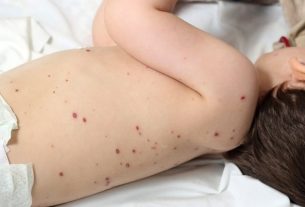
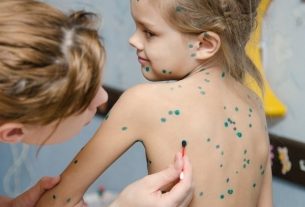
Chickenpox in adults tends to have more intense symptoms, especially if there was no vaccination during childhood, and the person may have a greater number of blisters on the body, compared to children, in addition to high fever, ear pain and sore throat, in some cases.
To prevent the transmission of chickenpox and the development of the disease, it is important to prevent contact with other people, especially those who have not yet had the disease or who have not been vaccinated, in addition to being important to avoid scratching the blisters that appear on the body. See how to avoid transmitting chickenpox.
Chickenpox symptoms in adults
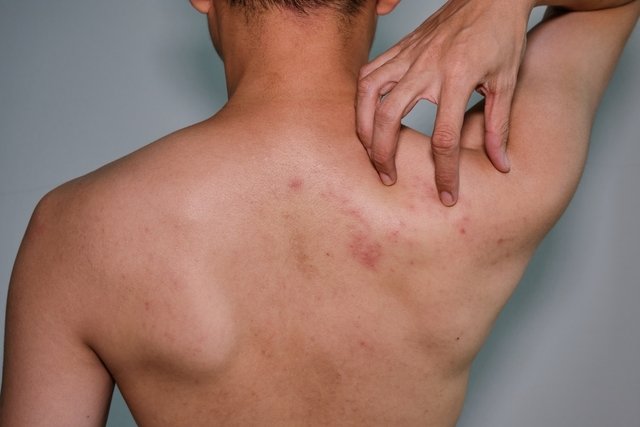
The symptoms of chickenpox in adults are the same as in children, however they tend to be more intense, with fever, tiredness, headache, loss of appetite, the appearance of lumps all over the body and intense itching. Learn about other chickenpox symptoms.
Possible complications
Complications from chickenpox can arise when treatment is carried out inappropriately or when the person’s body cannot overcome the virus on its own, as it is very weakened. In some cases, this may occur:
- Infections in other parts of the body, with a risk of sepsis;
- Dehydration;
- Encephalitis;
- Cerebellar ataxia;
- Myocarditis;
- Pneumonia;
- Transient arthritis.
These complications are suspected when the person begins to present symptoms such as an intense headache, the fever does not go down and other symptoms appear. Therefore, in the presence of these symptoms, it is important that the person goes immediately to the hospital so that the diagnosis can be made and the most appropriate treatment can be started.
What is the treatment like?
Treatment consists of the use of antiallergic medications to alleviate the symptoms of itchy skin blisters and medications to reduce fever, such as paracetamol or dipyrone.
It is also important to take some precautions, such as avoiding scratching the blisters on the skin with your nails, so as not to cause wounds on the skin or cause an infection, drinking plenty of fluids during the day and taking a bath with potassium permanganate to dry the blisters more quickly.
Furthermore, in people with a weakened immune system, such as in the case of HIV or who are undergoing chemotherapy treatment, the doctor may recommend the use of an antiviral, such as acyclovir, within the first 24 hours after the onset of symptoms.
Is it possible to get chickenpox twice?
It is possible to get chickenpox twice, however, it is a rare situation that occurs mainly when the immune system is weakened or when chickenpox was misdiagnosed the first time.
Typically, a chickenpox patient develops antibodies against the chickenpox virus after infection and, therefore, it is rare to catch chickenpox more than once. However, the chickenpox virus remains dormant in the body and can be reactivated, causing symptoms of shingles, which is the reactivation of the chickenpox virus, but in another form.
Can I get chickenpox even if I am vaccinated?
Chickenpox can infect a vaccinated individual, as the vaccine does not completely protect against the virus. However, these situations are rare and the symptoms are milder, disappearing in less time.
Normally, those who receive the chickenpox vaccine have fewer wounds spread across the body, and recovery takes less than 1 week. Learn more about the chickenpox vaccine.
Bibliography
- BRAZILIAN SOCIETY OF DERMATOLOGY. Chickenpox. Available at: <https://www.sbd.org.br/dermatologia/pele/doencas-e-problemas/catapora/65/>. Accessed on 02 Jul 2021
- GOLDMAN, Lee; SCHAFER, Andrew I. . Goldman-Cecil Medicine . 25.ed. Rio de Janeiro: Elsevier, 2018.
- BRAZILIAN SOCIETY OF PEDIATRICS. 2020 Vaccination Calendar. 2020. Available at: <https://www.sbp.com.br/imprensa/detalhe/nid/ja-esta-disponivel-o-calendario-de-vacinacao-2020/>. Accessed on May 17, 2020
- MINISTRY OF HEALTH. Chickenpox (Varicella): causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prevention. Available at: <http://saude.gov.br/saude-de-az/varicela-catapora>. Accessed on 03 Feb 2020
- COHEN, Jonathan. Chickenpox: treatment. BMJ Clin Evid. Vol.6, n.912. 1-13, 2015
- CENTERS FOR DISEASE CONTROL AND PREVENTION. Prevention and Treatment. Disponível em: <https://www.cdc.gov/chickenpox/about/prevention-treatment.html#treatments>. Acesso em 03 fev 2020

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13