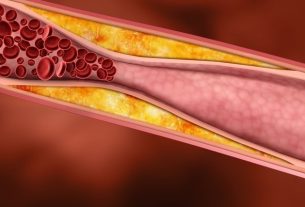
Carotid atheromatosis, or carotid stenosis, is a narrowing of the inside of one or both carotid arteries that can impair blood circulation to the brain. Its first sign may be a transient ischemic attack (TIA) or stroke.
This narrowing is normally caused by the accumulation of cholesterol in the vessel walls due to atherosclerosis and is more common in older men who smoke and do not exercise regularly.
Read too: Atherosclerosis: what it is, symptoms, causes and treatment
If carotid atheromatosis is suspected, it is recommended to consult a cardiologist. Treatment can be done with medications such as anticoagulants and to lower blood cholesterol or, in some cases, surgery, for example.
Main symptoms
In most cases, the first sign of carotid atheromatosis is an episode of transient ischemic attack, or TIA. In this case, symptoms may appear, such as muscle weakness and difficulty speaking or moving parts of the body, which disappear within 24 hours. Check out more symptoms of transient ischemic attack.
In the most serious cases, carotid atheromatosis can result in a stroke that can cause symptoms similar to those of a transient ischemic attack, but which do not resolve completely after treatment.
Read too: 12 stroke symptoms (and what to do)
However, carotid atheromatosis usually does not cause symptoms in the early stages, and it is common to be identified during a routine medical appointment or after imaging tests such as neck ultrasound.
Is carotid atheromatosis serious?
Carotid atheromatosis can be serious in some cases due to the risk of stroke. Especially when atheromatosis affects the internal carotid artery, is bilateral and/or the obstruction to blood flow is large, this risk is greater.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of carotid atheromatosis is normally made by a cardiologist or general practitioner taking into account the symptoms present, the person’s health history and the results of the carotid Doppler, which can check how blood is circulating through these arteries. Find out what carotid Doppler is and when it is indicated.
If you want to schedule an appointment, find a cardiologist closest to you using the tool below:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
Possible causes
Carotid atheromatosis is caused by the accumulation of cholesterol in one or both carotid arteries in the neck, resulting in their narrowing and making it difficult for blood to flow to the brain.
Furthermore, carotid atheromatosis is more common in older men who smoke, have a diet rich in fatty foods, do not do physical activity and have problems such as high cholesterol and/or high blood pressure.
Carotid atheromatosis is one of the possible consequences of atherosclerosis, which can also result in atheromatosis of other arteries in the body, such as the aorta and coronary arteries.
Read too: Aortic atheromatosis: what it is, symptoms, causes and treatment
How the treatment is carried out
Carotid atheromatosis is usually treated with medications that have an anticoagulant effect and reduce blood cholesterol, as well as measures to prevent cardiovascular diseases, such as controlling blood pressure and stopping smoking.
Furthermore, it is important to regularly follow up with your doctor to assess the size of the atheromatosis in the carotid arteries. If the obstruction becomes large, a referral may be made to a vascular surgeon to further assess the need for surgery.
However, especially if the person has a history of stroke episodes or transient ischemic attacks, treatment of carotid atheromatosis through surgery may be indicated to reduce the risk of new episodes.
Bibliography
- ARASU, Rohan; ARASU, Alexis; MULLER, Juanita. Carotid artery stenosis: An approach to its diagnosis and management. Aust J Gen Pract. Vol.50, n.11. 821-825, 2021
- PENN MEDICINE. Carotid Artery Disease. Disponível em: <https://www.pennmedicine.org/for-patients-and-visitors/patient-information/conditions-treated-a-to-z/carotid-artery-disease>. Acesso em 20 fev 2024
- CLEVELAND CLINIC. Carotid Artery Disease (Carotid Artery Stenosis). Disponível em: <https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16845-carotid-artery-disease-carotid-artery-stenosis>. Acesso em 20 fev 2024
- STATPEARLS. Carotid Artery Stenosis. 2022. Available at: <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK442025/>. Accessed on 20 Feb 2024
- SCHENONE , Aldo L; COHEN, Aaron; SHISHEHBOR, Mehdi H. Asymptomatic carotid artery disease: A personalized approach to management. Cleve Clin J Med. Vol.82, n.12. 855-63, 2015

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13