Infantile hemangioma is a benign tumor that affects blood vessels in parts of the body such as the head and neck, and is characterized by a red spot on the skin that grows rapidly in the first few months and generally disappears on its own over time.
This type of hemangioma is different from congenital hemangioma, which is typically noticed at birth. However, both types result from the abnormal multiplication of blood vessel cells in the skin. Understand better what a hemangioma is.
If you suspect infantile hemangioma, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist or doctor specialized in this type of tumor. Although specific treatment is not always necessary, the doctor may recommend medications, such as propranolol or prednisone, or surgery in some cases.
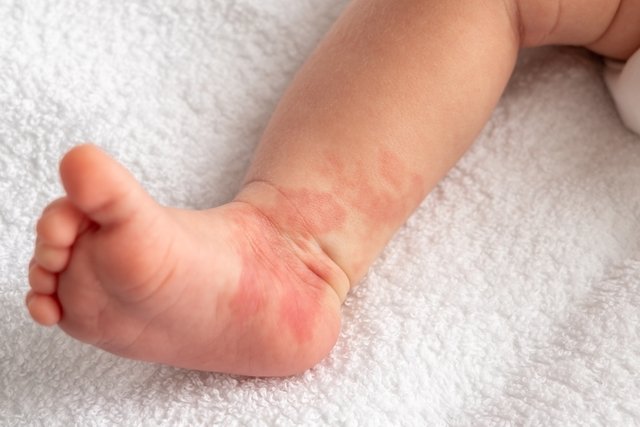
Infantile hemangioma symptoms
The main symptom of infantile hemangioma is the appearance of a red, raised spot on the skin in the first few weeks after birth. This spot can appear on the skin or mucous membranes of any part of the body, with the head and neck being the most common regions.
Although it is not normally present at birth, small spider veins can sometimes be noticed on the skin, known as telangiectasias, or an area of lighter or redder skin in the area before its appearance.
Read too: Telangiectasia: what it is, symptoms, causes and treatment
Infantile hemangiomas tend to increase in size quickly, especially in the first few months after they appear. However, the spot normally stops growing between 6 and 12 months of age and then begins to regress.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of infantile hemangioma is normally made by a pediatric dermatologist or pediatrician taking into account only the characteristics of the spot.
If you want to make an appointment, find a dermatologist closest to you using the tool below:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
Make an appointment with our Dermatologists and receive the personalized care you deserve.
However, it is common for the doctor to recommend imaging tests, such as ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging, to confirm the diagnosis and check whether there are malformations or abnormalities in other vessels or parts of the body.
Because it appears
It is believed that infantile hemangioma arises due to an abnormal response of cells that form blood vessels to stimuli such as hypoxia and hormones, resulting in the formation of a network of small anomalous vessels.
Read too: Hypoxia: what it is, symptoms, causes and treatment
Furthermore, infantile hemangioma appears to be more common in female babies with fair skin and a history of low birth weight, prematurity or twins, for example.
How the treatment is carried out
In most cases, infantile hemangioma does not require specific treatment and tends to disappear after 3 to 9 years, with only follow-up with a dermatologist being recommended to assess its regression.
However, depending on the characteristics of the hemangioma and the presence of complications, such as changes in vision or the appearance of wounds on the skin, the doctor may recommend medications, such as propranolol, prednisone or timolol, or their removal by surgery, for example.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13



