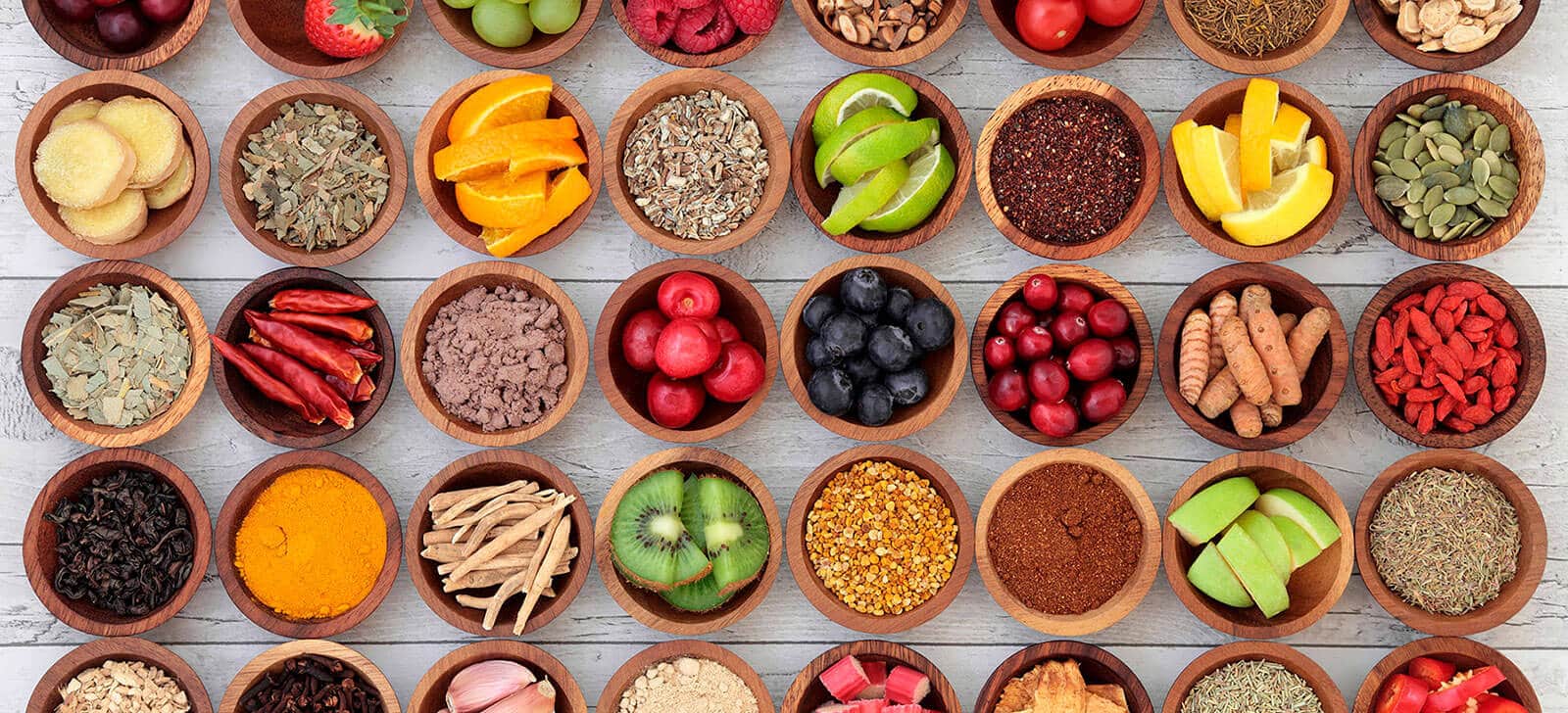
The Antioxidant, in general, is a molecule capable of acting against the action of free radicals, thus preventing the oxidation of cells.
Do you know what an antioxidant is? We can define it, in a simplified way, as a molecule that acts against the action of free radicals. Therefore, it is responsible for remedying or preventing cell oxidation from occurring, thus preventing them from causing possible damage to health or premature aging.
It is important to remember that currently, due to the large consumption of foods with chemical additives and exposure to stress, the consumption of foods rich in antioxidants becomes increasingly necessary. In fact, these are two main factors that contribute to cell oxidation.
So, are you curious to know how antioxidants act in our body? What are its types, functions and in what foods can we find it? So, continue reading and we, at Àrea de Mulher, will explain everything to you.
What is an Antioxidant?

