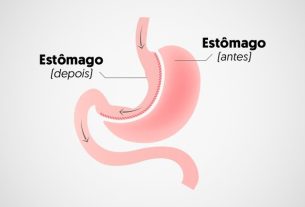
Treatment for acute diverticulitis is with a liquid diet or fasting, in addition to the use of antibiotics, such as Metronidazole and Ciprofloxacin, to reduce inflammation and infection in the large intestine.
This treatment can even be carried out at home, however, when there is a complicated attack of diverticulitis, with the formation of an abscess, fistula or intestinal obstruction, for example, it may be necessary to perform surgery to drain the secretion or remove the inflamed part of the intestine.
Diverticulitis is characterized by the inflammation of diverticula, which are small pouches that form in the intestine, which is diverticulosis, generally due to a diet poor in fiber and constipation. This inflammation can cause symptoms such as pain in the abdomen, nausea, vomiting, fever, constipation or diarrhea. Learn more about what causes diverticulitis and how to identify it.
1. Medicines
The gastroenterologist’s recommendation of medication for diverticulitis may vary according to the severity of the diverticulitis:
Uncomplicated diverticulitis
To treat uncomplicated acute diverticulitis, it is necessary to deinflame the intestine by fasting or following a liquid, residue-free diet. Antibiotics are also necessary, usually Metronidazole and Ciprofloxacin, for 7 to 10 days, as they are effective in controlling intestinal bacteria infection. Furthermore, the doctor may recommend the use of medicines for nausea, such as Metoclopramide and for abdominal pain, such as Hyoscine and Dipyrone, for example.
The doctor will also schedule a re-evaluation after about 5 days, however, if symptoms such as fever and abdominal pain worsen or become very intense during treatment, it is necessary to go to the emergency room.
Complicated diverticulitis
Complicated acute diverticulitis is treated in the hospital, with the use of intravenous antibiotics, and a surgical procedure may be necessary. In the case of an abscess, the surgeon may drain the accumulated secretion through a puncture.
2. Surgery
Surgery to remove part of the colon due to diverticulitis is indicated in cases of:
- Complicated acute diverticulitis, in which there may be abscesses, fistula, heavy bleeding, perforation or intestinal obstruction;
- Recurrent diverticulitis, that is, it happens more than once in the same person;
- Diverticulitis in people with weakened immunity, such as transplant recipients, people with HIV or kidney failure, for example, as new infections can put these people’s lives at risk.
The surgery can be performed via laparoscopy or conventional open surgery, performed in a surgical center and under general anesthesia. Surgery time is very variable and depends on the degree of inflammation of the diverticulitis and the amount of intestine removed. Generally, the person is discharged in about 3 days, and must recover at home, with medication to alleviate pain and discomfort, such as Dipirona, prescribed by the doctor, and following the diet advised by the hospital nutritionist.
3. Food
In cases of diverticulitis, nutrition is guided by a doctor and nutritionist, as for about 3 days, it is necessary to follow a liquid diet without residues, or fasting, to reduce the initial inflammation.
After treatment, the person must follow a diet that stimulates good bowel function, rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables and legumes. Furthermore, it may also be recommended to increase the consumption of probiotic foods, such as Activia yogurts, Yakult or Kefir, for example, as they protect the intestinal mucosa, regulate the intestine and strengthen the immune system. In this way, in addition to preventing the formation of new diverticula in the intestine, it is possible to prevent new inflammation. See more details on what nutrition should be like for diverticulitis.
4. Home remedies
Home remedies for diverticulitis aim to prevent the crisis, as they help to recover the intestinal wall, reducing the risk of inflammation. Some natural treatment options are chamomile and valerian tea and cat’s claw tea, for example, as they are rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatories. Check out other home remedy options for diverticulitis.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13