Bioplasty is an aesthetic procedure performed by a dermatologist or plastic surgeon, with the injection of biocompatible substances under the skin, and is normally recommended for people who wish to improve their appearance or delay the development of wrinkles, standardize facial contours, such as chin or nose, for example. example.
This technique can be done on any region of the body, but it is especially recommended for small areas such as the face, as it fills in spaces in the skin, giving a more youthful appearance.
Bioplasty is considered a safe procedure when performed by a specialized professional, such as a dermatologist or plastic surgeon, as it is an aesthetic treatment that has several risks, which can cause complications such as infection or allergies, and is not recommended for use on large areas of the body such as glutes or legs, for example.
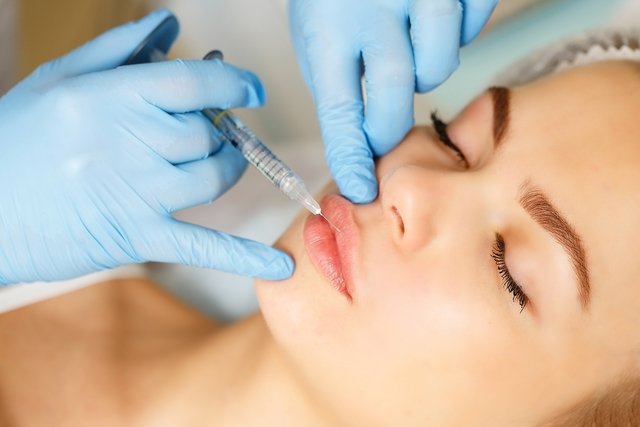
What is it for
Bioplasty is normally indicated for:
- Correct grooves and scars after surgery;
- Correct cheek imperfections and restore volume to this area of the face;
- Return the contours or volume lost with age;
- Smooth wrinkles around the mouth;
- Tune and lift the tip of the nose, as well as reduce the base of the nose;
- Delineate the chin, reduce imperfections and correct any type of asymmetry;
- Correct scars caused by severe acne;
- Increase the volume of the lips and allows you to define their limits;
- Returns elasticity to the skin of your hands and helps disguise wrinkles that appear naturally with age.
Furthermore, bioplasty allows you to lift the butt and give it more volume, however, as it is a large area, there is a greater chance of complications, due to the use of a high amount of biocompatible substances.
The benefits of bioplasty include better satisfaction with the body and better self-esteem, being a more economical procedure than other plastic surgeries and which can be performed quickly in an office.
How bioplasty is performed
Bioplasty is performed using local anesthesia, and consists of applying an injection of substances that are compatible with the human body. The implanted product helps to increase the volume of the region and support the skin by not being reabsorbed by the body and therefore has long-lasting results.
However, these substances should only be used in small doses and the person needs to be aware of the risks before opting for the procedure.
Possible health risks
The main risks of bioplasty are:
- Redness, swelling or pain at the application site;
- Hematomas of eruptions;
- Infections at the injection site;
- Chronic inflammation;
- Stiffening or deformity of the region;
- Formation of nodules on the skin;
- Death of the tissues where it is applied;
- Severe allergic reaction;
- Rejection by the body.
Bioplasty has many health risks, especially when it is applied in large quantities or when it is applied directly to the muscle. Furthermore, when poorly applied, bioplasty can cause deformations in the body’s shape, worsening self-esteem.
Due to all these possible complications, bioplasty should only be done to treat small areas and after talking to the doctor about all the risks.
If a person has symptoms of shortness of breath, chest pain, headache, changes in vision or speech, weakness, drowsiness or loss of consciousness, they should go to the emergency room as soon as possible. Bioplasty complications can appear 24 hours after its application or years after its application to the body.
Who shouldn’t do
Bioplasty should not be performed in the following situations:
- Children or teenagers under 18;
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women;
- History of allergies or anaphylactic reaction;
- Allergy to lidocaine or other anesthetics;
- Tendency to form thick scars;
- Wounds or skin infections;
- Pimples or cysts on the skin;
- Use of immunosuppressive medications;
- Cancer treatment;
- Inflammatory bowel disease;
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
Furthermore, bioplasty should not be performed in cases of allergy to the substances used to fill the skin, or by people who have undergone other aesthetic treatments in the last 6 months or are receiving ultraviolet light therapy.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13



