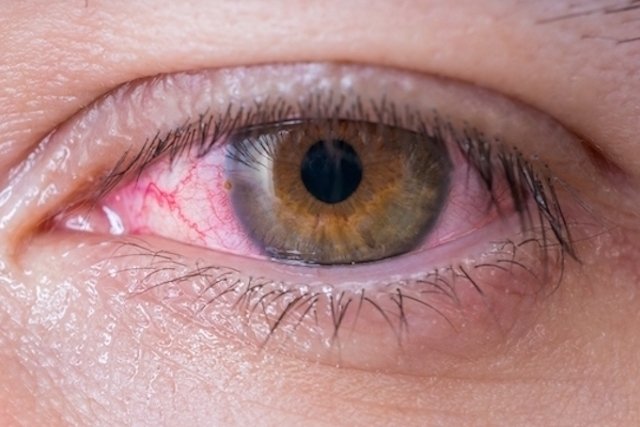
Treatment for conjunctivitis can include applying cold compresses or using artificial tears to help relieve symptoms of itchy eyes, redness, excessive tearing or swelling.
Depending on the type of conjunctivitis, the ophthalmologist may recommend treatment with anti-allergic, antiviral or antibiotic eye drops or ophthalmic ointments, such as ketotifen fumarate, acyclovir or tobramycin, for example.
Read too: How many days does conjunctivitis last? Viral, allergic and bacterial
tuasaude.com/quantos-dias-dura-a-conjuntivite
The treatment of conjunctivitis should always be carried out under the guidance of an ophthalmologist who can recommend the best medicines according to the cause of the conjunctivitis, which could be allergies or infections caused by viruses or bacteria.
Main treatments for conjunctivitis
Thus, depending on the type of conjunctivitis, treatment may vary:
1. Cold compresses
Applying cold compresses to the affected eye may be recommended by your ophthalmologist as it helps to reduce inflammation and relieve itching and discomfort from any type of conjunctivitis.
To make a cold compress, you must wet a sterile gauze pad in ice water, wring the gauze pad to remove excess water and apply it to the eyelid, with the eye closed, leaving it to act for a maximum of 15 minutes.
Then, the used gauze must be discarded. This procedure can be repeated every 2 hours, always using a new sterile gauze for each application.
2. Artificial tears
Artificial tears or lubricating eye drops or artificial tears, such as Lacril, Systane or Lacrima Plus, may be recommended by the ophthalmologist to relieve the feeling of sand in the eyes, itching or redness.
These lubricating eye drops or artificial tears contain substances such as carboxymethylcellulose, sodium carmellose or hypromellose, for example, which help clean the eye and keep it moist, relieving the symptoms of viral, allergic or bacterial conjunctivitis.
3. Anti-allergy
Antiallergic drugs, such as ketotifen fumarate, epinastine hydrochloride or fluorometholone acetate, are recommended by the ophthalmologist in the case of allergic conjunctivitis to help redness, itching, irritation, tearing or swelling in the eyes.
These remedies can be used in the form of eye drops, such as Relestat, Octifen, Lastacaft or Florate, which should only be used under medical advice.
Furthermore, in more serious cases of allergic conjunctivitis, in which the person also has nasal congestion, the ophthalmologist may also recommend antihistamines in the form of tablets, such as hydroxyzine or cetirizine, for example.
Read too: Antihistamines: what they are and main types
4. Mast cell stabilizing eye drops
Another treatment that may be indicated in the case of allergic conjunctivitis are mast cell stabilizing eye drops, such as disodium cromoglycate or nedocromil, for example.
These eye drops work by stabilizing mast cells, which are cells that release histamine, a substance responsible for allergic reactions and symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis.
In this way, mast cell stabilizing eye drops help to alleviate symptoms of intense itching in the eyes, constant tearing or redness in the eyes. Know how to identify the symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis.
During treatment for allergic conjunctivitis, it is still important to keep the allergy factor at bay and, therefore, it is recommended to avoid objects that accumulate dust or pollen, for example.
5. Decongestants
Decongestant eye drops are especially indicated to help relieve mild irritation or redness in the eyes caused by allergic conjunctivitis.
These eye drops, such as naphazoline hydrochloride, can be found under the trade names Colírio Moura, Lerin or Colírio Teuto, for example, and should only be used under the advice of an ophthalmologist.
Decongestant eye drops are contraindicated for people with glaucoma or who use monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) medications, such as isocarboxazid, phenelzine or tranylcypromine, for example.
6. Topical corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids in the form of eye drops or ophthalmic ointment are indicated in cases of allergic or viral conjunctivitis, such as prednisolone acetate or fluorometholone acetate.
Topical corticosteroids help reduce inflammation of the eye’s conjunctiva, relieving symptoms of swelling and redness, for example.
7. Antivirals
Antivirals in the form of ophthalmic ointment or eye drops, such as acyclovir, may be recommended by the ophthalmologist in cases of keratoconjunctivitis caused by the herpes simplex virus or herpes zoster, as they inhibit the multiplication of viruses, reducing the severity of the infection and accelerating recovery.
In more serious cases, the doctor may recommend the use of antivirals in tablet form, such as acyclovir, famciclovir or valacyclovir, for example.
Viral keratoconjunctivitis is the most contagious type of conjunctivitis and, therefore, throughout treatment it is very important to wash your hands after touching the eye and avoid sharing objects that may come into contact with the eye, such as glasses or makeup. Check out other simple habits that prevent the transmission of conjunctivitis.
Read too: Herpes in the eye (ocular): what it is, symptoms, causes and treatment
8. Antibiotics
Antibiotics in the form of eye drops or ointments, such as tobramycin and ciprofloxacin, may be indicated for the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis, as they help eliminate bacteria that cause this type of conjunctivitis.
Treatment is normally carried out by applying antibiotic eye drops or ointment to the affected eye, 3 to 4 times a day, for around 7 days.
In cases of conjunctivitis caused by gonorrhea or chlamydia, the ophthalmologist may recommend the use of oral antibiotics or in the form of an injection into the muscle, such as azithromycin or ceftriaxone, for example.
Read too: Eye drops for conjunctivitis: main options (and how to put them)
General care during treatment
Although treatment may vary depending on the type of conjunctivitis, there are some precautions that must be taken in any case, especially to alleviate symptoms. These precautions include:
- Apply a wet compress about the closed eye;
- Keep your eyes clean and dryby removing the ace oars;
- Avoid using contact lensesgiving preference to glasses;
- Don’t put on makeup In the eye;
- Wear sunglasses when going out on the street.
Furthermore, to avoid the transmission of conjunctivitis, you should also change pillowcases and towels daily, wash them separately, wash your hands several times a day, as well as avoid sharing objects that may come into contact with the eye, such as glasses, towels, pillowcases or makeup, for example.
Read too: 4 home remedies for conjunctivitis and how to prepare

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13