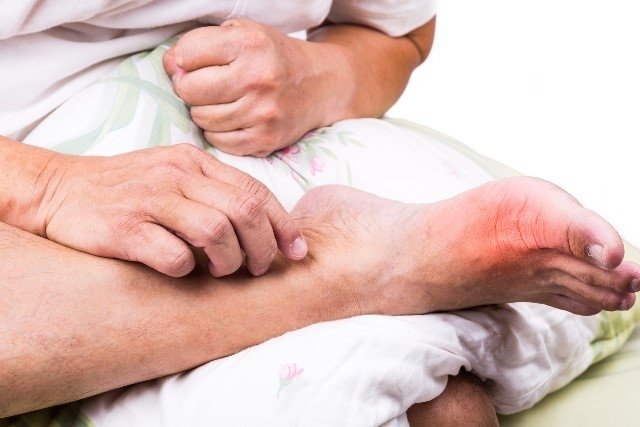
To treat gout disease, scientifically called Gouty Arthritis, it is recommended to take medications that act on uric acid, such as Colchicine, Allopurinol or Probenecid, which reduce uric acid in the body and the accumulation of urates in the joints. , as well as preventing the emergence of crises.
During a gout attack, in which there is intense inflammation and pain in the joint, the doctor usually advises the use of anti-inflammatory medications. The person who has this disease must also be careful with their diet throughout their lives to avoid worsening symptoms and complications that gout can generate, such as joint deformities and kidney damage, for example.
Gout is an inflammatory arthritis that can cause a lot of pain during attacks, which appear abruptly, caused by the crystallization of uric acid that is deposited inside the joints, generally in people who have high uric acid. Understand what causes gout and what the symptoms are.
Main pharmacy remedies
Gout treatment can be guided by a rheumatologist or a general practitioner, and can vary depending on whether the person is in a crisis or whether it is a maintenance treatment for the disease. The recommendations for each case are:
1. Treatment of gout attacks
To treat a gout attack, also called acute gout, your doctor will prescribe medications that help quickly relieve inflammation. The main ones include:
- Anti-inflammatoriessuch as Naproxen, Ketoprofen, Ibuprofen or Indomethacin, for example: they are indicated to alleviate the symptoms of arthritis, soon after the symptoms begin, and should be maintained until the crisis resolves, for about 1 week;
- Corticosteroidssuch as Prednisone, Prednisolone, Methylprednisolone or Triamcinolone, for example: they also have an anti-inflammatory effect, and can be used in tablets or injections that can be intramuscular or can also be applied directly to the affected joint, helping to obtain a better response quick and effective;
- Colchicine: it is another type of anti-inflammatory indicated to help relieve gout attacks quickly, and its effect is better when started within the first few hours of the onset of the attack. Learn more about how it works and how to use this medicine in Colchicine.
These medications should be used with caution, as advised by your doctor, as they can cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or increase the risk of gastric bleeding, especially if used incorrectly.
2. Control of uric acid
After the gout attack has resolved, preventative treatment can be started to prevent new attacks and reduce uric acid levels in the blood. It is especially indicated whenever the patient suffers two or more attacks per year, if they have tophi in the joints, chronic kidney disease or a history of kidney stones due to excess uric acid.
Some of the medications used include:
- Alopurinol: it is the main medicine used to control uric acid levels in the blood, reducing its levels and the possibility of accumulation in the joints;
- Uricosuric remediessuch as Probenecid: help increase the elimination of uric acid in the urine.
Other newer medications, such as Febuxostat or Pegloticase, are potent inhibitors of the formation of uric acid, and are also an option for treatment, if the others cannot be used, due to allergies or intolerances, for example. Also check out how to identify and combat high uric acid.
Diet changes
When eating for gout, it is recommended to avoid foods rich in proteins, such as shellfish, young animal meat and offal, as they affect purine metabolism and tend to increase the concentration of uric acid in the blood.
Another important tip is to increase your water intake and avoid alcoholic beverages, especially beer, giving preference to low-fat milk and yogurt.
Watch the video to adapt your diet:
Bibliography
- GELBER, A. C. Treatment Guidelines in Gout. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 48. 3; 659-678, 2022
- STAMP, L. K.; FARQUHAR, H. Treatment advances in gout. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 35. 4; 101719, 2021
- FENANDO, A.; ET AL. IN: STATPEARLS (INTERNET). TREASURE ISLAND (FL): STATPEARLS PUBLISHING. Gout. 2022. Available at: <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546606/>. Accessed on Sep 15, 2023
- DALBETH, N.; et al. Gout. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 5. 1; 69, 2019

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13