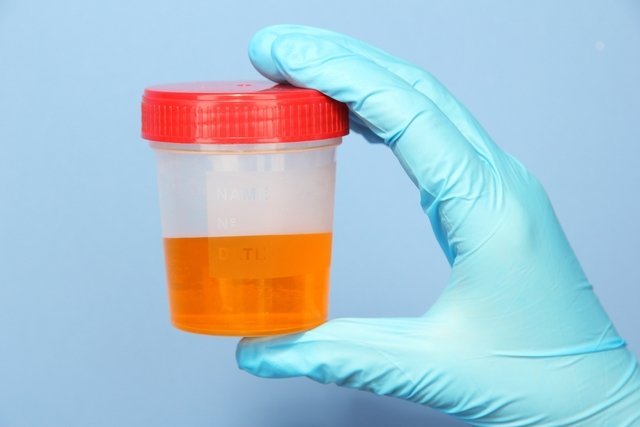
The presence of bilirubin in the urine is normally indicative of liver problems, such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, liver cancer or the presence of gallstones, and can be seen through the dark yellow to orange color of the urine, and must be confirmed through a blood test. urine.
Bilirubin is a product of the degradation of hemoglobin, becomes soluble in the liver, receiving the name direct bilirubin, is transported to the bile ducts and intestine, where it undergoes a degradation process, and is eliminated in the feces in the form of stercobilinogen and in urine in the form of urobilinogen.
When there are problems with the liver or bile ducts, direct bilirubin returns to the circulation and can be filtered by the kidneys and eliminated in the urine. Learn more about bilirubin.
Main causes
The main causes of bilirubin in urine are:
1. Hepatitis
Hepatitis is one of the main causes of bilirubin in the urine, as due to inflammation of the liver, conjugated bilirubin cannot follow the normal elimination route, returning to the circulation and being able to be filtered by the kidneys and eliminated in the urine.
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver that can occur due to virus infection, recurrent use of medication or due to an autoimmune disease, which can cause fever, headache, abdominal swelling and pale stools. Furthermore, when the disease is not identified and treated, jaundice may occur, in which the eyes and skin become yellow. See how to recognize the types of hepatitis.
What to do: If hepatitis is suspected, it is important to go to the general practitioner or hepatologist to order diagnostic tests, such as serology for hepatitis viruses, evaluation of liver enzymes and urine tests. When confirming hepatitis, the doctor can indicate the best treatment according to the type of hepatitis, which can range from rest and increased fluid intake, to the use of medications, such as Interferon, for example.
2. Cirrhosis
In cirrhosis, there is chronic and progressive inflammation of the liver, which causes this organ to no longer perform its functions correctly. Thus, as the liver is in the process of degeneration, bilirubin cannot travel to the bile ducts and intestine to be eliminated, returning to the circulation and being eliminated in the urine.
Liver cirrhosis can occur as a consequence of hepatitis, but is usually related to the frequent and excessive use of alcoholic beverages, resulting in symptoms such as weakness, excessive tiredness, weight loss without an apparent cause, lack of appetite, muscle atrophy and kidney failure. Learn about other symptoms of liver cirrhosis.
What to do: The treatment recommended by the general practitioner or hepatologist for cirrhosis varies according to the cause, and most of the time it is recommended to stop drinking alcohol and adopt a suitable one that includes vitamin supplementation so that there are no nutritional deficiencies. It is important that cirrhosis is identified and treated as quickly as possible so that the progression of the disease and, consequently, liver transplantation can be avoided.
3. Liver cancer
As in hepatitis and cirrhosis, in liver cancer the organ is in a process of inflammation and chronic degeneration, which favors the elimination of bilirubin directly in the urine.
This type of cancer is more common in people who have fatty liver or who frequently use anabolic steroids and symptoms appear when the disease is already in more advanced stages, such as abdominal pain, loss of appetite without apparent cause, excessive tiredness, skin and yellow eyes and constant nausea. Learn how to identify liver cancer.
What to do: If liver cancer is suspected, it is important to go to the hepatologist so that diagnostic tests can be carried out, such as abdominal ultrasound and computed tomography, for example. In addition, some laboratory tests may be recommended, such as liver enzyme measurement. If liver cancer is confirmed, the doctor may recommend surgical removal of the entire affected area and chemotherapy.
4. Gallstones
The presence of stones in the gallbladder can also lead to the appearance of bilirubin in the urine. This happens because due to the presence of stones, direct bilirubin cannot pass into the intestine, returning to the circulation, where it is filtered by the kidneys and eliminated in the urine.
Gallstones or stones arise due to changes in the composition of bile, which may be related to diet, lifestyle habits and prolonged use of contraceptives. The main sign of gallbladder stones is biliary colic, which corresponds to intense pain on the right side of the belly, as well as loss of appetite, diarrhea and yellow eyes and skin. Know the signs and symptoms of gallstones.
What to do: The most frequently indicated treatment in the case of gallstones is the removal of the gallbladder through a surgical process. Next, it is important that the person must have an adequate diet, rich in fruits, vegetables and whole foods and low in fats and fried foods.
Bibliography
- MEDSCAPE. Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia. Available at: <https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/178757-overview>. Accessed on 02 Jul 2019
- STRASINGER, Susan K.; DI LORENZO, Marjorie S. Urianalysis and body fluids. 5 ed. United States: E. A Davis Company, 2008. 68-69.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13