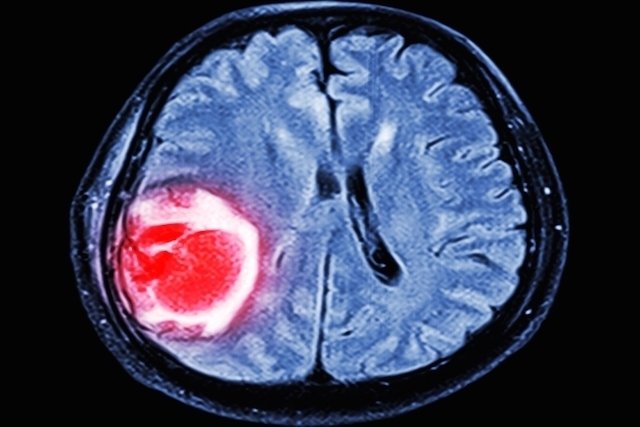
Cerebral thrombosis is a type of stroke that occurs when a blood clot clogs one of the arteries in the brain, which can lead to death or generate serious consequences such as speech difficulties, blindness or paralysis.
The symptoms of cerebral thrombosis are not very specific, with a very intense headache being mainly noted. This situation can happen to anyone, but it is more common in women due to the use of oral contraceptives and pregnancy. However, people who have a family history of cardiovascular disease or who have high blood pressure, for example, also have an increased risk of cerebral thrombosis.
It is important that if cerebral thrombosis is suspected, the person goes to the hospital so that the diagnosis can be made and, thus, the most appropriate treatment can be initiated, which involves the use of medication to alleviate symptoms and dissolve the clot.
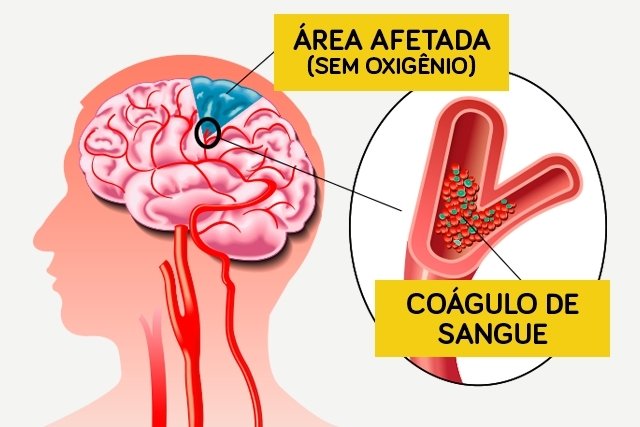
Cerebral thrombosis symptoms
Symptoms that help identify cerebral thrombosis are:
- Intense headache;
- Tingling or paralysis on one side of the body;
- Mouth cake;
- Difficulty speaking and understanding;
- Changes in vision;
- Dizziness and loss of balance.
The symptoms of thrombosis can be nonspecific, so the diagnosis can be more complicated. However, in the presence of these signs and symptoms, it is recommended to immediately call an ambulance by calling 911 or go to the emergency room immediately. During this time, if the person faints and stops breathing, cardiac massage should begin.
How the diagnosis is made
The diagnosis of cerebral thrombosis is made by a general practitioner or neurologist by evaluating the signs and symptoms presented by the person and the results of laboratory and imaging tests.
The doctor usually recommends carrying out a blood count, coagulogram and D-dimer dosage, in addition to indicating the performance of imaging tests, such as magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, angiography, venography and/or ultrasound to visualize the presence of a thrombus and/or changes in the brain that are suggestive of thrombosis.
Make an appointment with your nearest doctor to assess your risk of cerebral thrombosis:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
Main causes
Cerebral thrombosis can happen to any healthy person, with a higher risk of occurring in the following situations:
- High blood pressure;
- Diabetes;
- Overweight;
- High blood cholesterol levels;
- Excessive intake of alcoholic beverages;
- Heart problems, such as cardiomyopathy or pericarditis;
- Use of oral contraceptives;
- Pregnancy;
- Thrombophilia;
- Dehydration;
- Use of drugs of abuse;
- Performing lumbar puncture or neurosurgical procedures.
Furthermore, the risk of cerebral thrombosis is also higher in people with untreated diabetes, postpartum women and a family history of heart disease or stroke.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for cerebral thrombosis should be started as soon as possible in the hospital, as it is necessary to take injections of anticoagulants, such as heparin, directly into the vein, to dissolve the clot that is clogging the brain artery.
In addition, the doctor may recommend the use of thrombolytic medications, antibiotics, in cases where there is an infection, antiepileptic drugs or acetazolamide to reduce intracranial pressure.
In some cases, the doctor may recommend surgery to remove the clot from the brain, called thrombectomy, so that blood flow is restored through the affected blood vessel.
After treatment, it is advisable to stay in hospital for between 4 and 7 days, so that constant observation of your health status can be carried out, as, during this period, there is a greater chance of suffering internal bleeding or cerebral thrombosis occurring again.
Is there a cure for cerebral thrombosis?
Cerebral thrombosis can be cured, especially when treatment is started within the first hour after symptoms appear, but the risk of sequelae depends on the affected region and the size of the clot.
Main sequelae of cerebral thrombosis
Depending on how long the cerebral thrombosis lasted, sequelae may arise due to injuries caused by the lack of oxygen in the blood. The consequences can include various problems, from changes in speech to paralysis, and their severity depends on the time the brain was without oxygen.
To treat the sequelae, the doctor may recommend physiotherapy or speech therapy consultations, for example, as they help to recover some of the abilities that were lost. See more about the most common sequelae and how recovery is achieved.
Bibliography
- CLEVELAND CLINIC. Thrombectomy. Disponível em: <https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/22897-thrombectomy#:~:text=is%20a%20thrombectomy%3F-,A%20thrombectomy%20is%20a%20surgery%20to%20remove%20a%20blood%20clot,be%20limb%20or%20life%2Dthreatening.>. Acesso em 27 jun 2023
- JOHNS HOPKINS MEDICINE. Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis (CVST). Disponível em: <https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/cerebral-venous-sinus-thrombosis>. Acesso em 27 jun 2023
- CLEVELAND CLINIC. Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis. Disponível em: <https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22560-cerebral-venous-sinus-thrombosis>. Acesso em 27 jun 2023
- BALIEIRO, Laura G.; LIMA, Leonardo V.; TARTUCE, Taísa M. et al. Cerebral Venous Thrombosis: General Aspects and Diagnostic Methods. Braz. J. Where. Rev. Vol 3. 1 ed; 797-801, 2020
- GOLDMAN, Lee; SCHAFER, Andrew I.. Goldman-Cecil Medicina. 25.ed. Rio de Janeiro: Elsevier, 2018. pp. 2480-2492.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13