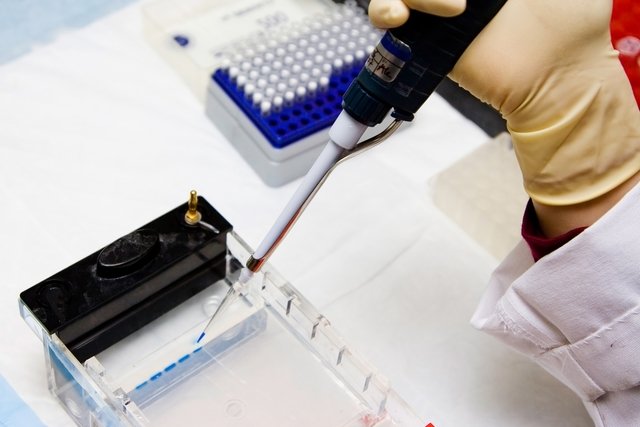
Electrophoresis is a laboratory technique carried out with the aim of separating DNA, RNA or protein molecules according to their size and electrical charge.
This technique is simple and low-cost and allows the diagnosis of diseases, such as sickle cell anemia, to check the expression of proteins or to identify microorganisms.
Electrophoresis is used as a routine technique in laboratories and research projects, and depending on the purpose of this examination, other tests may be necessary to reach certain diagnoses.
What is it for
Electrophoresis is used to:
- Identify viruses, fungi, bacteria and parasites, this application being more common in research projects;
- Paternity test;
- Check protein expression;
- Identify mutations, being useful in diagnosing leukemias, for example;
- Analyze the types of circulating hemoglobin, which is useful in diagnosing sickle cell anemia;
- Assess the amount of proteins present in the blood;
- Diagnose conditions that affect plasma cells, such as Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia, monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), or primary amyloidosis.
Protein electrophoresis can also be used to help diagnose thyroid problems, diabetes, liver disease, and some autoimmune diseases.
Depending on the purpose of the electrophoresis, it may be necessary to carry out other complementary tests, such as a blood count, kidney and liver function tests or x-rays, for example, for the doctor to conclude the diagnosis.
Types of electrophoresis
Electrophoresis to identify microorganisms is most commonly carried out in research laboratories, however, for diagnostic purposes, electrophoresis can be used to identify hematological diseases and diseases that evolve with an increase in the amount of proteins, the main types of electrophoresis being:
1. Hemoglobin electrophoresis
Hemoglobin electrophoresis is a laboratory technique performed to identify the different types of hemoglobin circulating in the blood, making it possible to identify the presence of diseases related to hemoglobin synthesis.
The type of hemoglobin is identified through electrophoresis at a specific pH, ideally between 8.0 and 9.0, with a band pattern that can be compared to the normal pattern, allowing the presence of abnormal hemoglobin to be identified.
What it is made for: Hemoglobin electrophoresis is performed to investigate and diagnose diseases related to hemoglobin synthesis, such as sickle cell anemia and hemoglobin C disease, in addition to being useful in differentiating thalassemias. Learn how to interpret hemoglobin electrophoresis.
2. Protein electrophoresis
Protein electrophoresis is a test requested by a doctor to assess the amount of proteins circulating in the blood and thus identify diseases.
This test is carried out using a blood sample, which is centrifuged to obtain plasma, which is the part of the blood made up, among other substances, of proteins.
After electrophoresis, a band pattern can be visualized and, subsequently, a graph indicating the amount of each protein fraction, which is essential for diagnosis.
What it is made for: protein electrophoresis allows the doctor to investigate the occurrence of multiple myeloma, dehydration, cirrhosis, inflammation, liver disease, pancreatitis, lupus and hypertension according to the band pattern and the graph presented in the examination report. Understand how it is done and how to understand the results of protein electrophoresis.
How it is made
To perform electrophoresis, you must:
- Prepare an agarose or polyacrylamide gel, depending on the objective of performing the technique. In addition, you must have a buffer solution, electrophoresis tank, molecular weight marker and a substance capable of allowing samples to be viewed when exposed to UV or LED light;
- Place each sample into a well of the gelmixing a small amount of molecular weight marker;
- Place a positive control in one of the wells., which is the substance that we know what it is, and in another well, the negative control, to guarantee the validity of the reaction. In both wells, there must also be a molecular weight marker;
- Place the gel in the electrophoresis vat, if not, with the specific buffer solution, and turn on the device so that an electric current is generated capable of generating a potential difference and separating particles according to their charge and size. The electrophoretic run time varies according to the objective of the procedure, and can last up to 1 hour;
- Visualize the electrophoresis result using the transilluminator. When the gel is placed under UV or LED light, it is possible to visualize the band pattern: the larger the molecule, the smaller its migration, getting closer to the well, while the lighter the molecule, the greater the migratory potential. .
For the reaction to be validated, the bands of the positive control must be visualized and nothing must be seen in the negative control, otherwise this indicates that there has been contamination, and the entire process must be repeated.
Bibliography
- UNIVERSITY ROCHESTER MEDICAL CENTER. Protein Electrophoresis (Blood). Disponível em: <https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=167&contentid=protein_electrophoresis_serum>. Acesso em 22 set 2023
- BIOSPHERE ENCYCLOPEDIA, KNOWLEDGE SCIENTIFIC CENTER. Electrophoresis: concepts and applications. 2015. Available at: <http://www.conhecimento.org.br/enciclop/2015c/agrarias/Eletroforese.pdf>. Accessed on September 24, 2019
- PLANT. What is electrophoresis and why is it important?. Available at: <https://kasvi.com.br/o-que-e-eletroforese-e-qual-a-sua-importancia/>. Accessed on September 24, 2019

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13