A herniated disc is a condition that affects the discs between the vertebrae of the spine, which when pressed change shape, which can put pressure on nearby nerve roots, causing symptoms such as back or neck pain, tingling or numbness in the arms or legs. .
The most common cause of a herniated disc is dehydration and weakening of the intervertebral discs due to the natural aging of the body, but it can also arise from injuries or trauma to the spine, poor posture or repetitive efforts.
Read too: Back pain: 13 main causes and what to do
A herniated disc, also called disc herniation, can affect the lumbar, cervical or thoracic spine and treatment is carried out by an orthopedist who may recommend the use of medication, physiotherapy or surgery, in the most serious cases.
Symptoms of a herniated disc
The main symptoms of a herniated disc are:
- Neck pain, which can radiate to the shoulder, arm or hands;
- Pain in the middle of the spine, which can also affect the ribs,
- Pain in the lower back or along the path of the sciatic nerve affecting the buttocks, thighs, legs and heels;
- Difficulty moving your neck or moving your legs;
- Tingling sensation and/or loss of strength in the arm, hands, legs or feet;
- Change in bladder or bowel function.
The symptoms of a herniated disc may vary according to the vertebra in the spine affected, and the pain usually worsens with movement and may worsen when coughing, laughing and having a bowel movement or urinating, and may appear suddenly or worsen over time.
Read too: 10 symptoms of a herniated disc (and how to confirm)
It is important to consult an orthopedist whenever symptoms of a herniated disc appear, to carry out tests, confirm the diagnosis and type of hernia, and thus be able to recommend the most appropriate treatment.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of a herniated disc is made by the orthopedist initially by evaluating symptoms, health history and physical examination.
Make an appointment with an orthopedist in the nearest region:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
In addition, the doctor should order an X-ray to check the alignment of the spine and the integrity or destruction of the vertebrae, as well as an MRI or CT scan to evaluate the disc, its thickness, the exact location of the hernia and the type of hernia. .
Types of disc herniation
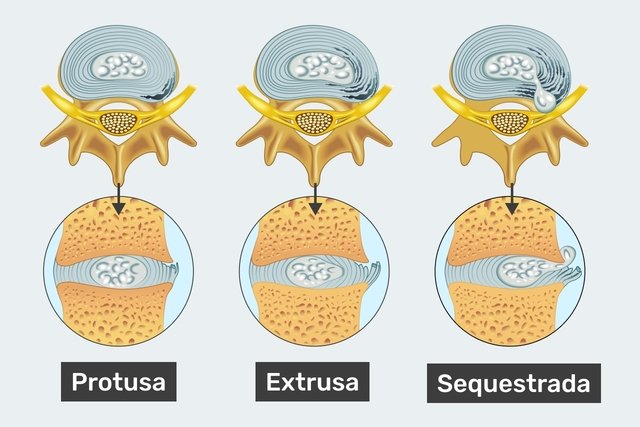
Disc herniation can be classified by its location or according to the deformity of the vertebral disc.
1. Types by location
Disc herniation can be classified into some types according to the region of the spine where it occurs:
- Cervical disc herniation: affects the neck region;
- Thoracic disc herniation: affects the mid-back region;
- Lumbar disc herniation: affects the lower back region.
It is important that the location and type of disc herniation is identified through imaging tests, as this allows the orthopedist to indicate the most appropriate treatment for the situation.
2. Types of disc deformity
Furthermore, disc herniation can also be classified according to the shape of the intervertebral disc, the main ones being:
- Protruded disc herniation: it is the most common type, when the nucleus of the disc remains intact, but the oval shape is already lost;
- Extruded disc herniation: when the core of the disc is deformed, forming a ‘drop’;
- Sequestered disc herniation: when the nucleus is very damaged and can even divide into two parts.
Sequestered disc herniation is the most serious type of disc herniation and causes the most intense symptoms.
Possible causes
A herniated disc is caused by deformity of the intervertebral disc, which loses its shape, resulting in compression of nearby nerves, leading to symptoms.
Some factors can contribute to the development of a herniated disc, such as:
- Degeneration, dehydration and weakening of the disc as the body ages;
- Bad posture;
- Genetic factors;
- Obesity or overweight;
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Smoking habit;
- Trauma or injuries to the spine.
Other factors that can also increase the risk of a herniated disc are carrying very heavy objects or working with repetitive movements, as happens in professions such as dentists, nurses, painters or drivers, for example.
Read too: Degenerative disc disease: what it is, symptoms, causes and treatment
Disc herniation during pregnancy
A herniated disc that was diagnosed before becoming pregnant can worsen during pregnancy, causing intense back pain that can put pressure on nerve roots, such as the sciatic nerve.
When the sciatic nerve is affected, a woman may experience pain in the back, buttock or behind the thigh.
Read too: Sciatic nerve pain: what it is, symptoms and how to relieve it
This happens because during pregnancy, progesterone leads to increased laxity in all the ligaments in the body, and as the spine also has ligaments, these become more elastic and end up allowing the vertebra to slip a little, which can aggravate or cause a problem. disc herniation.
During pregnancy, you can use painkillers or medications recommended by your obstetrician. See the main treatments for herniated discs during pregnancy.
How the treatment is carried out
The treatment of a herniated disc must be guided by the orthopedist according to the symptoms presented, location and severity of the hernia.
In general, the recommended treatment is:
- Analgesics and anti-inflammatories, such as ibuprofen, naproxen or paracetamol;
- Muscle relaxants, such as cyclobenzaprine;
- Opioids, such as codeine or tramadol;
- Medicines for neuropathic pain, such as gabapentin, pregabalin or amitriptyline;
- Corticosteroids, in the form of injections directly into the spine, performed by the orthopedist;
- Physiotherapy, with equipment, stretching and individualized exercises;
- Exercises, such as RPG, hydrotherapy or Pilates guided by a physiotherapist;
- Surgery, in cases where the use of medication or physiotherapy was not sufficient or when the hernia is very serious.
During treatment, it is recommended that the person stay away from the activities that caused the hernia, do not make efforts and do not practice any type of physical activity. Check out more details on the treatment for herniated discs.
Check out these and other tips in the following video:
Bibliography
- DYDYK, AM; NGNITEWE MASSA, R.; MESFIN, FB IN: STATPEARLS (INTERNET). TREASURE ISLAND (FL): STATPEARLS PUBLISHING. Disc Herniation. 2023. Available at: <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441822/>. Accessed on January 18, 2024
- AMIN, R.; et al. Lumbar Disc Herniation. Curr Rev Musculoskeletal Med. 10. 4; 507–516, 2017
- ZHANG, AS; et al. Lumbar Disc Herniation: Diagnosis and Management. Am J Med. 136. 7; 645-651, 2023
- OU-Yang, DC; et al. Genetics of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Curr Osteoporosis Rep. 21. 1; 56-64, 2023
- WANG, S.; et al. Classification of cervical disc herniation myelopathy or radiculopathy: a magnetic resonance imaging-based analysis. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 13. 8; 4984-4994, 2023

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13




