There are two types of cerebrovascular accident (CVA), which are classified according to the cause of the decrease in blood flow to a certain region of the brain:
- ischemic stroke: which appears when a clot clogs a cerebral vessel, interrupting blood circulation;
- hemorrhagic stroke: which happens when a vessel in the brain ruptures, reducing the amount of blood that passes through that vessel.
Although they occur differently, both types of stroke cause similar symptoms such as loss of strength or sensitivity in an area of the body, difficulty speaking, dizziness and blurred vision. Therefore, the type of stroke cannot be identified through symptoms, and is normally only confirmed in the hospital, through an MRI or CT scan.
In any case, a stroke is always a medical emergency situation that must be identified as quickly as possible and treated in the hospital, as the most important factor in this type of situation is the time that passes from the appearance of the first symptoms until the patient is stabilized. A good way to identify a stroke is to take the SAMU test – see how to take the SAMU test and when to call for medical help.
The main differences between ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke are explained below:
1. Ischemic stroke
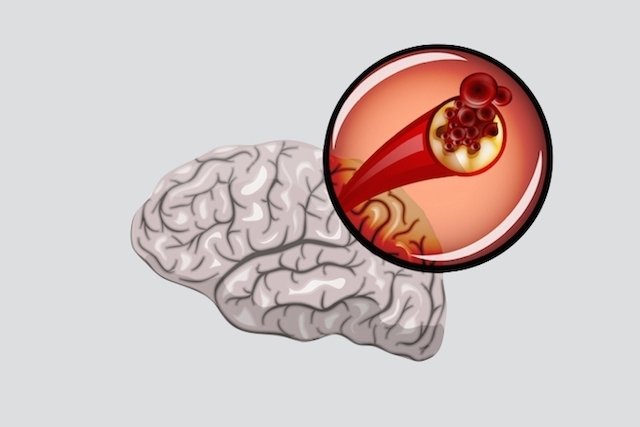
Ischemic stroke occurs when there is a fatty plaque in one of the cerebral vessels or when a clot, which formed elsewhere in the body, manages to reach the brain vessels, causing a blockage that prevents blood from reaching some region of the brain. brain.
Furthermore, other main differences in relation to hemorrhagic stroke are the causes and form of treatment:
- Main causes: high cholesterol, atherosclerosis, atrial fibrillation, sickle cell anemia, coagulation diseases and changes in heart function.
- How the treatment is carried out: It is usually done with medicines, administered directly into the vein, which thin the clot, but may also include surgery to remove the clot if the medicines do not work. See in more detail how stroke is treated.
Furthermore, it is common for ischemic stroke to have a better prognosis than hemorrhagic stroke, as it is usually easier to treat, which reduces the time from the first symptoms appearing until the patient is stabilized, also reducing the risk of sequelae. .
In some cases, transient ischemic stroke may also occur, in which the symptoms last, in most cases, about 1 hour, and then disappear without leaving any sequelae. This type can also be known as pre-stroke, which is why it is important to go to the emergency room for an evaluation and start appropriate treatment to prevent it from developing into a stroke.
2. Hemorrhagic stroke
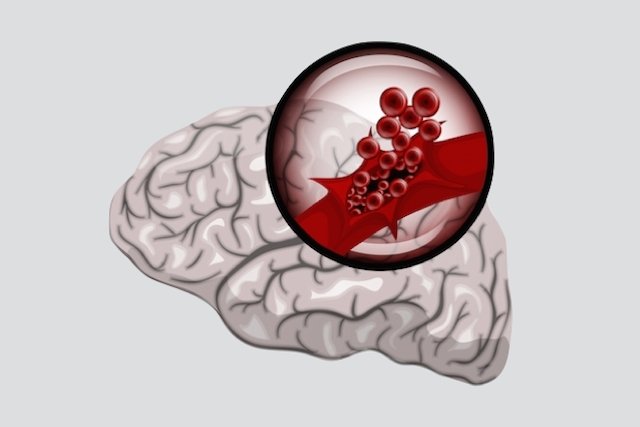
Unlike ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke does not occur due to the blockage of a cerebral vessel, but rather due to the rupture of a vessel, which means that the blood cannot continue passing to some region of the brain. Furthermore, in hemorrhagic stroke there is also an accumulation of blood in or around the brain, which increases cerebral pressure, further aggravating symptoms.
In this type of stroke, the most common causes and treatment are:
- Main causes: high blood pressure, excessive use of anticoagulants, aneurysm and strong blows to the head, for example.
- How the treatment is carried out: It usually starts with the administration of medication to reduce blood pressure, but in many cases surgery may be necessary to correct damage to the brain’s vessels. Find out more about how stroke is treated.
Typically, hemorrhagic stroke has a worse prognosis than ischemic stroke, as it can be more difficult to control the bleeding.
Bibliography
- AMERICAN STROKE ASSOCIATION. Ischemic Stroke (Clots). Disponível em: <https://www.stroke.org/en/about-stroke/types-of-stroke/ischemic-stroke-clots>. Acesso em 20 mai 2020
- AMERICAN STROKE ASSOCIATION. Hemorrhagic Stroke (Bleeds). Disponível em: <https://www.stroke.org/en/about-stroke/types-of-stroke/hemorrhagic-strokes-bleeds>. Acesso em 20 mai 2020

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13