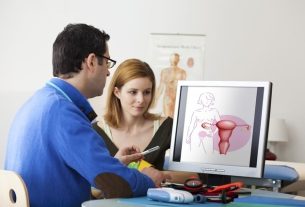
Female gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that can cause symptoms in some women, such as pain in the stomach, burning when urinating, discomfort during intercourse or vaginal discharge, depending on the location of the infection.
This infection is caused by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeaeor gonococcus, and can affect the mucosa of the vagina, rectum, urethra, pharynx or eyes, depending on how contact with the contaminated secretions occurred.
Read too: Gonorrhea: what it is, symptoms, transmission, types and treatment
If female gonorrhea is suspected, it is recommended to consult a gynecologist, infectious disease specialist or general practitioner. Treatment is usually done with antibiotics, and may also be indicated for recent sexual partners.
Main symptoms
The main symptoms of female gonorrhea are:
- Pain in the lower abdomen and/or during sexual intercourse;
- Yellowish vaginal, anal or urethral discharge;
- Anal and/or vaginal bleeding, in this case, outside the menstrual period;
- Burning or pain when urinating;
- Itching in the anal region;
- Sore throat and swelling in the neck;
The symptoms of female gonorrhea vary according to where the bacteria settles, and it is common for gonorrhea to cause no or few symptoms in women, especially when it affects the mucosa of the urethra, rectum or oropharynx.
In most cases, female gonorrhea affects the cervix, causing it to become inflamed. Therefore, especially when left untreated, it can worsen, resulting in pelvic inflammatory disease and complications such as infertility and chronic pelvic pain.
Read too: 27 gonorrhea symptoms (female, male and baby) and online test
In addition, female gonorrhea can also cause inflammation of the Bartholin glands in the woman’s genital region in some cases, causing symptoms such as fever, increased sensitivity and/or pain in the area. Check out the main symptoms of bartholinitis, inflammation of the Bartholin glands.
Online symptom test
To find out if you have gonorrhea, please select the symptoms you present:
This test is a tool that serves as a means of guidance only. Therefore, it is not intended to provide a diagnosis and does not replace consultation with an infectious disease specialist or gynecologist.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of female gonorrhea is normally made by a gynecologist, infectious disease specialist or general practitioner based on the symptoms presented and the results of the analysis of samples of secretions collected from places where the bacteria are suspected to be present.
If you want to make an appointment, you can find a gynecologist closest to you using the tool below:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
What causes female gonorrhea
Female gonorrhea is caused by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeaealso known as gonococcus, when it comes into contact with the mucosa of the vagina, rectum, pharynx or eyes, where it can settle and multiply.
Like other sexually transmitted infections, female gonorrhea is more common in sexually active young women who have sex without using a condom and have more than one sexual partner and/or a history of other STIs.
Read too: Sexually transmitted infections: top 10 STIs, treatment (and cure)
How to stick
Female gonorrhea is transmitted by contact between the mucosa of the vagina, urethra, rectum, pharynx or eyes of a woman with contaminated secretions from a person with gonorrhea, mainly the semen released at the time of ejaculation.
Therefore, the main way of transmitting gonorrhea to women is through vaginal, anal or oral sexual contact without using a condom with an infected person. Understand better how you get gonorrhea.
However, a pregnant woman with gonorrhea can also transmit the infection to her baby at the time of birth. In this case, the bacteria is normally transmitted by contact of the woman’s genital secretions with the mucous membrane of the baby’s eyes or oropharynx.
Read too: Gonorrhea during pregnancy: risks and treatment
How the treatment is carried out
Typically, there is no difference in the treatment of female and male gonorrhea. In most cases, the treatment of gonorrhea in the cervix, urethra, rectum or pharynx is done with intramuscular injection of ceftriaxone 500mg in a single dose. Find out how gonorrhea is treated.
Furthermore, especially in cases where it was not possible to rule out chlamydia infection, the doctor may also associate oral antibiotics with the treatment, such as azithromycin 1g in a single dose or doxycycline 100mg for 7 days.
To ensure a cure for gonorrhea, it is important that recent sexual partners are evaluated by a doctor and, if indicated, also undergo treatment. It is also recommended to avoid sex without a condom until at least 7 days after both parties finish treatment to avoid reinfection.
Read too: How to cure gonorrhea

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13