Cyanosis is the blue or purplish discoloration of the skin, nails or lips, caused by changes in blood circulation or in the oxygenation of hemoglobin, one of the components of red blood cells. Cyanosis can be caused by exposure to cold, but is often related to conditions such as heart failure, asthma, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Whenever it is persistent or recurrent, cyanosis must be diagnosed and treated by a doctor, who will evaluate the health history, perform physical examinations and request additional tests to identify the cause, thus indicating the most appropriate treatment.
As cyanosis can be considered a serious condition, it is recommended to seek medical attention as soon as this sign appears, especially if it is accompanied by symptoms such as shortness of breath, tiredness, chest pain and cough, to avoid complications.
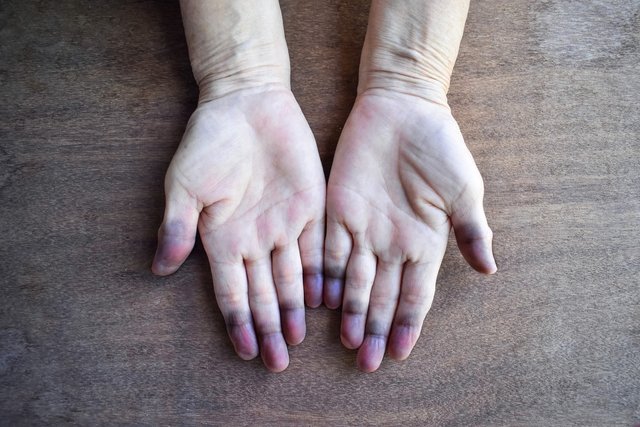
Types of cyanosis
According to the speed, flow of blood circulation and amount of oxygenated blood reaching the organs, cyanosis can be classified into:
1. Cyanosis of extremities
In cyanosis of the extremities, the flow and speed of blood circulation is reduced, with there not being sufficient circulation of oxygenated blood throughout the body.
This type of cyanosis, also known as peripheral, appears only in the upper and lower extremities of the body, such as the tips of fingers and toes, nails, tip of the nose, ears, tongues, gums and lips.
In addition to the blue or purplish color, in this type of cyanosis the extremities may also be colder and blood pressure may be lower.
2. Central cyanosis
Central cyanosis occurs when the blood arriving in the arteries has little or no oxygen, where this sign appears across the entire surface of the body and in the mucous membranes. In addition to the blue or purple color on the skin, symptoms such as difficulty breathing and higher blood pressure may also be present in this type of cyanosis.
3. Mixed cyanosis
This type of cyanosis occurs when both the flow and speed of blood circulation are reduced, and the blood that reaches the arteries has little or no oxygen.
Main causes
Cyanosis can be caused by any condition that alters blood oxygenation and transport, and can occur in adults and children. The main causes of cyanosis are:
- Lung diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary emphysema or pneumonia;
- Cardiovascular diseases, such as heart failure, atherosclerosis, congenital heart disease and thrombosis;
- Beta blocker medications, used to treat high blood pressure, such as carvedilol, bisoprolol and metoprolol;
- Tetralogy of Fallot, or blue baby syndrome, which is a genetic disease characterized by changes in the functions of the heart, reducing the amount of oxygen that circulates in the body;
- Exposure to cold air or cold water, which cause contraction of blood vessels, reducing blood circulation in the extremities of the body;
- high hemoglobin, which can be caused by situations, such as dehydration and kidney tumor, leading to other symptoms, such as dizziness and loss of vision, for example.
Furthermore, situations such as exposure to high altitudes, polycythemia, generalized infections and Raynaud’s syndrome may also be related to the onset of cyanosis.
How the diagnosis is made
The diagnosis of cyanosis must be made by a doctor, who generally assesses the person’s physical condition and health history. In addition, the doctor may also request some additional tests, such as a blood test, X-ray, electrocardiogram, ultrasound and computed tomography, to identify the possible cause of cyanosis and indicate the most appropriate treatment.
Another test that may also be requested by the doctor is arterial blood gas analysis, a blood test that assesses the efficiency of oxygen exchange in the blood, thus checking the functioning of the lungs. See how the arterial blood gas analysis is performed.
How the treatment is carried out
The treatment of cyanosis should always be carried out under the guidance and supervision of a doctor. As cyanosis is a symptom that can be related to different types of situations, treatment should be recommended according to the cause of this symptom, as follows:
- Medicines: digoxin, hydralazine and isosorbide are medications that may be indicated for heart failure, because they increase the strength of the heart and relax the blood vessels, making it easier for the heart to pump blood;
- Surgery: this procedure is indicated to correct changes in the structure or function of the heart, improving blood circulation in cases of tetralogy of Fallot and congenital heart disease;
- Ventilation or oxygen therapy: They are indicated to improve oxygenation and breathing, in cases of asthma, pneumonia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, for example.
In the case of cyanosis caused by prolonged exposure to cold temperatures, using hot water bottles and warmer clothing can help combat this symptom.
Bibliography
- NHS. Blue skin or lips (cyanosis). Disponível em: <https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/blue-skin-or-lips-cyanosis/>. Acesso em 23 mai 2022
- NATIONAL LIBRARY OF MEDICINE. Blue discoloration of the skin. Available at: <https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003215.htm>. Accessed on May 23, 2022
- STATPEARLS PUBLISHING LLC.. Cyanosis. 2022. Available at: <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482247/>. Accessed on May 23, 2022
- FILHO, B, Fred et al. Cyanosis and purpura in the fingers – foundations of differential diagnosis, regarding a case. Journal of the Portuguese Society of Dermatology and Venereology. Vol.72. 4.ed; 1-4, 2014
- Porto & Porto. Medical Semiology. 8 ed. Rio de Janeiro: Guanabara Koogan, 2019.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13



