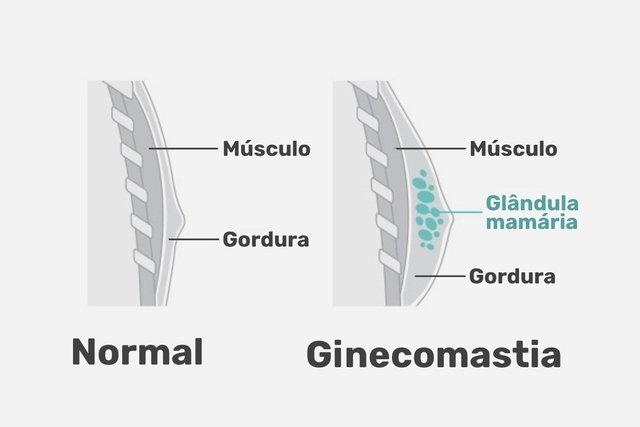
Gynecomastia is the enlargement of breasts in men, due to excess tissue in the mammary gland, which can occur due to an imbalance in the levels of estrogen and testosterone hormones, obesity or the use of medication, for example.
This condition, also called male gynecomastia, occurs more frequently in adolescence, but it can also occur in newborns or the elderly, and affect one breast or both, and generally tends to disappear spontaneously.
However, if there is no improvement, you should consult an endocrinologist to assess the type and cause of gynecomastia and thus indicate the most appropriate treatment that can be carried out using medication or surgery, for example.
Gynecomastia symptoms
The main symptoms of gynecomastia are:
- Enlargement of one or both breasts;
- Difference in size from one breast to another;
- Increased sensitivity in the breast or nipples;
- Breast pain, especially in adolescents;
- Swelling in the affected breast;
- Larger or darker areola, in some cases.
When gynecomastia occurs in just one breast, it is called unilateral gynecomastia, whereas when it occurs in both breasts, it is called bilateral gynecomastia.
When it occurs in both breasts, there is generally an uneven increase, which can cause self-esteem problems in men.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of gynecomastia is made by an endocrinologist or general practitioner, through the evaluation of symptoms, health history and medication use, family history of gynecomastia, in addition to a physical examination of the breasts, neck, thyroid, armpits and testicles.
Make an appointment with an endocrinologist in the nearest region:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
In addition, the doctor must order tests that measure the amount of estrogen and testosterone hormones in the body, as well as tests to evaluate the function of the kidneys, liver and thyroid.
In some cases, your doctor may order mammography, MRI or CT scans of your breasts, an ultrasound of your testicles if necessary, or a biopsy of your breast tissue to rule out conditions with similar symptoms, such as breast cancer, lymphoma. or dermoid cyst, for example.
Possible causes
Male gynecomastia is caused by a hormonal imbalance, in which there is a decrease or blockage of the effects of testosterone or an increase in the amount of estrogen in the body.
Some factors can cause this hormonal imbalance, such as:
- Normal hormonal changes at birth, adolescence or adulthood;
- Obesity or malnutrition;
- Hypogonadism or hyperthyroidism;
- Infection in the testicle;
- Klinefelter syndrome;
- Renal or hepatic failure or cirrhosis of the liver;
- Use of anabolic steroids or estrogen-containing medications;
- Consumption of drugs, such as marijuana, amphetamines or heroin.
Furthermore, gynecomastia can also arise due to breast cancer, tumors in the testicle, adrenal gland or pituitary gland, as they lead to a hormonal imbalance.
Gynecomastia in men can also occur as a side effect of taking medications such as omeprazole, cimetidine, captopril, amlodipine, digoxin, amiodarone, amitriptyline or clomipramine, for example.
Additionally, treating cancer with chemotherapy or radiotherapy, or treating HIV infection, can lead to breast enlargement in men, causing gynecomastia.
Types of gynecomastia
Gynecomastia can be classified into some main types according to the size of the breast, excess skin and the characteristics of the breast tissue, the main ones being:
- Grade 1 gynecomastia: there is a small increase in the breast around the areola, due to the appearance of a mass of concentrated breast glandular tissue, as if it were a button around the areola, with no excess skin, but one breast may be slightly larger than the other;
- Grau gynecomastia 2a: there is a moderate increase in the breast, without excess skin, and the mass of breast tissue is generally concentrated in the lower part of the breast, close to the chest, and in this case, there may be an accumulation of fat, which can be seen through clothing;
- Grade 2b gynecomastia: it is the same as grade 2a gynecomastia, however, in this case, there is excess skin on the breast;
- Grade 3 gynecomastia: is the most advanced stage in which the mass of breast tissue is widely spread throughout the breast, and there is excess fat and skin in the area.
The treatment of each type of gynecomastia depends on the amount of skin and the size of the breast, and should always be recommended by an endocrinologist.
How the treatment is carried out
The treatment of gynecomastia must be guided by a gynecologist and usually consists of:
1. Medical follow-up
Medical monitoring only aims to assess breast development, mainly in cases of gynecomastia in newborns, which occurs due to the effects of the mother’s estrogen in the uterus and generally disappears within 2 to 3 weeks after birth.
Another type of gynecomastia that is considered normal and that can require medical monitoring is male gynecomastia of adolescence due to puberty, which disappears spontaneously, generally within 6 months to two years. Discover the main changes in the body during puberty.
2. Use of medicines
Treatment with medication may be indicated by the endocrinologist when the breasts do not reduce spontaneously or when swelling, pain or sensitivity is noted in the affected breast.
The remedies that can be used to treat male gynecomastia are:
- Tamoxifen or clomiphene citrate: act by blocking the effects of estrogen in the body;
- Anastrozole or letrozole: they act by preventing the formation of estrogen, which leads to a decrease in the levels of this hormone in the body;
- Testosterona, dihidrotestosterona ou danazol: which act by increasing testosterone levels in the body.
These medications should only be used under the supervision of an endocrinologist and with specific doses for each person.
3. Surgery
Surgery for gynecomastia is recommended by the doctor to reduce the size of the affected breast in cases where the gynecomastia does not disappear naturally within 2 years, when it interferes with daily activities or causes embarrassment in the man.
In addition, surgery may also be recommended in cases where medications have not been able to reduce the size of the breast or when breast cancer is suspected. See the symptoms of male breast cancer and treatment.
The main types of surgery that can be done for gynecomastia include:
- Liposuction: which consists of removing fat from the breast, but not the mammary glands;
- Mastectomy: consists of removing tissue from the mammary gland, made with small cuts in the skin, which allows for faster recovery.
In adolescence, it is recommended to wait for the end of puberty to undergo surgery, to reduce the risk of gynecomastia reappearing.
The surgeries take around an hour and a half and are performed with sedation and local or general anesthesia, depending on the plastic surgeon who will perform the surgery. During surgery, a half-moon-shaped cut is made around the nipple to remove excess breast tissue, which is then sent for analysis to rule out the possibility of cancer.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13