Audiometry is a hearing test that serves to evaluate a person’s hearing ability in interpreting sounds and words, allowing the detection of important hearing changes, especially in people who work in very noisy environments.
There are two main types of audiometry exams: tonal and vocal. Tonal allows you to know what range of frequencies the person can hear, while vocal focuses more on the ability to understand certain words.
This exam must be carried out in a special booth, isolated from noise, lasts around 30 minutes, does not cause pain and is generally carried out by a speech therapist.
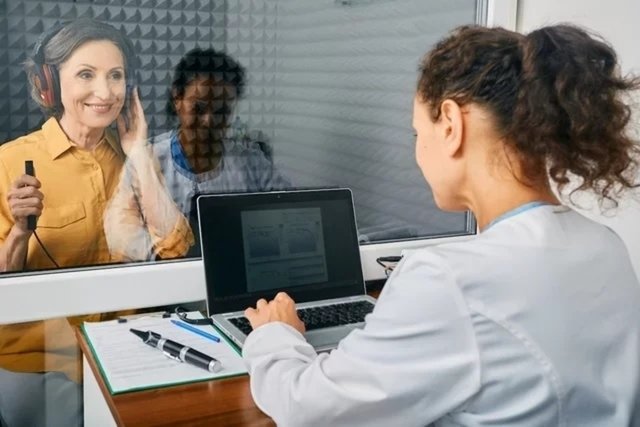

Main types of audiometry
There are two main types of audiometry, which are:
1. Audiometria tonal
Pure tone audiometry is an exam that evaluates a person’s hearing capacity, allowing them to determine their lower and upper hearing threshold, in a frequency spectrum that varies between 125 and 8000 Hz.
The auditory threshold is the minimum level of sound intensity that is necessary so that the pure tone can be perceived half of the times it is presented, for each frequency.
2. Vocal audiometry
Vocal audiometry assesses a person’s ability to understand certain words, to distinguish certain sounds, which are emitted through headphones, with different sound intensities. In this way, the person must repeat the words spoken by the examiner.
How to prepare for the exam
No special preparation is required to take this exam. However, in some cases, it may be recommended that the person avoids being exposed to loud and constant noise for the 14 hours beforehand.
How audiometry is performed
The audiometry exam takes place inside a cabin isolated from other noises that could interfere with the exam. The person uses special headphones and must indicate to the speech therapist, by raising a hand, for example, when they hear sounds, which can be emitted at different frequencies and alternately to each ear.
This exam does not cause any pain and lasts approximately half an hour.
Exam result
There are different types and degrees of hearing loss, so the inability to hear pure sounds below 25 dB indicates some hearing loss.
In detailed audiometry, hearing is normal when it is possible to hear sounds from 250 to 8000 Hz at 25 dB or less.
The amount and type of hearing loss can help guide the possible cause and the possibility of recovering hearing. Some diseases that may be associated with hearing loss are labyrinthitis, Meniere’s syndrome, perforated eardrum or acoustic trauma due to very loud sounds, for example.
How to prevent hearing loss
To prevent hearing loss, it is important to follow some WHO recommendations, such as:
- Keep the volume of audio devices low;
- Use well-fitting headphones and, if possible, with noise cancellation;
- Use earplugs in noisy places.
Exposure to loud sounds causes temporary hearing loss or ringing in the ears. However, prolonged or repeated exposure can cause permanent hearing damage, leading to irreversible hearing loss.
Bibliography
- MOUNT SINAI. Audiometry. Disponível em: <https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/tests/audiometry#:~:text=Audiometry%3B%20Hearing%20test%3B%20Audiography%20(,nerves%20of%20the%20inner%20ear.>. Acesso em 04 out 2023
- CDC. Audiometry procedures manual. 2003. Available at: <https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/nhanes_03_04/AU.pdf>. Accessed on October 4, 2023
- WHO. Occupational health: hearing measurement. 2022. Disponível em: <https://www.who.int/es/news/item/02-03-2022-who-releases-new-standard-to-tackle-rising-threat-of-hearing-loss>. Acesso em 04 out 2023

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13