The hepatitis B vaccine is indicated to protect against infection by all known subtypes of the hepatitis B virus, in adults and children. This vaccine induces the formation of antibodies against the hepatitis B virus and is part of the child’s basic vaccination schedule.
Unvaccinated adults can also get the vaccine, which is recommended especially for healthcare professionals, people with hepatitis C, alcoholics or people with other liver diseases.
The hepatitis B vaccine is produced by different laboratories and is available at vaccination stations and clinics.
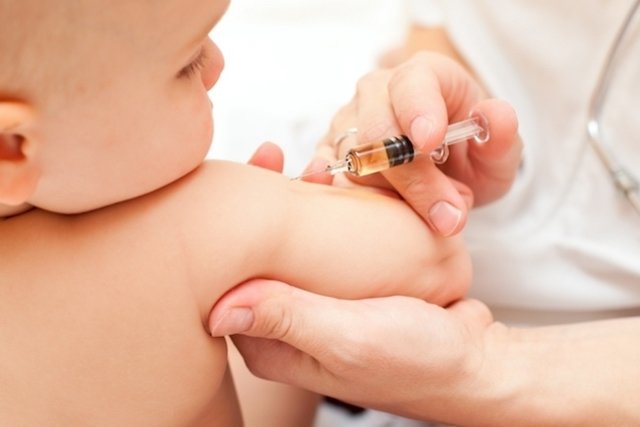
When vaccination is indicated
The hepatitis B vaccine is part of the free vaccination schedule and, therefore, is normally administered to the baby in the first hours after birth, with the 2nd and 3rd doses being administered at 1 and 6 months, respectively.
However, the vaccine can also be administered to adults who did not receive the vaccine in childhood. Administration during adulthood is recommended especially for people at higher risk of getting hepatitis B, such as:
- Health professionals;
- Patients who frequently receive blood products;
- Workers or residents in institutions;
- People at greater risk due to their sexual behavior;
- Injectable drug users;
- Residents or travelers to hepatitis B virus endemic areas;
- People with sickle cell anemia;
- Patients who are candidates for organ transplantation;
- People in contact with patients with acute or chronic HBV infection;
- People with chronic liver disease.
Even if the person does not belong to a risk group, they can be vaccinated against the hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B vaccine during pregnancy
The hepatitis B vaccine is the most effective form of prevention to avoid contamination by the hepatitis B virus and, consequently, transmitting it to the baby, therefore, all pregnant women who have not received the vaccine should take it before get pregnant.
If the benefits outweigh the risks, the vaccine can also be taken during pregnancy and is recommended for pregnant women who have not been vaccinated or who have an incomplete vaccination schedule.
How it is administered
Children: The vaccine must be administered intramuscularly, in the thigh region, by a healthcare professional.
- 1st dose: first 12 hours of life;
- 2nd dose: 1st month of age;
- 3rd dose: 6 months of age.
Adults: The vaccine must be administered intramuscularly, into the arm.
- 1st dose: Age not determined;
- 2nd dose: 30 days after the 1st dose;
- 3rd dose: 180 days after the 1st dose.
In special cases, the interval between each dose may be shorter.
Possible side effects
Some of the most common side effects that may occur after administration of the vaccine are irritability, pain and redness at the injection site, fatigue, loss of appetite, headache, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and abdominal pain, malaise and fever. .
Who shouldn’t take
The hepatitis B vaccine should not be administered to people with known hypersensitivity to any of the components of the formula.
Furthermore, it should also not be administered to pregnant or breastfeeding women, unless recommended by a doctor.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13