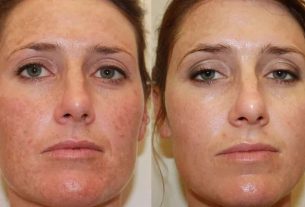
Glycolic acid is a type of alpha hydroxy acid produced from sugar cane and other sweet vegetables, used in the manufacture of aesthetic products, as it is easily absorbed by the skin, and can be used to reduce expression lines, treat acne or lighten blemishes on the skin.
Glycolic acid can be found in the composition of creams, gels, lotions, soaps or serums, for daily use, or it can have a stronger concentration for carrying out peelswhich must be carried out by a dermatologist or beautician.
The use of glycolic acid must be recommended by the dermatologist, according to the objective of the treatment, as the products contain different concentrations of glycolic acid, and in higher concentrations it can cause skin irritation or redness, especially in sensitive skin.

What is it for
Glycolic acid is typically indicated for:
- Promote skin rejuvenation;
- Reduce or prevent wrinkles and expression lines;
- Keep skin firm and soft;
- Reduce sagging;
- Increase skin hydration;
- Soften and brighten the skin;
- Keep pores clean;
- Promote skin exfoliation;
- Prevent acne and ingrown hairs;
- Correct scar caused by acne;
- Lighten skin blemishes caused by acne, melasma or the sun;
- Increase firmness and softness to the skin;
- Control skin oil;
- Help with the treatment of stretch marks.
Glycolic acid is capable of promoting cell renewal through exfoliation and peeling of the skin, in addition to stimulating collagen production, ensuring the firmness and elasticity of the skin.
Furthermore, due to the removal of dead cells, glycolic acid facilitates the absorption of other substances used on the skin, such as moisturizers or whitening products, for example.
Treatment with glycolic acid should be recommended by a dermatologist, who will be able to advise on the ideal form of use and quantity for each skin type.
How to use
Before starting to use glycolic acid, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist so that the skin can be assessed and the best product with adequate concentrations of glycolic acid can be recommended.
Glycolic acid can be used during your morning or evening routine. When applied in the morning, it is recommended that the face is first washed with soap and water or a cleansing gel suitable for the skin type and then a serum is applied to ensure skin protection. After it dries, you must apply the product with glycolic acid, prioritizing the areas to be treated, and then the sunscreen. When applied at night, it is recommended to wash your face and then use glycolic acid.
When used in cosmetic products, in the form of creams or lotions, glycolic acid is found in concentrations of 1 to 10%. As for aesthetic procedures, such as peeling, this acid can be found in concentrations of up to 70% depending on the objective of the treatment. Understand how the peeling.
Possible side effects
Although glycolic acid is a product considered safe, in some people, especially those with more sensitive skin, it can cause redness, burning, sensitivity to light, a burning sensation on the skin and, if it causes injuries, cause hypertrophic scars.
To avoid these unwanted effects, it is recommended that any skin treatment be recommended by a dermatologist, who will be able to assess the skin type and what should be done safely for each person.
Furthermore, it is important to apply sunscreen daily, with SPF 30 or more, as recommended by the dermatologist according to the skin type, as the skin can become more sensitive, increasing the risk of sunburn.
Who shouldn’t use
Glycolic acid should not be used by pregnant women or by people who have active skin infections, sunburn, eczema, skin inflammation, active herpes simplex, or very sensitive skin.
Furthermore, it should also not be used on people with dark skin, as it can cause blemishes on the skin.
Bibliography
- VALLE-GONZÁLEZ, ER; et al. pH-Dependent Antibacterial Activity of Glycolic Acid: Implications for Anti-Acne Formulations. Sci Rep. 10. 1; 7491, 2020
- LIU, H.; et al. Evidence-based topical treatments (azelaic acid, salicylic acid, nicotinamide, sulfur, zinc, and fruit acid) for acne: an abridged version of a Cochrane systematic review. J Evid Based Med. 13. 4; 275-283, 2020
- SAMPLE, E.; et al. Clinical efficacy and reflectance confocal microscopy monitoring in moderate-severe skin aging treated with a polyvinyl gel containing retinoic and glycolic acid: An assessor-blinded 1-month study proof-of-concept trial. J Cosmet Dermatol. 20. 1; 310-315, 2021
- SHARAD, J. Glycolic acid peel therapy – a current review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 6. 281-8, 2013
- SARKAR, R.; et al. Comparative Study of 35% Glycolic Acid, 20% Salicylic-10% Mandelic Acid, and Phytic Acid Combination Peels in the Treatment of Active Acne and Postacne Pigmentation. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 12. 3; 158-163, 2019
- THOMAS, JR; et al. Effects of topicals on the aging skin process. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 21. 1; 55-60, 2013
- FDA. Glycolic Acid. 2016. Available at: <https://www.fda.gov/media/101373/download>. Accessed on June 29, 2021
- YOKOMIZO, Vania Marta F.; BENEMOND, Tania Maria H.; CHISAKI, Chinobu; BENEMOND, Paula H. Chemical peels: review and practical application. Surg Cosmet Dermatol. Vol 5. 1 ed; 58-68, 2013
- CHANDRASHEKAR, BS; ASHWINI, KR; VASANTH, Vani; NAVALE, Shreya. Retinoic acid and glycolic acid combination in the treatment of acne scars. Indian Dermatol Online Journal. Vol 6. 2 ed; 84-88, 2015
- Sharad Jaishree. Glycolic acid peel therapy – a current review. Clinical, Cosmeti. 6. 281–288., 2013

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13