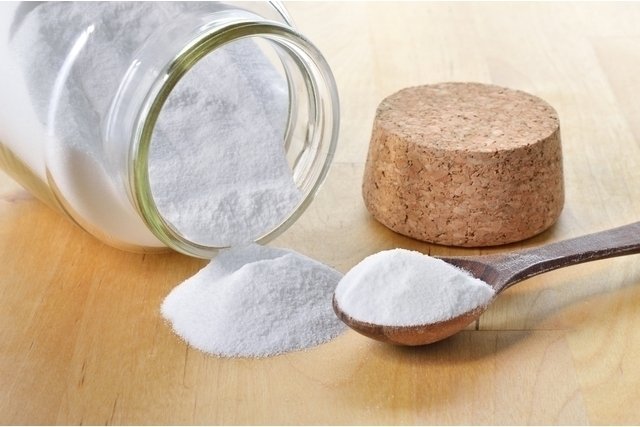
Borax, also known as sodium borate, sodium tetraborate or disodium tetraborate, is a mineral in powder form widely used by the industry in the production of cleaning and hygiene products and, due to its antiseptic, antifungal and antibacterial properties.
In cosmetic products, borax is widely used as a preservative or emulsifier in moisturizers, shampoos, exfoliants or sunscreen, as well as being part of the composition of creams or ointments for topical use, produced to treat skin lesions or mycoses, for example.
Borax is sold in drugstores and chemical stores, and should be used according to the doctor’s recommendation, because the amount and way of using this substance varies depending on the objective of the treatment. Furthermore, borax when ingested can cause poisoning with symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach pain, convulsions and fever.

What is it for
The main indications for borax are:
1. Treatment of mycoses
Due to its fungicidal properties, sodium borate can be used in the manufacture of solutions and ointments to treat mycoses, such as athlete’s foot or candidiasis, for example.
2. Skin injuries
Some ointments containing sodium borate in their composition may be indicated to treat skin lesions, helping to alleviate symptoms related to dry skin, sunburns, insect bites and other skin infections.
3. Mouthwash
Because it has antiseptic and antimicrobial properties, borax can be used in the manufacture of mouthwashes to help treat mouth wounds and to disinfect the mouth, preventing the appearance of cavities.
Mouthwash should not be ingested, but only used as a mouthwash and spit out immediately.
4. Bath salts
Borax can also be used to prepare bath salts, as it leaves the skin softer and smoother.
What is the difference between borax, boric acid and boric acid?
Borax, boric acid and boric acid contain boron, which is a chemical element in their composition.
However, borax is a combination of boric acid with sodium salts, widely used for household cleaning, while boric acid is used especially as an insecticide, as it causes poisoning in the stomach and nervous system of insects.
Boricated water, on the other hand, is a 3% solution made with boric acid, and is normally indicated as an antiseptic, antibacterial and antifungal to help treat skin irritations, infections in the external ear or mild burns, as long as medical advice is provided. See all the indications for boricated water.
Possible side effects
When applied to the skin, borax can cause side effects such as irritation, skin blisters or skin rash. When inhaled, borax can cause irritation to the eyes, nose, throat and lungs.
Additionally, it is believed that excessive exposure to borax can harm male reproduction by decreasing sperm count and libido.
Therefore, the use of borax should only be done with the guidance and supervision of a doctor.
Can Borax cause poisoning?
Borax is not recommended for oral use, that is, it should not be ingested.
This is because borax is highly absorbed by the gastrointestinal system and can cause poisoning even in small quantities.
The main symptoms of borax poisoning are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, drop in blood pressure, seizures, stomach pain, skin rashes and kidney failure.
In these cases, you should go to the emergency room immediately, as borax poisoning can be life-threatening.
Who shouldn’t use
Borax is contraindicated for children under 3 years of age and should not be used in large quantities or for a long time, as it can be absorbed into the bloodstream and cause toxicity, and its use should not be prolonged for more than 2 to 4 weeks.
Furthermore, it should also not be used in people who are hypersensitive to sodium borate or other components contained in the formula.
Borax should not be ingested, but only applied under the skin if directed by a doctor.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13