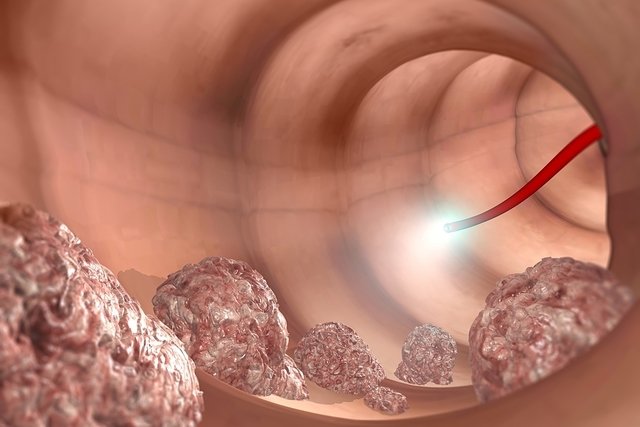
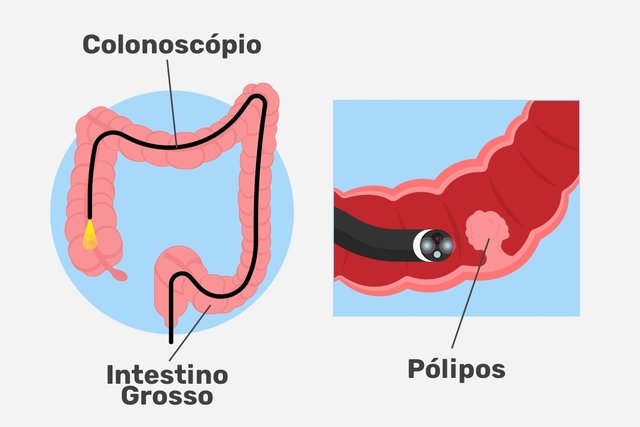
Colonoscopy is an exam that assesses the health of the intestine, and is mainly indicated to identify the presence of polyps, intestinal cancer or other types of changes in the intestine such as colitis, varicose veins or diverticular disease.
A colonoscopy exam is normally recommended by a gastroenterologist when there are symptoms that may indicate important intestinal changes, such as bleeding or persistent diarrhea, and can also be routinely recommended for people over 50 years of age for colon cancer screening. Check out the symptoms of bowel cancer and when to worry.
To perform a colonoscopy, it is necessary to carry out special preparation with adjustments in diet and the use of laxatives, so that the intestine is clean and the changes can be visualized. Generally, the exam does not cause pain, as it is carried out under sedation, however, some people may feel discomfort, swelling or pressure in the abdomen during the procedure.
What is it for
Colonoscopy is typically used to:
- Look for polyps, which are small tumors, or signs suggestive of colon cancer;
- Identify causes of bleeding in feces;
- Assess persistent diarrhea or other changes in bowel habits of unknown origin;
- Diagnose colon diseases such as diverticulosis, intestinal tuberculosis, ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease, for example;
- Investigate causes of anemia of unknown origin;
- Carry out a more detailed assessment when changes are found in other tests, such as testing for occult blood in feces or doubtful images in barium enema, for example. Check out the other tests recommended to detect bowel cancer.
Furthermore, the exam can be indicated as a therapeutic method, as it also allows the cauterization of blood vessels that may be bleeding or even decompression of intestinal volvulus.
During the colonoscopy exam, it is also possible to perform procedures such as biopsy collection or even the removal of polyps.
See more details about the importance of colonoscopy in diagnosing bowel cancer in the following video with Dr. Alexandre Palladino:
Colonoscopy preparation
In order for the doctor to be able to perform the colonoscopy and visualize the changes, the colon must be completely clean, that is, without any residue of feces or food and, for this, special preparation must be made for the exam, which must be indicated by the doctor or clinic that will perform the exam.
It is important that the person has an easily digestible diet 2 to 3 days before the exam, depending on the doctor’s advice, and that in the 24 hours before the exam the person has a liquid diet, so that waste is not produced in the large intestine. .
In addition, it may also be recommended to use laxatives, such as a mannitol-based solution, which helps cleanse the intestine. It is also recommended that the use of some medications be suspended before the exam, such as ASA, anticoagulants, Metformin or insulin, for example, according to the doctor’s recommendation. It is also necessary to be accompanied to the exam, as sedation may make the person drowsy, and it is not recommended to drive or work after the exam.
What should a colonoscopy diet be like?
The diet for colonoscopy should be started 2 to 3 days before the exam, when the patient can start eating an easily digestible and semi-liquid diet, based on vegetables and unpeeled fruits, cooked or in the form of porridge, bread, rice and white pasta, liquids, juices without fruit pulp, meat, fish and boiled eggs, and yogurt without fruit or pieces, avoiding milk, fruits, nuts, vegetables, legumes and cereals.
Furthermore, the day before the colonoscopy, it is recommended that the person follow a liquid diet, which should include fat-free soups and broths. See more details on what the colonoscopy diet should be like.
How colonoscopy is performed
Colonoscopy must be performed by a gastroenterologist and is performed by introducing a thin tube through the anus. This tube has a camera attached to it that allows you to view the inside of the intestine (the intestinal mucosa). During the exam, small amounts of air are injected into the intestine to improve visualization.
Because the exam can be uncomfortable, colonoscopy is performed under sedation. The exam lasts between 20 and 60 minutes and then it is recommended to recover for around 2 hours before returning home.
What is virtual colonoscopy
Virtual colonoscopy is also an examination that evaluates the intestine, however it is performed using computed tomography to obtain images of the intestine, and a colonoscope with a camera is not necessary to capture images. During the exam, a tube is introduced through the anus that injects air into the intestine, facilitating the observation of its interior and possible changes.
Virtual colonoscopy has some limitations, such as difficulty in identifying small polyps and the impossibility of performing a biopsy, which is why it is not a faithful substitute for normal colonoscopy. Understand how virtual colonoscopy is performed.
Bibliography
- BATISTA RR, LIMA RFC, FONSECA MFM, TODINOV LR, Formiga GJS. Indications for colonoscopy versus finding polyps and colorectal neoplasms. Rev bras Coloproct, 2011;31(1): 64-70.. Available at: http://www.scielo.br/pdf/rbc/v31n1/v31n1a09.pdf
- Brazil. Ministry of Health. Department of Health Care. Department of Primary Care.. Tracking / Ministry of Health, Department of Health Care, Department of Primary Care. n. 29. Brasília: Ministry of Health, 2010. pp. 75-77.
- Maria Ana Rafael, Rita Carvalho. DIAGNOSTIC AND THERAPEUTIC COLONOSCOPY IN ADULTS. 2019. Available at: <https://repositorio.hff.min-saude.pt/bitstream/10400.10/2309/1/Sess%C3%A3o%20HFF%202019_Colonescola.pdf>.
- Department of Health Quality of the NHS. Diagnostic/Therapeutic Colonoscopy in Adults. Standards of the General Directorate of Health (Portugal), 2017. National Health System/ Portugal. Available at: https://www.spg.pt/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/i023947.pdf.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13