Bone densitometry is an imaging test widely used to diagnose osteoporosis, as it allows the density of bones to be assessed, checking whether there has been bone loss. Bone densitometry is recommended by a doctor when a person has risk factors for osteoporosis, such as menopause, alcoholism, aging or a sedentary lifestyle, for example.
Bone densitometry is a simple, painless exam that does not require preparation to be carried out, it is only recommended that the person informs whether they take any medication or have undergone a contrast exam in the 3 days prior to the densitometry exam.

What is it for
Bone densitometry is considered the main test to identify loss of bone mass, and is considered the gold standard for diagnosing osteopenia and osteoporosis.
Bone densitometry examination is indicated when factors are observed that lead to a decrease in bone mass or that increase the risk of developing diseases, such as:
- Aging;
- Menopause;
- Family history of osteopenia or osteoporosis;
- Frequent use of corticosteroids;
- Primary hyperparathyroidism;
- Smoking habit;
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Gastrointestinal diseases or kidney stones;
- Large caffeine consumption;
- Nutritional deficiencies.
The bone densitometry test is important because it indicates the person’s bone mass, and is essential for the doctor to check the risk of developing osteoporosis or osteopenia and the chance of fractures occurring, and can indicate strategies to avoid these situations. Furthermore, this exam is indicated as a way to monitor the person and the response to treatment based on the analysis of bone density over time.
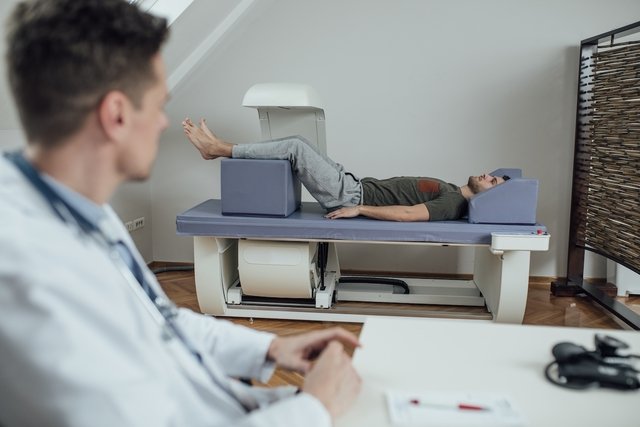
How bone densitometry is performed
Bone densitometry is a simple test that does not cause pain or discomfort and does not require preparation to be carried out. The exam is quick, lasts between 10 and 15 minutes, and is carried out with the person lying on a stretcher, motionless, until a device records radiological images of their body.
Despite being simple, the bone densitometry exam is not recommended for pregnant women, obese people or those who have undergone a contrast exam approximately 3 days before the densitometry exam, because it may interfere with the exam results.
How to understand the result
The result of bone densitometry is indicated through scores that indicate the amount of calcium present in bones that are:
1. Score-Z, which is recommended for younger people, estimates the possibility of the person suffering a fracture, for example, and can be interpreted as follows:
- Value up to 1: Normal Result;
- Value below 1 to – 2.5: Indicative of osteopenia;
- Value below – 2.5: Indicative of osteoporosis;
2. Score-T, which is more suitable for the elderly or women after menopause, who are more likely to develop osteoporosis, which may be:
- Value greater than 0: Normal;
- Value up to -1: Borderline;
- Value below -1: Indicative of osteoporosis.
Bone densitometry should be performed at least once a year for women over 65 years of age and men over 70 years of age and periodically, according to the doctor’s guidance, for people who have already been diagnosed with osteopenia or osteoporosis with the aim of checking the response to treatment.
Bibliography
- ANDRADE, Simone A. F. The importance of bone densitometry examination. UNILUS Teaching and Research Magazine. Vol 13. 30 ed; 2016
- NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS FOUNDATION. Bone Density Exam/Testing. Disponível em: <https://www.nof.org/patients/diagnosis-information/bone-density-examtesting/>. Acesso em 20 jan 2020

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13