Antioxidants are substances present in our body and in foods, whose main role is to protect healthy cells against the oxidizing action of free radicals.
But after all, what are free radicals? They can be defined as oxygen atoms, which are released during breathing or when food is corrupted in cells to produce energy.
When in excess in the body, free radicals can cause changes in cell membranes, modification of DNA and aging. Its increase may occur due to smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, consumption of foods with chemical additives, etc.
Main functions:
- Antioxidants neutralize the action of free radicals;
- Prevent oxidative stress;
- It is anti-inflammatory;
- Antioxidant contributes to skin health and rejuvenation;
- Helps protect against sun damage;
- They help prevent heart disease.
Types of non-enzymatic system antioxidants:

Beta-carotene and lycopene: They are natural dyes present in fruits and vegetables, associated with the prevention of carcinogenesis and atherogenesis, as they protect cells, such as lipids, proteins and DNA, from undergoing oxidation. Furthermore, they are precursors of vitamin A.
Flavanoides: set of substances produced by plants to help protect against solar radiation and combat pathogenic organisms.
Vitamina A (retinol): Capable of combining with free radicals, before they cause damage to the body.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid): Capable of fighting free radicals in an aqueous environment, such as what exists inside the cell.
Copper: Influence on the action of the superoxide dismutase enzyme, therefore, is essential for the proper functioning of the endogenous self-defense system.
Zinc: Like copper, it acts on the enzyme superoxide dismutase.
Vitamin E (tocopherols): Soluble in fat, therefore, it acts to protect cell membranes (formed by lipids) from the action of free radicals. In addition, it protects lipoproteins, which act in the transport of cholesterol.
Glutathione: Considered the most powerful antioxidant in the body, glutathione has the ability to enhance the action of antioxidants such as vitamins C and E, coenzyme Q10 and alpha lipoic acid.
List of foods rich in antioxidants

Turmeric: Also known as turmeric, turmeric is rich in antioxidants that help prevent cardiovascular diseases.
Cocoa: Rich in substances that contribute to heart health and circulation (polyphenols).
Carrot: A source of beta-carotene, carrots help prevent diseases, such as macular degeneration, cataracts and blindness.
Green Tea: Helps prevent cellular damage that promotes the development of tumors.
Flaxseed: Contains antioxidants that strengthen the immune system. Therefore, it reduces the chances of diseases in general.
Coconut oil: Rich in vitamin E, coconut oil is essential against cell aging. Furthermore, it helps in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases.
Red fruits: Cherry, strawberry, raspberry and blueberry are fruits rich in protoanthocyanidin, an antioxidant that strengthens blood and lymphatic vessels. Therefore, it improves circulation.
Tomato: Rich in lycopene, tomatoes reduce the risk of developing prostate, lung and stomach cancer.
Garlic: It helps reduce blood pressure and lower bad cholesterol levels and increase good cholesterol levels.
Astaxanthin: Considered the most powerful antioxidant in the world, astaxanthin works to eliminate free radicals, without any negative effects or pro-oxidant activity.
Curiosities about: Myth or truth?

Are free radicals villains? Myth! Radicals perform essential metabolic functions, such as converting nutrients from food into energy. However, they must have normal levels in the body.
Does food help with oxidative stress? True! When inappropriate, the diet can act as a pro-oxidant, thus favoring oxidative stress. However, on the other hand, a diet with adequate portions of vegetables and fruits helps to neutralize the action of free radicals.
Does oxidative stress cause the development of disease? True! The imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants can cause chronic inflammation in the body, which is responsible for diseases such as obesity, rheumatoid arthritis, cancer and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Are there supplements rich in antioxidants? True! Some supplements have bioactive compounds with antioxidant functions in their composition. However, they should only be consumed with the prescription of a professional.
The more antioxidants the better? Myth! In fact, free radicals have important roles to play in the body.
Are all antioxidants the same? Myth! Each one has a role in the functioning of our body.
Do foods lose antioxidants when cooked? True! However, it all depends on the type of food.
So, what did you think of this article? Take the opportunity to check out: Juice for immunity – What they are, how to make them and the best foods.
Scientific references:
Antioxidant Properties and Nutritional Composition of Matcha Green Tea
Free radicals and the main antioxidants in the diet. Nutrition Magazine
Astaxanthin decreased oxidative stress and inflammation and enhanced immune response in humans
Sources: Ecycle, Ocean Drop, Saúde Abril.
Image sources: Nova Natural, Brainstorm, Imeb, Natural Herb,Eycle.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13