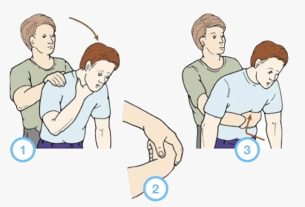
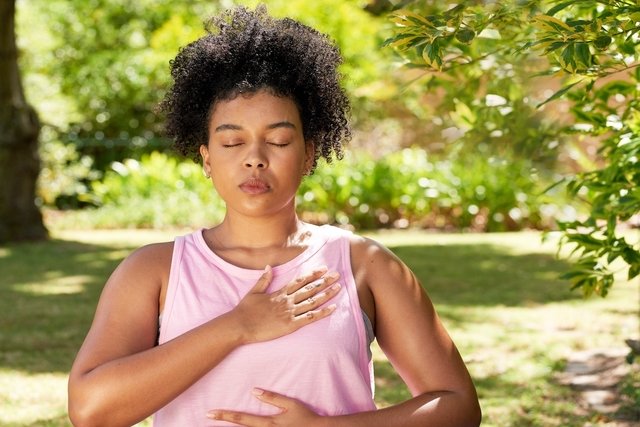
To quickly control tachycardia, better known as a racing heart, it is recommended to breathe deeply for 3 to 5 minutes, cough hard 5 times or put a cold compress on your face, as this helps control your heartbeat.
Tachycardia occurs when the heart rate is above 100 bpm, and can be caused by stress, anxiety or consumption of drinks containing caffeine, but it can also be indicative of health problems, such as arrhythmias, heart failure or heart attack, for example. See the main causes of tachycardia.
These techniques can help control tachycardia, however, if it lasts more than 30 minutes, happens during sleep, the person faints or has symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath or tingling in the arm, you should call SAMU on 192 or take the person immediately to the emergency room, as this may indicate a heart problem that requires immediate treatment with a cardiologist.

How to slow down your heart
Some techniques that can help normalize your heartbeat are:
- Deep breathinhaling air through the nose and exhaling air through the mouth slowly 5 times;
- Stand up straight and bend your torso towards the legs;
- Put a cold compress on your face or wash your face in cold water for 20 to 30 seconds;
- Take a cold shower or drink a glass of ice water;
- To cough with force 5 times;
- Hold the breath and strain as if you were evacuating;
- Blow, releasing air slowly with the mouth half-closed 5 times;
- Count the numbers from 60 to 0, slowly and looking up;
- Perform the Valsalva maneuver, holding your breath, holding your nose with your fingers and then forcing the air out, applying pressure. See how to do the Valsalva maneuver correctly.
After using these techniques, the symptoms of tachycardia, which can include tiredness, shortness of breath, malaise, a feeling of heaviness in the chest, palpitations and weakness, will begin to decrease, eventually disappearing after a few minutes.
If the tachycardia lasts more than 30 minutes, or the person has numbness on one side of the body or faints, it is recommended to call SAMU on 192, as these symptoms may indicate a problem with the heart, which requires treatment in the hospital, which may include the use of medication directly into a vein.
Don’t ignore your symptoms!
Medicines to control tachycardia
If tachycardia occurs several times in everyday life, it is recommended to consult a cardiologist who may request tests such as an electrocardiogram, echocardiogram or even a 24-hour Holter so that the heart rate is monitored and is appropriate for the person’s age. See what the normal heart rate values are for each age.
After the doctor analyzes the tests, he or she may recommend medications to control tachycardia, such as amiodarone or flecainide, these are normally used when you have a disease that causes sinus tachycardia and, therefore, should only be taken under the guidance of a doctor.
However, some anxiolytic medications, such as alprazolam or diazepam, can help control tachycardia, especially when it is caused by excessive stress. Typically, these medications are prescribed by the doctor to be used when the person presents intense symptoms of anxiety.
Natural treatment for tachycardia
Some natural measures can be taken to reduce the symptoms of tachycardia and these measures are mainly related to lifestyle changes such as avoiding drinking drinks with caffeine and alcohol and stopping smoking.
Furthermore, it is important to maintain a healthy diet, with less fat and sugar, and exercise, as this helps to release endorphins in the body, which are substances responsible for the feeling of well-being.
It is also necessary to carry out activities that reduce stress and anxiety, such as meditation, for example. Here’s how to get rid of stress.
When to go to the doctor
It is recommended to go to the emergency room immediately or consult a cardiologist when tachycardia:
- It takes more than 30 minutes to disappear;
- There are symptoms such as chest pain that radiates to the left arm, tingling, numbness, headache or shortness of breath;
- Appears more than twice a week;
- Fainting.
In these cases, the cause of tachycardia may be related to a more serious heart problem and treatment must be guided by a cardiologist.
Bibliography
- HOEVELMANN, J.; et al. Irregular, narrow-complex tachycardia. Cardiovasc J Afr. 29. 3; 195-198, 2018
- MAHTANI, AU; NAIR, DG Supraventricular Tachycardia. . . . North Am Clin Med. 103. 5; 863–879,
- AL-ZAITI, SS; MAGDIC, K.S. Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am. 28. 3; 309-16, 2016
- CHIN, A.; et al. An approach to the patient with a suspected tachycardia in the emergency department. S Afr With J. 106. 3; 246-50, 2016
- HEALTH DIRECT AUSTRALIA. Tachycardia. 2023. Available at: <https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/tachycardia>. Accessed on 03 Nov 2023

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13