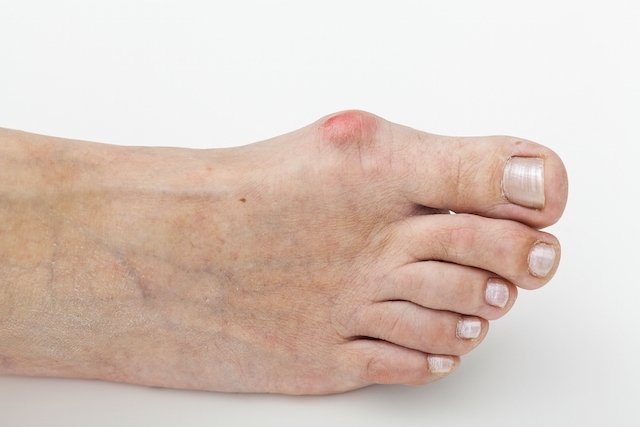
A bunion is a bony protrusion that most often forms on the big toe, the hallux. A bunion is caused by a misalignment of the foot joint, which can arise due to wearing tight shoes or high heels, or even due to poor foot formation or rheumatoid arthritis, for example.
In addition to the protrusion on the bone, a bunion, which is scientifically known as hallux valgus, can be accompanied by symptoms such as pain, redness or numbness in the affected toe.
The presence of a bunion can be quite uncomfortable and, therefore, it is important to consult an orthopedist to begin the most appropriate treatment and prevent the toes from continuing to misalign, increasingly affecting daily life and quality of life.

Main symptoms
Bunion symptoms vary according to the misalignment of the foot joint, the main ones being:
- Change in the shape of the foot, with the formation of a protrusion on the side of the foot;
- Deviation of the affected finger towards the other fingers;
- Redness in the affected finger;
- Pain in the finger or joint, especially when walking;
- Burning sensation when trying to bend the finger;
- Numbness in the affected finger;
- Swelling of the affected finger joint.
In addition, calluses may appear on the skin of the bunion and it may even be difficult to wear normal shoes.
It is important that the bunion is evaluated by an orthopedist or physiotherapist, especially when it causes symptoms, so that the most appropriate treatment can be indicated.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of a bunion is made by the orthopedist through a physical examination of the foot, evaluation of health and family history, in addition to an X-ray examination of the foot to assess the degree of deformity of the joint.
Generally, no other tests are necessary, however, if the doctor suspects diseases that may be causing the bunion, such as rheumatoid arthritis, tests such as complete blood count, C-reactive protein (CRP) or antinuclear antibody test may be requested, for example. .
Possible causes
The exact cause of bunions is not fully known, however, some factors seem to contribute to their development, such as:
- Family history of bunion;
- Foot malformations;
- Shortest first big toe bone;
- Flat foot;
- Excessive flexibility of the foot ligaments;
- Rheumatoid, gouty or psoriatic arthritis;
- Poorly healed fracture of the big toe bone;
- Trauma, dislocation or sprain of the big toe;
- Connective tissue disorders such as Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, or Down syndrome;
- Imbalance of the foot muscles caused by stroke, cerebral palsy or myelomeningocele.
Wearing tight shoes or high heels can also cause foot deformities over time, leading to the appearance or worsening of bunions.
How the treatment is carried out
Bunion treatment must be guided by an orthopedist with the aim of relieving symptoms or returning the toe to its original position.
The main treatments for bunions that may be recommended by your doctor are:
1. Wear comfortable shoes
Wearing comfortable shoes, with a wide toe box, that have more space for the toes, or padded shoes, can help alleviate pain when walking.
Furthermore, you should avoid wearing high heels and tight shoes to avoid worsening symptoms and joint deformity.
2. Use orthotics
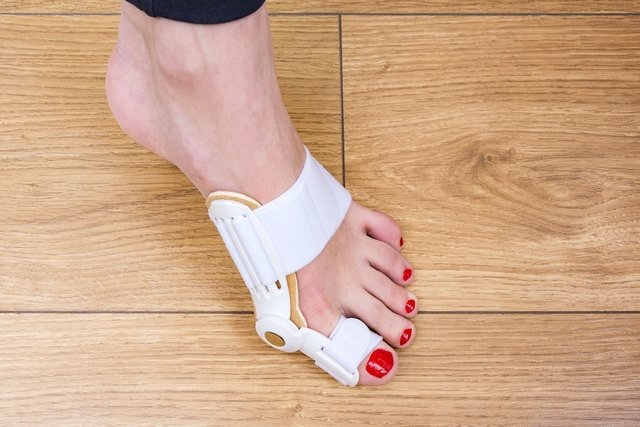

The use of orthoses may be recommended by the doctor with the aim of trying to reposition the joint. However, they are not very efficient and do not change the deformity.
These orthoses can be found in pharmacies or drugstores, and can be used daily, for as long as determined by the doctor.
3. Apply cold compresses
Applying cold compresses to your bunion helps reduce pain and relieve swelling, especially after standing for a long time. However, applying cold compresses is not recommended for people who have circulation problems in their feet.
To make an ice pack, you must place ice inside a thermal bag or place the gel bag in the freezer to cool, and then wrap the bag or gel bag in a clean, dry towel and apply it to the bunion, leaving it to act for 15 to 20 minutes, 2 to 3 times a day. See also other ways to take care of bunions and alleviate symptoms.
4. Do physical therapy
Physiotherapy may be recommended by the orthopedist in conjunction with the physiotherapist, to relieve pain and swelling in the bunion.
Physiotherapy treatment must be chosen by the physiotherapist on an individual basis, and the use of equipment, such as ultrasound, may also be recommended to break down soft tissue adhesions, helping to reduce the pain and inflammation of the bunion.
5. Taking medicine
Treatment with medication may be recommended by the doctor with the aim of relieving pain, redness or swelling in the affected foot joint, and the use of analgesics or anti-inflammatories in the form of tablets, such as paracetamol or ibuprofen, for example, may be recommended. .
Furthermore, the doctor may also recommend the use of anti-inflammatory ointments applied directly to the bunion, such as Cataflan or Voltaren, for example.
6. Corticosteroid injection
The doctor can also inject a corticosteroid directly into the joint with the bunion, which is generally indicated when other treatment options have not been effective in relieving bunion symptoms.
Generally, the application of corticosteroid injection is done as a way to avoid surgical treatment.
7. Have surgery
Bunion surgery may be recommended by an orthopedist in cases where no other treatment option has been effective, and the pain persists, causing difficulty in walking.
There are several surgical techniques that can be performed by the doctor, which depend on the severity of the bunion, and can be done with the aim of removing the damaged tissue around the bunion, repositioning the toe by shaving or removing part of the affected bone, realigning the bones or until the bones of the affected joint unite. See how bunion surgery is performed and what recovery is like.
Post-operative physiotherapy can be performed as an aid to recovery.
How to prevent bunions
The best way to try to avoid developing a bunion is to wear comfortable shoes that allow you to move your toes freely.
Shoes with very high heels can also increase pressure on the toes, making it easier for bunions to appear, so it is not recommended to wear shoes or sandals with heels more than 5 cm high.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13