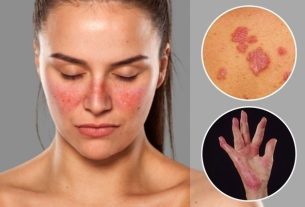
Gestational urticaria is a skin irritation characterized by the appearance of rashes, which are reddish spots on the skin, intense itching and swelling on the belly, breasts and hips, or throughout the body.
Gestational urticaria can be caused by factors such as stress, food allergies, insect bites or medications. Furthermore, this condition can also arise due to sensitivity to certain hormones common during pregnancy.
Read too: Urticaria: what it is, symptoms, causes, types and treatment
In the presence of symptoms indicative of gestational urticaria, it is important to consult an obstetrician or dermatologist, so that a general assessment can be carried out and appropriate treatment can be indicated, including some simple measures, such as applying cold compresses and using body moisturizers, or, in some cases, , the use of antihistamine medications.

Main symptoms
The main symptoms of gestational urticaria are:
- Rashes, which are raised spots on the skin;
- Intense itching and/or burning;
- Pink or red plaques on the skin;
- Swelling of the skin.
These symptoms can be located on the belly, breasts and hips, or spread throughout the body, being more common in the 1st and 3rd trimester of pregnancy, lasting a few hours and disappearing without leaving any marks.
However, the spots may appear again on other parts of the body, remaining for around 6 weeks, this type of hives being known as chronic urticaria.
Read too: Chronic urticaria: what it is, symptoms, causes and treatment
In cases of a severe allergic reaction, or anaphylaxis, other symptoms may also appear, such as swelling of the lips, tongue, throat or eyes, difficulty breathing or fainting. In these cases, you should seek medical attention immediately.
How the diagnosis is made
The diagnosis of gestational urticaria is made by an obstetrician or dermatologist, through evaluation of the symptoms and signs presented, and the woman’s health history.
If you want to assess your risk of gestational urticaria, make an appointment with the specialist closest to your area:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
In addition, the doctor may also order tests, such as blood, feces and urine, and skin biopsy, to identify the cause of urticaria or differentiate the diagnosis from other conditions with similar symptoms, such as papules and pruritic urticarial plaques of pregnancy (PPUG). ), gestational pemphigoid and gestational cholestasis.
Read too: Gestational cholestasis: what it is, symptoms, risks and treatment
Possible causes
Some of the possible causes of gestational urticaria are:
- Insect bites;
- Foods, such as peanuts, eggs, seafood;
- Excessive stress;
- Extreme heat or cold;
- Use of medications;
- Allergy to cleaning products, cleaning products or some plants.
In rare cases, gestational urticaria can also be caused by sensitivity to normal changes in hormone levels during pregnancy, such as prolactin, leptin, estrogen and progesterone, for example.
It is important to remember that urticaria during pregnancy is not a disease and, therefore, does not affect the baby’s development or harm labor.
What is the treatment like?
Treatment must be indicated by the doctor, using loratadine, cetirizine, levocetirizine and fexofenadine, which are oral antihistamine medications considered safe for the treatment of gestational urticaria.
Furthermore, in some cases, the doctor may also recommend the use of oral corticosteroids, such as prednisone and prednisolone, in small doses and for a short period of time.
Read too: Corticosteroids: what they are, what they are for, types and side effects
However, the use of oral medications during pregnancy is only done after the obstetrician evaluates the benefits for the woman and the possible risks for the baby.
Other care
Some precautions that can help alleviate the symptoms of gestational urticaria are:
- Use moisturizers to help relieve itching;
- Avoid very hot baths;
- Make cold compresses on the skin, with gauze or cotton, to reduce itching;
- Avoid scratching the affected area;
- Avoid contact with allergenic foods and products.
In addition, it is also recommended to do leisure activities, such as meditation, yoga, reading, walks in natural parks and practicing physical exercise regularly, as they help reduce stress.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13