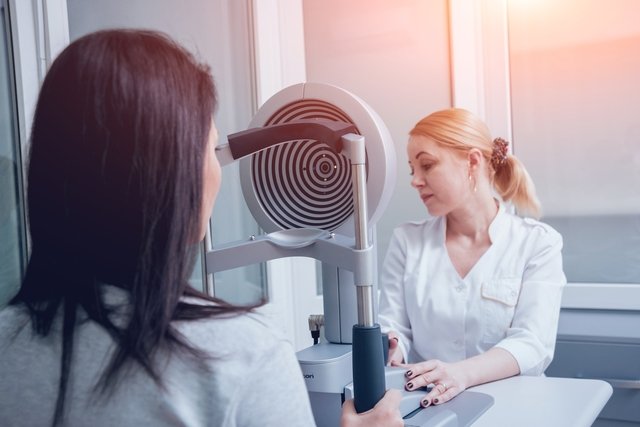
Keratoscopy, also called corneal topography or corneal topography, is an ophthalmological examination widely used in the diagnosis of keratoconus, which is a degenerative disease characterized by deformation of the cornea, which ends up acquiring a cone shape, causing difficulty in seeing and greater sensitivity to light.
This exam is simple, carried out in the ophthalmology office and consists of mapping the cornea, which is the transparent tissue in front of the eye, identifying any changes in this structure. The result of the corneal topography can be indicated by the doctor immediately after carrying out the exam.
Despite being most used in the diagnosis of keratoconus, keratoscopy is also widely performed pre- and post-operatively in ophthalmological surgeries, indicating whether the person is fit to perform the procedure and whether the procedure had the expected result.

What is it for
Corneal topography is done to identify changes in the surface of the cornea, and is mainly performed to:
- Measure the thickness and curvature of the cornea;
- Diagnosis of keratoconus;
- Identification of astigmatism and myopia;
- Evaluate the adaptation of the eye to the contact lens;
- Check for corneal degeneration.
Furthermore, keratoscopy is a procedure frequently performed in the pre-operative period of refractive surgeries, which are surgeries that aim to correct changes in the passage of light, however not all people who have changes in the cornea are able to undergo the procedure. , as is the case of people with keratoconus, because due to the shape of the cornea, they are not able to perform this type of surgery.
Therefore, in the case of keratoconus, the ophthalmologist may recommend the use of prescription glasses and specific contact lenses and, depending on the degree of change in the cornea, may recommend other surgical procedures. Understand how keratoconus is treated.
Corneal topography can also be done post-operatively, being important to check whether the change has been corrected and the cause of poor vision after refractive surgery.
How it is made
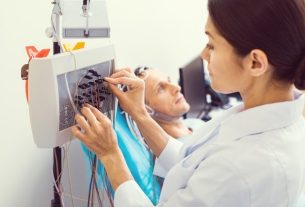
Keratoscopy is a simple procedure, carried out in the ophthalmology office and lasting between 5 and 15 minutes. To carry out this exam, it is not necessary to dilate the pupil, because it will not be evaluated, and it may be recommended that the person does not wear contact lenses 2 to 7 days before the exam, but this recommendation depends on the doctor’s advice and the type of contact lenses. of lens used.
To perform the exam, the person is positioned in a device that reflects several concentric rings of light, known as Placido’s rings. The cornea is the structure of the eye responsible for the entry of light and, therefore, depending on the amount of reflected light, it is possible to check the curvature of the cornea and identify changes.
The distance between the reflected light rings is measured and analyzed by software on a computer that is associated with the equipment. All information obtained from the emission of light rings is captured by the program and transformed into a color map, which must be interpreted by the doctor. Based on the colors present, the doctor can check changes:
- Red and orange are indicative of greater curvatures;
- Blue, violet and green indicate flatter curvatures.
Therefore, the redder and orange the map, the greater the change in the cornea, indicating that other tests are necessary to complete the diagnosis and initiate appropriate treatment.
Bibliography
- INSTITUTE OF OPHTHALMOLOGY OF CURITIBA. Corneal Topography. Available at: <https://ioc.med.br/blog/topografia-de-cornea/>. Accessed on October 11, 2019
- INSTITUTE OF OPHTHALMOLOGY OF RIO DE JANEIRO. What is Cornea. Available at: <https://www.iorj.med.br/o-que-e-cornea/>. Accessed on October 11, 2019
- PARAOPTOMETRIC RESOURCE CENTER. Understanding Corneal Topography. Disponível em: <https://www.aoa.org/Documents/optometric-staff/Articles/Understanding-Corneal-Topography.pdf>. Acesso em 11 out 2019
- BOWLING, Brad. Clinical Ophthalmology: a systematic approach. 8 ed. Rio de Janeiro: Elsevier, 2016. 173; 213.
- YANOFF, Myron; DUKER, Jay S. Ophthalmology. 3 ed. Rio de Janeiro: Elsevier, 2011. 210-213.
- MARTIN, Raul. Cornea and anterior eye assessment with placido-disc keratoscopy, slit scanning evaluation topography and scheimpflug imaging tomography. Indian Journal of Ophtalmology. Vol 66. 3 ed; 360-366, 2018
- BRAZILIAN CATARACT AND REFRACTIVE SURGERY ASSOCIATION. Keratometry or Computerized Corneal Topography or Computerized Corneal Keratoscopy. Available at: <https://brascrs.com.br/auxiliares/tecnologos-oftalmicos-ortoptistas/ceratometria-ou-topografia-computadorizada-de-cornea-ou-ceratescola-computadorizada-da-cornea/>. Accessed on October 11, 2019
- PANAMERICAN VISION INSTITUTE. Computerized Keratoscopy. Available at: <https://www.ipvisao.com.br/site/exames-ceratescola_computadorizada>. Accessed on October 11, 2019

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13