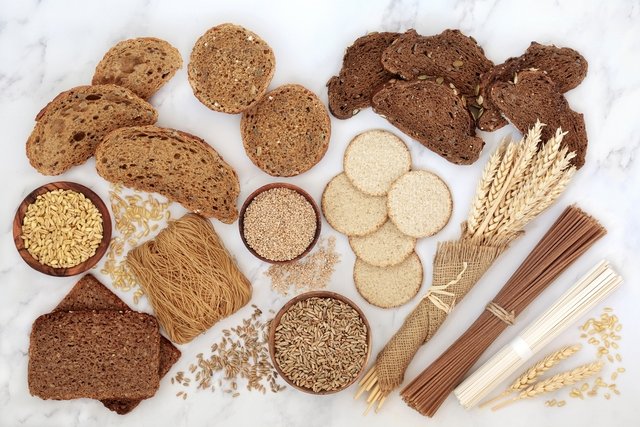
Celiac disease is a chronic autoimmune disease caused by permanent intolerance to gluten, which is the protein present in wheat, rye, malt and barley, provoking an immune system response capable of causing inflammation and damage to the intestine.
Celiac disease is caused by genetic changes and can occur in both children and adults and includes symptoms such as diarrhea, headache, swollen belly, irritability, tiredness and weight loss.
The diagnosis of celiac disease must be made by a gastroenterologist, or general practitioner, who will evaluate the signs and symptoms presented by the person, and request tests to confirm the diagnosis, such as genetic testing, endoscopy and blood tests.

Main symptoms:
The main symptoms of celiac disease are:
- Diarrhea;
- Constipation;
- Weight loss;
- Stomach ache;
- Excess gases;
- Swollen belly;
- Fatigue.
Furthermore, as this condition decreases the absorption of nutrients by the body, celiac disease can also cause anemia and osteoporosis.
Symptoms of Celiac Disease in Children
Symptoms of celiac disease in children include delayed development and growth, weight loss, vomiting, chronic diarrhea, bloated belly, loss of muscle mass, iron deficiency anemia, irritability and discomfort.
Symptoms of non-classical celiac disease
In addition to the classic symptoms, some people may have non-classic celiac disease, which may or may not cause gastrointestinal symptoms.
The main symptoms of non-classic celiac disease are:
- Swollen belly;
- Dor abdominal;
- Diarrhea;
- Tiredness;
- Constipation;
- Headache or migraine.
- Skin changes, such as dermatitis, wounds and psoriasis;
- Loss of appetite.
In addition, this type of celiac disease can also cause irritability, folic acid and/or vitamin B12 deficiency, infertility, late menstruation, early menopause, tooth enamel defects, anxiety, irritability, miscarriage, premature birth or newborn birth. with short stature.
Difference between gluten intolerance and celiac disease
Gluten intolerance is the inability or difficulty in digesting gluten, which causes symptoms such as diarrhea, pain and abdominal bloating. However, in gluten intolerance the person does not have allergies or autoimmune changes and intestinal damage decreases with the exclusion of gluten from the diet. Understand more about gluten intolerance.
Celiac disease is an immune system response to gluten that causes inflammation and permanent damage to the intestine. Although the symptoms of celiac disease are similar to those of gluten intolerance, this condition causes irreversible damage to the intestine, even after removing gluten from the diet.
How the diagnosis is made
The diagnosis of celiac disease is made by a gastroenterologist or general practitioner, through evaluation of the symptoms and signs presented by the person and family history, as celiac disease has mainly genetic causes.
If you want to make an appointment, you can find the gastroenterologist closest to you using the following tool:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
The doctor may also request some examinations and tests, such as urine, feces and blood tests, to check antibody levels; genetic testing; and endoscopy with intestinal biopsy, an examination that evaluates the structure of the intestine and checks for any signs that indicate celiac disease.
When initial tests and examinations are inconclusive, the doctor may also recommend excluding gluten from the diet and then request a second intestinal biopsy.
Main causes
Although the exact cause of celiac disease is not yet known, it is believed that this disease is caused by a genetic change inherited from parents or family members that causes the immune system to react, causing inflammation, damage to the intestine and making it difficult to absorb nutrients. .
How the treatment is carried out
Celiac disease has no cure and, therefore, treatment must be carried out throughout life, and it is mainly advised to exclude foods and medicines that contain gluten, helping to improve the person’s quality of life and avoid the symptoms of this disease.
1. Gluten-free diet
It is essential to exclude foods with gluten from your diet, such as wheat, rye, malt and barley, and products prepared with these cereals, such as bread, pasta, beer, cakes and biscuits, for example. See what the diet should be like for celiac disease.
The diet should also prioritize foods rich in iron and folate, especially if the person is deficient in these minerals. Furthermore, it is important to always read the product label to check whether or not the food contains gluten before consuming it.
Oats can be included in the diet, however, it is essential to check whether the manufacturer has the gluten-free certification seal for this product.
It is important to consult a nutritionist specialized in gluten-free diets, especially during the first year after diagnosis of the disease, so that an individualized eating plan can be created to prevent nutrient deficiencies.
2. Supplements
As many people with celiac disease may be deficient in fiber, iron, calcium, zinc, folate, vitamin B12 and vitamin D, the use of supplements may also be recommended by a doctor or nutritionist.
3. Medicines
The use of medicines for celiac disease is generally only indicated for people who also have dermatitis herpetiformis or in cases of refractory celiac disease, which is when the person does not improve or temporarily improves with the removal of gluten from the diet.
Prescribed medications may include prednisolone, azathioprine, cyclosporine or other medications used to reduce inflammatory or immunological reactions, which should only be used under the guidance of a gastroenterologist.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13