The gastric balloon, also known as an intragastric balloon, is a technique that consists of placing a balloon inside the stomach to occupy some of the space and promote the feeling of satiety, reducing the need to eat a lot or very frequently, which favors weight loss.
To place the balloon, an endoscopy is usually done where the balloon is placed in the stomach and then filled with saline. This procedure is quite quick and carried out under sedation, meaning it is not necessary to be hospitalized.
Despite being a simple procedure, the gastric balloon is only indicated for people with a BMI greater than 35 kg/m2 or at 30 kg/m2 who have other associated diseases, in addition to being recommended that the balloon be removed after 6 months, resulting in the loss of around 13% of body weight.
When is indicated
The gastric balloon is indicated in cases where the degree of obesity is very high, where the Body Mass Index (BMI) is greater than 35 kg/m2. Furthermore, it is recommended for people with a BMI greater than 30 kg/m2 and other associated diseases such as high blood pressure, diabetes or sleep apnea, for example. It can also be indicated for people diagnosed with obesity and who do not wish to undergo bariatric surgery or who have no indication for surgery.
There is no age limit at which the balloon can be inserted, however, in the case of children, it is recommended to wait until the end of the growth phase, as the degree of obesity may decrease over time.
If you think the gastric balloon could be a solution for you, use our tool to schedule a consultation with a bariatric surgeon and clarify all your doubts:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
How the surgery to place the balloon is performed
Placing the intragastric balloon takes, on average, 30 minutes and the person does not need to be hospitalized, they should only rest for two to three hours in the recovery room before being discharged and returning home. Before starting the procedure, the person is sedated to facilitate the placement of the balloon.
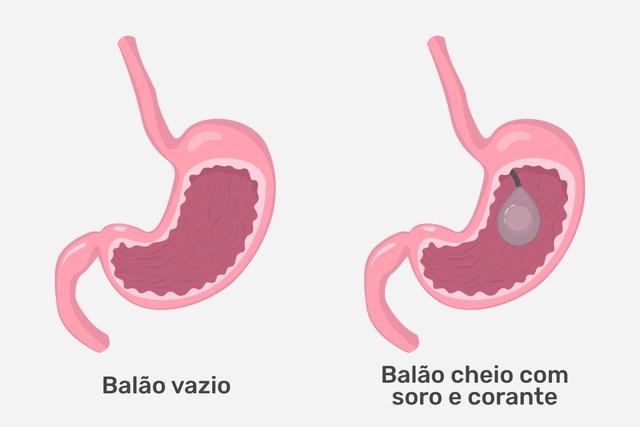
After sedation, flexible tubes are introduced through the mouth into the stomach with a micro camera at the tip that allows the inside of the stomach to be observed and then the balloon is introduced through the mouth while still empty and is then filled inside the stomach with serum and a blue liquid, which is used to turn urine or feces blue or greenish if the balloon ruptures.
To guarantee weight loss and results while using the balloon, it is very important to follow a diet guided by a nutritionist, low in calories, and which should be adapted in the first month after the procedure. Find out more about what your diet should be like after surgery.
Furthermore, it is also important to follow a regular exercise program, which, along with your diet, must be maintained after removing the balloon, to prevent you from gaining weight again.
When and how to remove the balloon
Removal of the gastric balloon is generally done 6 months after its placement and the procedure is similar to placement, with the liquid being aspirated and the balloon removed through endoscopy with sedation. The balloon must be removed as the balloon material is degraded by stomach acids.
After removal, it is possible to place another balloon 2 months later, however, this is often not necessary, as if the person adopts a healthy lifestyle they can maintain weight loss without using the balloon.
Risks of balloon placement
Placing an intragastric balloon to lose weight can cause nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain during the first week, while the body adapts to the presence of the balloon. In rarer cases, the balloon can rupture and go into the intestine, causing obstruction and causing symptoms such as a swollen belly, constipation and greenish urine. In these cases, you must go to the hospital immediately to have the balloon removed.
When not indicated
The placement of the gastric balloon is not recommended for people who have a hiatal hernia measuring more than 5 cm, active stomach or duodenal ulcers, inflammatory bowel disease, gastrointestinal neoplasia, oropharyngeal changes, changes in the coagulation process, active intestinal bleeding, varicose veins, alcoholism or psychiatric illnesses.
Furthermore, it is not recommended for pregnant women or people who are taking anticoagulant or anti-inflammatory medications or who have cardiovascular, pulmonary or cerebrovascular diseases.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13



