Herpangina is a disease caused by viruses Coxsackieenterovirus or herpes simplex virus that affects babies and children between the ages of 3 and 10, causing symptoms such as sudden fever, mouth ulcers and sore throat.
Herpangina symptoms can last up to 12 days and there is no specific treatment, only comfort measures are recommended to alleviate symptoms and aid recovery.
Herpangina is normally a mild situation that lasts a few days, but in rare cases some children may present complications such as changes in the nervous system and heart or lung failure, and therefore in case of suspicion, you should always go to the pediatrician to evaluate the condition. case and initiate the most appropriate treatment.
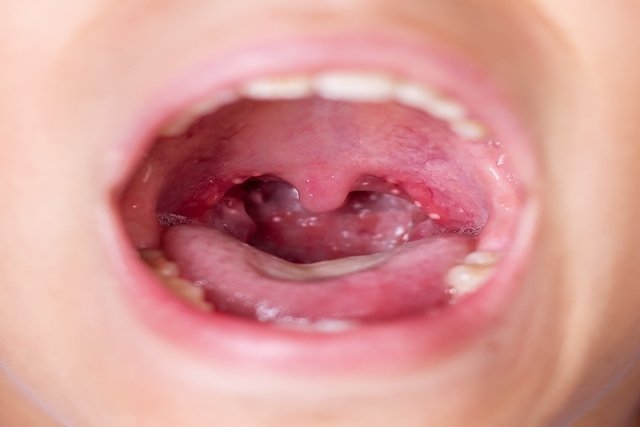
Main symptoms
The main symptoms of herpangina are:
- Appearance of blisters in the mouth and throat, which when burst leave whitish spots
- Sudden fever, which usually lasts 3 days;
- Sore throat;
- Red and irritated throat;
- Small white wounds inside the mouth with a reddish circle around it. The child may have 2 to 12 small canker sores inside the mouth, measuring less than 5mm each;
- Canker sores are usually found on the roof of the mouth, tongue, throat, uvula and tonsils, and can remain in the mouth for 1 week;
- Bumps may appear in the neck region.
Symptoms can appear between 4 and 14 days after contact with the virus and it is not uncommon for a child to present symptoms about 1 week after being in a waiting room with other sick children waiting for an appointment or in crowded places with poor conditions. hygiene, for example.
How the diagnosis is made
The diagnosis of herpangina is made by observing the symptoms, but the doctor may request tests to confirm the disease, such as isolating the virus from one of the sores or blisters in the throat or mouth.
In the case of a herpangina epidemic, however, the doctor may choose not to request more specific tests, with the diagnosis being based on the similarity of symptoms presented by other children in the same period.
How to get herpangina
Contagion by the virus responsible for herpangina can happen when a child comes into contact with the secretions of a person infected with the disease, whether through a sneeze or cough, for example. However, the virus can also be found in feces and, therefore, dirty diapers and clothes can also promote the spread of the disease.
Thus, as it is an easily transmitted disease, babies and children who attend nurseries and daycare centers are most at risk due to the contact they have with each other.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for herpangina involves relieving symptoms, without the need for specific antiviral medications. Therefore, the pediatrician may recommend treatment at home with the use of antipyretic medication, such as Paracetamol, to relieve fever, and anti-inflammatories and topical anesthetics in children over 2 years of age.
Also find out how to soothe your baby’s sore throat.
How should the diet be
Due to the presence of sores in the mouth, the act of chewing and swallowing can be painful, therefore, it is recommended that the diet be liquid, pasty and low in salt, with the consumption of non-citrus juices, soups and purees, for example. Furthermore, natural yogurt is a good option for keeping the baby fed and hydrated, especially since cold foods are more easily accepted by the child.
It is recommended to offer plenty of water to keep the child well hydrated, so that they can recover faster. In addition, plenty of rest is also recommended, avoiding overstimulating the child so that they can rest and sleep adequately.
Signs of improvement or worsening
Signs of improvement in herpangina are a decrease in fever within 3 days, an improvement in appetite and a decrease in sore throat.
However, if this does not happen or if other symptoms such as seizures appear, for example, you should return to your pediatrician for a new evaluation. Although it is rare, complications such as meningitis may arise, the treatment of which must be carried out in isolation in the hospital. See how viral meningitis is treated.
How to avoid transmission
Washing your hands frequently and always after changing your child’s diaper or clothes is a simple measure that can help prevent the spread of this disease to other children. Using an alcohol gel solution after changing a diaper is not enough and should not replace washing your hands properly. See how to wash your hands correctly to avoid spreading diseases in this video:
Bibliography
- DI PRINZIO, Anama; BASTARD, Dolores P.; TORRE, Ana Clara; MAZZUOCCOLO, Luis Daniel. Hand-foot-and-mouth disease in adults caused by Coxsackievirus B1-B6. Brazilian Annals of Dermatology. Vol 97. 3 ed; 321-325, 2022
- UNA-SUS. Oral health in primary health care: emergencies, communicable diseases, pregnant women, postpartum women and people with disabilities. 2021. Available at: <https://ares.unasus.gov.br/acervo/html/ARES/24522/1/Folder-MANIFESTA%C3%87%C3%95ES%20BUCAIS%20DOS%20ENTEROV%C3%8DRUS% 20HUMANOS_17-01-22.pdf>. Accessed on 14 Dec 2022

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13




