Aphthous stomatitis is the frequent appearance of canker sores, blisters or ulcerations in the mouth, and is more common in babies, children or people who have a weakened immune system.
Canker sores and wounds from aphthous stomatitis can, in some cases, appear every 15 days and can be triggered by stress, hormonal changes or changes in the immune system, and can also occur due to mineral and vitamin deficiencies, especially vitamin B12.
The treatment of aphthous stomatitis must be guided by the dentist or doctor according to its cause, severity of symptoms and frequency with which they occur, and improved oral hygiene or use of anti-inflammatory or anesthetic medications, for example, may be recommended.
Sensitive content
This image may contain content that is uncomfortable for some people.
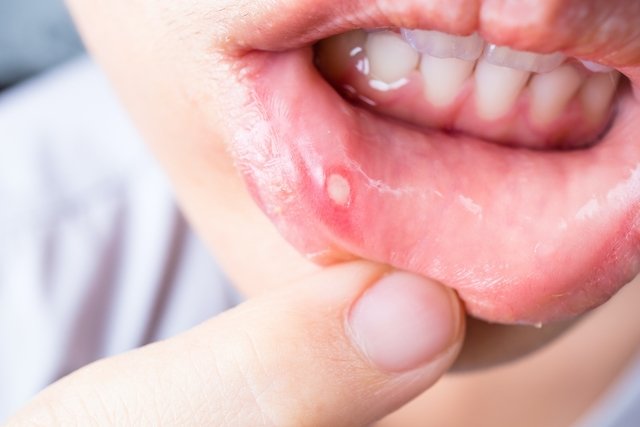
Main symptoms
The main symptom of aphthous stomatitis is the appearance of canker sores, blisters or sores in the mouth that are oval in shape and less than 1 cm in diameter. Canker sores and wounds can be painful, make it difficult to drink and eat, and can cause greater sensitivity in the mouth.
Although stomatitis appears more easily on the lips, in some cases it can also appear on the roof of the mouth, throat and gums, which can be even more uncomfortable. Learn about other symptoms of stomatitis.
Possible causes
Aphthous stomatitis can appear at any time, without there being a triggering factor. However, some situations can favor the appearance of canker sores and wounds in the mouth, the main ones being:
- Family history of the disease;
- Trauma to the mouth, lips, roof of the mouth, throat and gums;
- Poor oral hygiene;
- Virus infection, such as the herpes virus;
- Hormonal changes, which are more common in women;
- Nutritional deficiencies, mainly folic acid and vitamin B12;
- Changes in the immune system, as in the case of autoimmune diseases and HIV infection, for example;
- Celiac disease;
- Emotional or physical stress;
- Exposure to toxins, such as nitrates;
- Smoking habit.
Furthermore, aphthous stomatitis can be caused by an allergy to sodium lauryl sulfate present in toothpaste or mouthwash, or due to greater sensitivity to foods, such as cinnamon, cheese or citrus fruits, for example.
Types of stomatitis
According to the characteristics, size and quantity of canker sores that form in the mouth, stomatitis can be classified into:
1. Aphthous stomatitis of the minor type
This type of stomatitis is the most common and is characterized by small canker sores, measuring approximately 10 mm, which generally take between 10 and 14 days to disappear and heal. In this type of stomatitis, the canker sores have a rounded shape, gray or yellowish in color and reddish edges.
2. Aphthous stomatitis of the major type
This type of stomatitis causes larger canker sores, which can reach 1 cm in size and can take days to months to completely heal due to their size. This type of stomatitis is less common, and when canker sores appear, they appear in smaller quantities, leaving scars in the mouth.
3. Herpetiform stomatitis
In the case of herpetiform stomatitis, the canker sores appear in outbreaks, they are normally very small, ranging from 1 to 3 mm in size and generally appear in large numbers, with 100 canker sores occurring per episode.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of aphthous stomatitis is made by the dentist or general practitioner through the assessment of the lesion in the mouth, the frequency with which the aphthous ulcers appear and their characteristics, in addition to checking which factor favors the appearance of stomatitis, which are generally not necessary exams.
However, when aphthous stomatitis is severe, persistent or appears frequently, the doctor may order blood tests as they allow them to identify the cause of the symptoms, such as vitamin B12, folic acid or iron deficiency, or neutropenia, which is the weakening of the immune system.
In addition, the doctor may order other tests to diagnose diseases that can cause aphthous stomatitis, such as anti-endomysial antibodies and anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies, to detect celiac disease, or an HIV test.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for aphthous stomatitis must be guided by a doctor or dentist with the aim of relieving symptoms such as pain and discomfort, in addition to helping ulcers heal.
Therefore, some anti-inflammatory medications, such as triamcinolone, anesthetics, such as benzocaine, or antiseptics, such as chlorhexidine or hydrogen peroxide, for example, may be recommended to be used directly on the cold sore, according to the doctor’s instructions.
In the case of severe or recurrent aphthous stomatitis, treatment with laser application can be carried out by the dentist. In cases of nutritional deficiency, the doctor or nutritionist may recommend the use of nutritional supplements.
In addition, it may also be recommended to use natural and homeopathic remedies such as quercetin, red mangrove bark extract, licorice extract or propolis that help reduce the symptoms presented. Check out other natural remedy options for stomatitis.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13