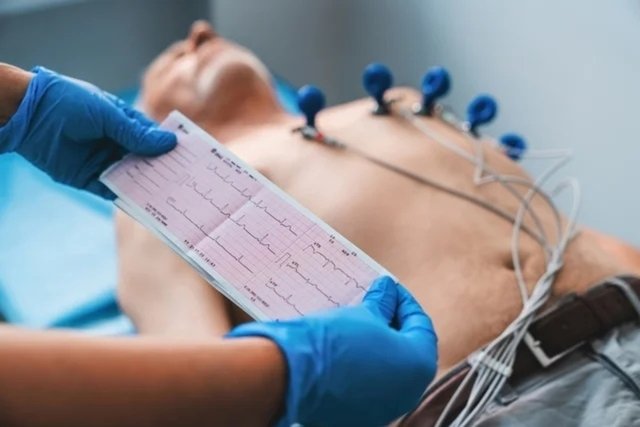
The electrocardiogram, or ECG, is an exam carried out to evaluate the electrical activity of the heart, thus observing the rhythm, quantity and speed of its beats. This exam is carried out using a device that draws graphs on this information about the heart.
The electrocardiogram is capable of identifying some diseases, such as arrhythmias, murmurs or even heart attacks, and must be performed and interpreted by a cardiologist.
The ECG is simple and quick and is considered normal when 60 to 100 beats per minute are identified. It is considered altered when less than 60 or more than 100 beats per minute are identified, and each case must be evaluated by the cardiologist and decide whether there is an indication to carry out other complementary tests to evaluate the functioning of the heart.
When is indicated
The electrocardiogram evaluates the activity of the heart, checking the frequency of heartbeats per minute, and is indicated in cases of:
- Cardiac arrhythmiaswhich can occur due to accelerated, slow or untimely heartbeats, which can present symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness or fainting;
- Acute myocardial infarctionwhich can be the cause of pain or burning in the chest, dizziness and shortness of breath;
- Inflammation of the walls of the heartcaused by pericarditis or myocarditis, which can be suspected when there is chest pain, shortness of breath, fever and malaise;
- Heart murmurdue to changes in the valves and walls of the heart, which generally cause dizziness and shortness of breath;
- cardiac arrestbecause in this case, the heart loses its contraction activity and, if it is not quickly reversed, it causes death.
This exam is also requested by the cardiologist to monitor the improvement or worsening of diseases, and also whether medications for arrhythmia or pacemakers are being effective.
How is done
The electrocardiogram is a simple and quick exam that does not require preparation, it is only recommended that the person avoid using creams in the chest area and shave the hair present in the area, if any, as this will ensure adequate fixation of the electrodes.
This exam can be carried out in the hospital, clinics or in the cardiologist’s office, and is carried out with the person lying on a stretcher with the placement of electrodes, which are connected to the electrocardiogram device, on the chest, wrists and ankles. It is important that the places where the electrodes will be placed are properly degreased.
The electrodes capture the heartbeat, which is recorded on the device and “released” in the form of a graph, which is analyzed by the cardiologist.
What does the result mean
The result of the electrocardiogram must be evaluated by the cardiologist taking into account the person’s health and family history. Thus, according to the number of beats per minute (bpm), the result can be classified as normal or abnormal:
- Normal result: indicates that the heart is beating at a regular rhythm, usually between 60 and 100 bpm;
- Abnormal result: indicates that the heart is beating slower or faster than ideal, that is, less than 60 bpm or more than 100 bpm.
In addition to the heart rhythm, the result may be abnormal when it presents changes suggestive of enlarged heart cavities, heart blockages, heart attack, pericarditis, among others.
After evaluating the result, especially abnormal results, the doctor may recommend carrying out additional tests to identify the cause of the change in heartbeat, such as echocardiogram, Holter monitoring and exercise testing, for example. Discover other tests that evaluate the heart.
Bibliography
- BRAZILIAN SOCIETY OF CARDIOLOGY. Resting Electrocardiogram Interpretation Guideline. 2003. Available at: <https://www.scielo.br/j/abc/a/JcS5MCwnr6jgn7CnMpVNz9c/?lang=pt&format=pdf>. Accessed on 10 Nov 2021

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13