CMPA is a food allergy to one or more proteins present in cow’s milk, such as casein, lactoglobulin, lactalbumin, serum albumin and immunoglobulins, which occurs mainly when the baby or child ingests or has contact with cow’s milk.
Also known as allergy to cow’s milk protein, APLV can occur immediately or after a few hours or days, after ingestion or contact with products containing this protein, causing the appearance of signs and symptoms, such as hives, vomiting, diarrhea and child growth retardation. Learn about other symptoms of food allergies in children.
CMPA usually appears in babies and children, because the immune system is still developing at this stage of life, however, in rarer cases, it can also appear in adults. The diagnosis of CMPA must be made by a doctor by evaluating the signs and symptoms, carrying out the food intolerance test and the exclusion test, for example.
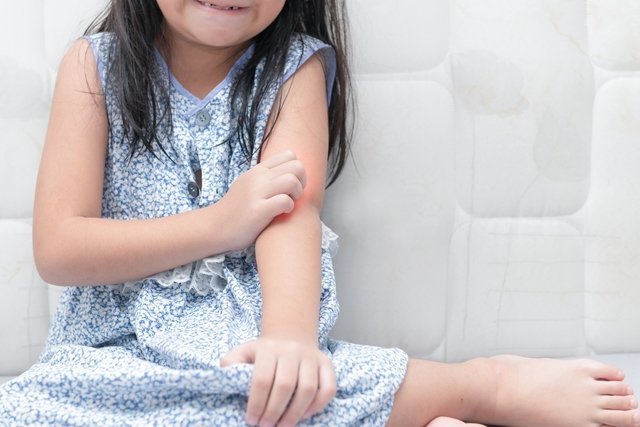
Main symptoms
The symptoms of CMPA after consuming cow’s milk vary according to the type of immune system reaction, and may appear immediately after, or up to a week after, ingestion or contact with cow’s milk.
1. Symptoms of immediate reactions
Symptoms of immediate reactions to CMPA occur within a few minutes or, at most, up to 2 hours after ingestion or skin contact with cow’s milk and include:
- Redness, inflammation and itching of the skin;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Diarrhea;
- Dor abdominal;
- Cough or wheezing;
- Runny nose and stuffy nose;
- Itchy eyes and watering.
Furthermore, in more serious cases, symptoms such as difficulty breathing, shortness of breath and a feeling of discomfort in the throat may also appear, which is a situation known as anaphylactic shock and must be treated immediately to avoid further complications. See how to identify anaphylactic shock and find out what to do.
2. Symptoms of delayed reactions
Late CMPA reactions may appear hours or days after ingestion or skin contact with cow’s milk, causing the following signs and symptoms:
- Stools with the presence of blood;
- Reflux;
- Constipation;
- Inflammation in the esophagus;
- Anemia;
- Inflammation in the intestine;
- Inflammation in the lungs.
Furthermore, other signs, such as irritability, decreased appetite and decreased growth, may also appear in a late reaction to CMPA.
Online symptom test
To find out the chances of your baby having an allergy, please indicate the symptoms below:
This test is a tool that serves as a means of guidance only. Therefore, it is not intended to provide a diagnosis or replace consultation with an allergist, immunologist or pediatrician.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of APLV must be made by a general practitioner, or pediatrician, by evaluating the signs and symptoms presented after consuming products with cow’s milk. The doctor may also order some tests, such as a blood test and an allergy skin test, a test that involves placing substances that can cause allergies on the arm or forearm to check for signs of allergies on the skin. Understand how allergy skin testing is done.
In addition, the doctor can also perform exclusion tests, where specific foods are removed from the diet to see if the signs and symptoms improve, until the food that is causing the allergy is identified.
If signs improve with the removal of cow’s milk from the diet, the doctor may also perform an oral provocation test, which is an assessment where the child consumes small amounts of milk in a hospital and symptoms are observed.
It is important to remember that the diagnosis of APLV can take from 3 days to 4 weeks, because it depends on the severity of the allergy and the speed with which symptoms appear and disappear.
How the treatment is carried out
CMPA treatment must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor, where it is recommended to exclude cow’s milk and its derivatives, such as ice cream, cheese, butter and cakes, from the diet. In the case of children, the pediatrician should recommend infant formulas that do not contain cow’s milk.
The pediatrician may recommend some supplements to avoid vitamin and mineral deficiencies, which can cause diseases such as scurvy, which is a lack of vitamin C, or beriberi, a type of anemia caused by a lack of vitamin B1, for example.
Can a baby be allergic to its mother’s milk?
Babies who are fed exclusively with breast milk may also present symptoms of CMPA, as part of the protein in cow’s milk consumed by the mother passes into breast milk, causing allergies in the baby. In these cases, the mother is advised to exclude products with cow’s milk and dairy products from the diet.
Difference between lactose intolerance and CMPA
Lactose intolerance is a syndrome where the intestine does not produce lactase, which is the enzyme responsible for digesting lactose, the sugar present in milk and dairy products, causing symptoms such as excess gas, cramps and diarrhea, for example. Discover the main symptoms of lactose intolerance.
In APLV, in addition to gastrointestinal symptoms, the person may also present symptoms similar to an allergy, such as redness and itching of the skin, runny nose, blocked nose and, in more severe cases, may have difficulty breathing, shortness of breath and a feeling of discomfort in the throat, a condition known as anaphylactic shock.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13