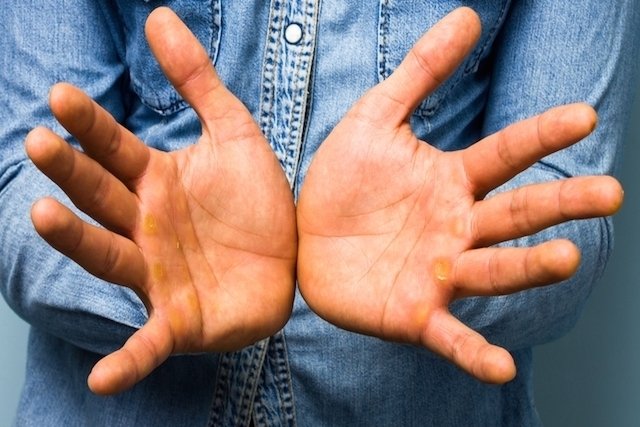
Hand allergy, also known as hand eczema, is a type of allergy that appears when the hands come into contact with an aggressive agent, causing skin irritation and leading to the appearance of some signs and symptoms such as redness and itching in the hands.
Typically, this allergy is caused by hand contact with soaps, detergents and other cleaning products, and is more common in people with a genetic predisposition and who work with these substances, for example.
If you suspect a hand allergy, it is important to consult a dermatologist or immunologist to confirm the diagnosis and begin the most appropriate treatment, which may involve anti-allergy medications and anti-inflammatory ointments, in addition to avoiding contact with possible irritating products and materials.
Sensitive content
This image may contain content that is uncomfortable for some people.
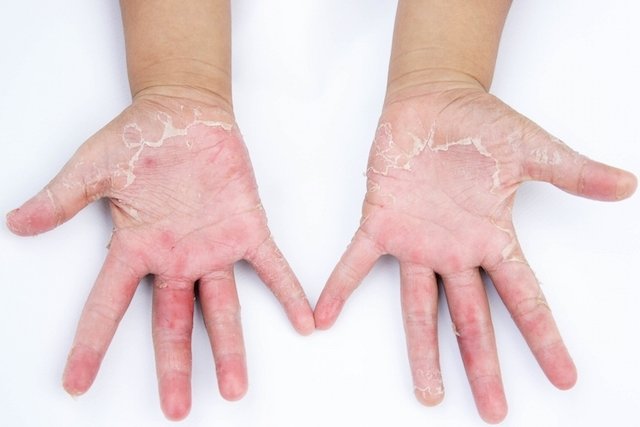
Hand allergy symptoms
The main symptoms of hand allergies are:
- Itch;
- Redness;
- Dry skin;
- Swelling;
- Cracked hands;
- Skin peeling
- Bubbles;
- More sensitive skin;
- Skin thickening.
Hand allergies can take up to 3 days to appear after contact with irritating products or materials, and it is common for allergies to affect both hands at the same time or just specific parts, such as the palms or fingertips.
Furthermore, symptoms such as nail deformities, skin thickening and cracking tend to appear especially when the allergy is not treated properly. Learn more allergy symptoms.
Online symptom test
To find out if you have an allergy, please select the symptoms you are experiencing:
This test is a tool that serves as a means of guidance only. Therefore, it is not intended to provide a diagnosis or replace consultation with an allergist, immunologist or general practitioner.
Possible causes
Hand allergies are usually caused by contact with cleaning products, soap, detergents, oils and creams, which can cause skin irritation, especially when perfumed.
Some of these products remove the skin’s natural protection, making it easier to dehydrate, which makes the skin on your hands drier and more unprotected.
Other possible causes of hand allergies include the use of jewelry, such as rings and bracelets, the use of gloves made from materials such as wool or cotton, frequent exposure to cold or heat and frequent rubbing of the hands with clothes, for example.
Furthermore, hand allergies are more common in people with a genetic predisposition and who work as painters, hairdressers, cleaning employees and general services, due to frequent contact with chemical products.
Can hand allergies be emotional?
Hand allergies can worsen or be caused by emotional changes, such as stress or anxiety, in some people and, normally, other symptoms such as excessive worry and difficulty sleeping are also present. Understand better what emotional allergy is.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for hand allergies can be done with anti-allergy medications, such as hydroxyzine and cetirizine, and corticosteroid ointments, which should be used according to the doctor’s instructions, to reduce inflammation and relieve itching.
In cases of chronic allergy, when the allergy persists for more than 4 weeks and does not respond well to treatment, other medications may be indicated, such as azathioprine, methotrexate or cyclosporine.
Furthermore, when there are signs of infection in the hands, such as pain, intense redness, worsening swelling and wounds with pus, the dermatologist may also recommend the use of antibiotics.
Hand allergy ointments
The commonly recommended hand allergy ointments are those that contain corticosteroids, such as betamethasone or dexamethasone. However, especially when there is no response to treatment, other ointments, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, may also be recommended by the doctor. Check out the main ointments with corticosteroids.
Home treatment
In case of hand allergies, it is recommended:
- Use rubber gloves whenever washing dishes or clothes and when using cleaning products, to avoid direct skin contact with chemicals;
- Avoid washing your hands excessivelyespecially with hot water and very perfumed soaps;
- Apply neutral moisturizing cream on your hands after washing;
- Avoid scratching your handsso as not to cause injury.
Furthermore, it is also important to try to identify and avoid contact with possibly irritating products and materials, such as wool, cotton or nylon, which may be present in clothes and gloves, for example, and soaps, creams or scented oils.
Bibliography
- MONTORO, J. et al. Stress and allergy. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. Vol.19. 40-47, 2009
- STATPEARLS. Eczema. 2022. Available at: <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538209/>. Accessed on 30 Dec 2022
- STATPEARLS. Contact Dermatitis. 2022. Available at: <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459230/>. Accessed on 30 Dec 2022
- TORRES, Tiago et al. Update on Atopic Dermatitis. Acta Med Port. Vol.32, n.9. 606-613, 2019
- NEDOROST, Susan T. Allergic Contact Sensitization in Healthy Skin Differs from Sensitization in Chronic Dermatitis: Atopic, Occupational Wet Work, and Stasis Dermatitis. Dermatol Clin. Vol.38, n.3. 301-308, 2020

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13




