Breast candidiasis is an infection caused by the fungus Candida albicans which causes symptoms such as redness and pain in the nipple, wounds in the nipple with more difficult healing, itching in the area and the appearance of cracks in the skin, in some cases.
The fungus Candida albicans it can be found naturally on the skin, without causing any symptoms. However, it can proliferate as a result of breastfeeding, hormonal changes or decompensated diabetes, for example. See more about candidiasis on the skin.
Treatment for breast candidiasis must be carried out under the guidance of a mastologist or dermatologist, who may recommend the use of medication in the form of an ointment or tablet to help combat the fungus and thus alleviate symptoms.
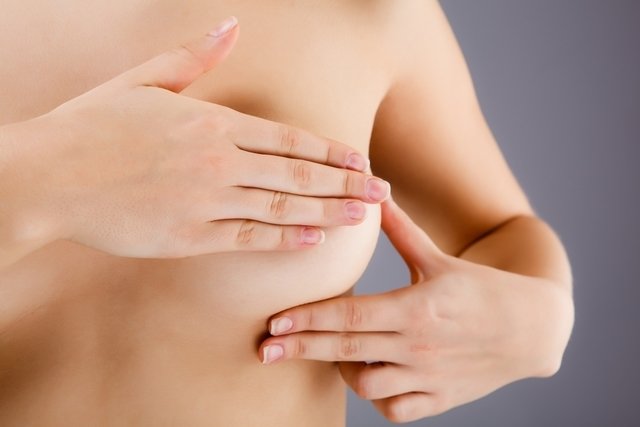
Symptoms of candidiasis in the breast
The main symptoms of breast candidiasis are:
- Pain in the nipple;
- Small wound on the nipple with difficulty healing;
- Part of the nipple may be whitish;
- The affected nipple may be shiny;
- Burning nipple;
- Itching and redness in the breast, including the underside;
- Appearance of cracks in the skin, in some cases.
Breast candidiasis is considered a type of systemic candidiasis and not all symptoms are always present at the same time, but the stabbing pain and small wound are present in all cases.
How the diagnosis is made
The diagnosis of breast candidiasis can be made by a dermatologist or mastologist based on the assessment of the signs and symptoms presented by the person. It is usually not necessary to carry out specific tests, but the doctor may take a small scrape of the area to confirm the fungus responsible and its sensitivity and resistance profile.
Make an appointment with the closest dermatologist to evaluate your symptoms and begin the most appropriate treatment:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
Who is most at risk
Breast candidiasis is more common as a result of breastfeeding, due to hormonal changes and frequent contact with the baby’s saliva. Furthermore, people who have more compromised immunity, have thyroid changes, decompensated diabetes or have used antibiotics or corticosteroid ointment are at greater risk of having this type of candidiasis.
How the treatment is carried out
The treatment of candidiasis in the breast must be carried out in accordance with the advice of a breast specialist or dermatologist, with the use of antifungals in the form of an ointment with nystatin, clotrimazole, miconazole or ketoconazole being recommended for 2 weeks, in accordance with the doctor’s advice. In cases where the use of these antifungals is not sufficient, the use of fluconazole tablets may be recommended for around 15 days.
Furthermore, it is also important to keep the breast always dry and clean, as this will prevent the proliferation of the fungus. If breastfeeding, it is important to observe whether the baby presents symptoms of oral candidiasis and it is necessary to treat it at the same time as the mother undergoes treatment to prevent it from infecting the woman again. See how to identify and treat candidiasis in babies.
Bibliography
- MONTOVANI, Jessica Antonia P . Occurrence of nipple candidiasis in nursing mothers in the city of Londrina-PR. Course Completion Work, 2017. State University of Londrina.
- CAMPOS, Aracieli R. Breast pain during breastfeeding: challenges in etiological diagnosis. Postgraduate thesis, 2018. Federal University of Uberlândia.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13