is made by the gynecologist during a gynecological examination, in which it is possible to feel the location of the cervix and uterus to determine which side it is tilted.
In addition, imaging tests may also be requested, such as a pelvic or transvaginal ultrasound.
To check the position of the uterus and investigate the possibility of an inverted uterus, make an appointment with your nearest gynecologist:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
Possible causes
The main causes of an inverted uterus are:
- Endometriosis;
- Pregnancy;
- Uterine adhesions;
- Fibroids;
- Menopause.
Furthermore, some people can be born with a retroverted uterus without this being associated with any health problems.
Inverted uterus and pregnancy
The uterus in an inverted position does not cause infertility and does not hinder fertilization or the continuation of the pregnancy. However, during pregnancy the inverted uterus can cause incontinence, back pain and pain when urinating or having a bowel movement, but it is not common for it to cause complications during pregnancy or childbirth.
Furthermore, birth in the case of an inverted uterus can be normal, and a cesarean section is not necessary for this reason alone. In most cases, until the 12th week of pregnancy, the uterus adopts a position closer to normal, facing forward and remaining under the bladder, which facilitates normal birth.
In cases where pregnancy does not occur, it is possible that this is due to some health condition, such as endometriosis or fibroma, for example.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for an inverted uterus must be guided by a gynecologist, who may recommend hormonal therapy, in the case of endometriosis, or laparoscopic surgery to reposition the uterus over the bladder. In some cases, the doctor may consider removing the uterus, this procedure being called hysterectomy.
Another type of treatment is the placement of a small silicone pessary to keep the uterus tilted forward, as well as its manual repositioning by the doctor. If the position is maintained, the doctor may recommend performing Kegel exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor.
Bibliography
- CLEVELAND CLINIC. Retroverted Uterus. Available at: <https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/23426-retroverted-uterus>. Accessed on May 25, 2023
- BETTER HEALTH CHANNEL. Retroverted uterus. Disponível em: <https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/retroverted-uterus#a-range-of-causes-for-a-retroverted-uterus>. Acesso em 25 mai 2023
- AUSTRALIAN J ULTRASOUND MED. The retroverted uterus: refining the description of the real time dynamic ‘sliding sign’. 2013. Available at: <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5029993/>. Accessed on September 11, 2020
- U.S. NATIONAL LIBRARY OF MEDICINE. Retroversion of the uterus. Available at: <https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001506.htm>. Accessed on September 11, 2020
- DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES AU. Retroverted uterus. Available at: <https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/retroverted-uterus>. Accessed on September 11, 2020

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13