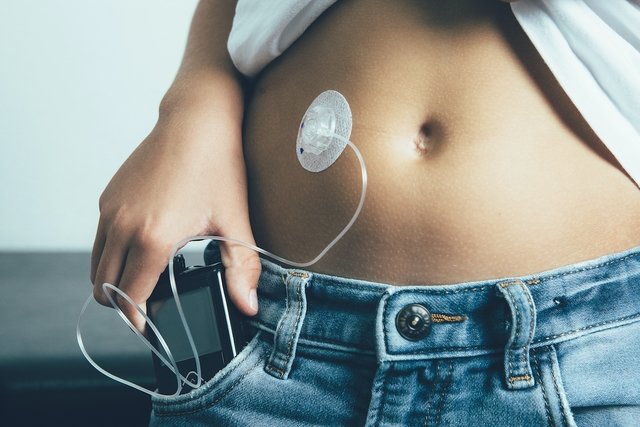
An insulin pump is an electronic device that is connected to the body and releases insulin continuously for 24 hours and in very small doses according to the person’s needs. It is recommended in cases of type 1 or type 2 diabetes, as it works by imitating the functioning of of the pancreas.
Generally, the insulin pump or insulin infusion pump uses rapid-acting and/or short-acting insulin, as the pump is programmed to release small amounts of insulin throughout the day, continuously to maintain blood sugar levels. within normal values.
This device can be worn attached to the waist or arm, and connected to the body by a small cannula with a flexible needle in the abdomen and should only be used with the recommendation of an endocrinologist. Furthermore, its use must be guided by a nurse or diabetes educator.
What is it for
The insulin pump is used to treat type 1 or type 2 diabetes, in cases where the body’s production of insulin is not sufficient to control blood sugar levels.
The use of an insulin pump must be recommended by an endocrinologist, and regular medical monitoring is necessary to assess the adaptation to using the pump, as well as to check blood glucose control and the effectiveness of diabetes treatment.
Make an appointment with an endocrinologist in the nearest region:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
When is it indicated
The insulin pump is indicated in the following situations:
- Difficulty or forgetting to make insulin injections;
- Inadequate control of blood glucose levels, even using insulin injections;
- Large variations in blood sugar levels during the day;
- Fasting blood glucose levels above 140 to 160 mg/dL;
- Difficulty controlling nighttime blood glucose;
- Frequent or severe hypoglycemia crises;
- Need to have a higher quality of life;
- Gestational diabetes;
- Diabetes control in women who want to get pregnant.
Furthermore, the insulin pump is also a more comfortable option for treating diabetes.
How the insulin pump works
The insulin pump works by releasing insulin into the body continuously for 24 hours and/or in the form of a “bolus” through a catheter inserted under the skin of the abdomen, but it can also be used on the arm or thigh, for example, which These are the same injection sites for insulin injection.
The pump is approximately the size of a cell phone and releases insulin on a programmed basis, as if it were the pancreas, allowing better control of blood sugar.
Furthermore, it is also possible to use a computerized insulin pump with a glucose monitor, and in this case, the device checks blood sugar levels 24 hours a day and triggers an alarm when glucose levels are too low. or very high, based on normal blood glucose levels.
Care when using the insulin pump
When using an insulin pump, some precautions are important, such as:
- Replace the catheter every 2 to 3 daysand in the first few days it is normal to feel a little discomfort on the skin where it was inserted;
- Wash your hands and skin with water and neutral soap whenever changing the cannula;
- Alternate the location of the cannula placement the insulin pump;
- Check blood glucose levels throughout the day, through capillary blood glucose, at least 4 times a day, before each main meal and at night, before going to sleep. Learn how to measure glucose at home correctly;
- Perform capillary blood glucose 6 times a day, if blood glucose control is more difficult. Therefore, the doctor may recommend measuring blood glucose before and two hours after the three main meals of the day, and may also be asked to measure it at night;
- Inspect the skin in the region where the cannula is insertedin order to check for inflammation, infections or allergies at the site, such as redness or swelling.
Furthermore, before starting to use the insulin pump, the person must receive training on how to use the pump, given by a nurse or diabetes educator.
Advantages of the insulin pump
The insulin pump has the advantage of delivering amounts of insulin more accurately and precisely, without the need to take insulin injections during the day.
Additionally, the insulin pump helps you better control your blood sugar levels by offering a constant flow of insulin.
Possible complications
Some complications may occur when using an insulin pump, such as:
- Hyperglycemia;
- Hypoglycemia;
- Diabetic ketoacidosis;
- Infection in the skin, where the catheter is inserted.
Furthermore, other situations such as pump malfunction, cannula disconnection or incorrect pump configuration can impair insulin release, increasing the risk of complications.
Therefore, it is important to receive training before starting to use the insulin pump, to ensure that it works properly to receive the appropriate dose of insulin.
Where to buy the insulin pump
The insulin pump can be purchased directly from the manufacturer, which can be Medtronic, Roche or Accu-Chek, and the endocrinologist’s prescription must be presented.
The insulin infusion pump and materials can be provided by the SUS, however, a legal action is required with a detailed description of the patient’s clinical situation and the need for the doctor to use the pump and proof that the patient does not have conditions to acquire and maintain monthly treatment.
Bibliography
- STATE OF QUEENSLAND (QUEENSLAND HEALTH). Insulin infusion pump management Inpatient guidelines. 2016. Available at: <https://www.health.qld.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0021/437106/sdcn-insulin-guide.pdf>. Accessed on 28 Nov 2023
- MAIA, Frederico Fernandes Ribeiro; ARAÚJO, Levimar Rocha. Use of insulin infusion pump in the treatment of type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Minas Gerais Medical Magazine. 13. 3; 194-199, 2003
- NIMRI, R.; NIR, J.; PHILLIP, M. Insulin Pump Therapy. Am J Ther. 27. 1; e30-e41, 2020
- MINICUCCI, Walter José. Use of Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion Pump and its Indications. Arq Bras Endrocrinol Metab. 52. 2; 340-348, 2008

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13