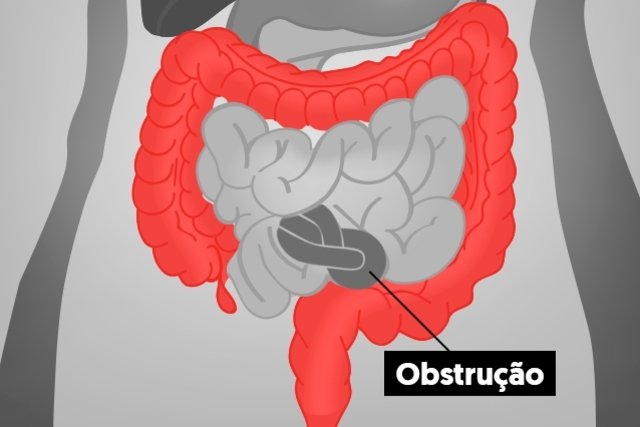
Intestinal obstruction is an emergency situation that occurs when feces cannot pass through the intestine due to a blockage in its path. In these cases, intestinal symptoms usually appear, such as difficulty passing or eliminating gas, bloating, nausea or abdominal pain, which may worsen over time.
Intestinal obstruction prevents the passage of digested food through the intestine and, therefore, feces, intestinal gases and digestive secretions end up accumulating, which increases pressure within the intestine and the risk of serious complications, such as intestinal perforation, infection generalized or death of intestinal tissue.
Whenever there is a suspicion of an obstruction in the intestine, it is advisable to immediately seek medical attention, to confirm the diagnosis and begin treatment, which is normally done with the administration of liquids through the vein, passage of a probe into the digestive tract or surgery, depending on the condition. gravity.
Possible symptoms
The most common symptoms of an intestinal obstruction are:
- Difficulty evacuating or eliminating gases;
- Swelling in the belly;
- Colicky abdominal pain that worsens over time;
- Decreased appetite;
- Nausea and vomiting.
There are still some cases in which the intestinal obstruction is partial, that is, it still allows some content to pass through. In these cases, there may still be gas elimination and the symptoms may be a little milder, however it is common for abdominal discomfort to be persistent.
The intensity of symptoms varies according to the cause and severity of the disease that causes the obstruction. Furthermore, symptoms may also vary according to the affected area, with vomiting and nausea being more common in small intestine obstruction, while abdominal bloating and constipation are more common in large intestine obstruction, for example. .
How to confirm the diagnosis
Normally, to identify intestinal obstruction, the doctor starts by evaluating the symptoms and palpating the belly with his hands, to try to identify any changes. You can also use the stethoscope to listen for noises in the belly that indicate whether the intestine is working properly or not.
When intestinal obstruction is suspected, it is necessary to carry out at least one diagnostic test, such as an x-ray or computed tomography, to confirm the diagnosis and observe where in the intestine the occlusion is located.
Possible causes of obstruction
There are many causes that can lead to the appearance of an obstruction in the intestine, from mechanical causes, in which there is a physical obstacle, as well as a functional obstruction, which is when the intestinal movements are paralyzed.
The main causes include:
- Intestinal cords, which are tissue adhesions on the walls of the intestine, more common in people who have already undergone abdominal surgery. Understand how abdominal bands form and how to treat them;
- Hernias;
- Intestinal tumor, mainly in the large intestine. See a list of bowel cancer symptoms;
- Diverticulitis;
- Inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn’s disease;
- Torsion of the intestine;
- Paralysis of bowel movements, called paralytic ileus, due to metabolic changes, such as lack of potassium in the blood;
- Bowel ischemia;
- Endometriose intestinal;
- Accumulation of worms;
- Post-radiation enteritis in cancer treatment;
- Lead poisoning.
Some of these causes can cause a complete and abrupt obstruction of the intestine, generating more serious symptoms, or just a partial obstruction or one that happens gradually, when the symptoms are milder and there are fewer health risks. However, all cases need appropriate treatment, as soon as possible.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for intestinal obstruction varies according to the location and severity of the symptoms and should always be carried out in the hospital, to avoid complications, which can be worsened if you try to use laxatives at home, for example.
In the case of a partial obstruction, with milder symptoms, it may normally only be necessary to administer fluids into the vein, to improve hydration and facilitate the passage of feces and liquids. In addition, you must also rest your bowels and, therefore, you must fast until the problem is resolved. Often, a tube is also placed from the nose to the stomach to remove excess gas and liquid, relieving pressure in the intestine.
In more serious cases, such as complete obstruction, in addition to the previous care, surgery is also necessary to treat the cause and unblock the intestine, allowing feces to pass again.
What are the possible risks and complications
Treatment of intestinal obstruction should be started as soon as possible to avoid possible complications such as:
- Dehydration;
- Bowel perforation;
- Generalized infection;
- Death of a part of the intestine.
All of these complications can be life-threatening as they contribute to inflammation, widespread infection and multi-organ failure. Therefore, whenever there is a suspicion that the intestine is not working properly, medical attention should be sought to identify whether there is a problem that needs to be treated.
Bibliography
- Paterson-Brown, Simon. et al . Essential topics in general and emergency surgery. 5 ed. Rio de Janeiro: Elsevier, 2017. p. 158-169.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13