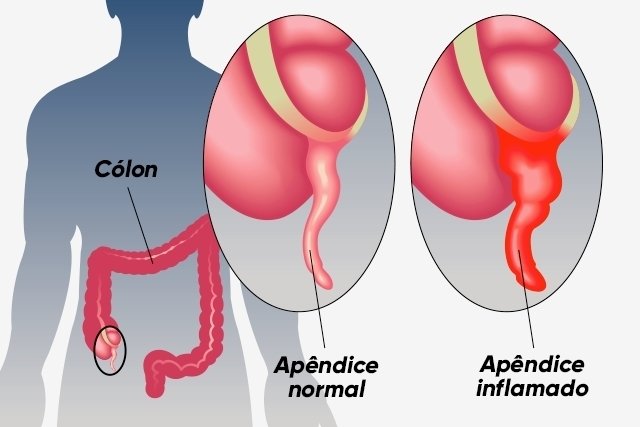
Acute appendicitis is inflammation of the cecal appendix, which is a small structure located on the right side of the abdomen and is connected to the large intestine. This condition normally occurs due to obstruction of the organ mainly by feces, resulting in symptoms such as abdominal pain, low fever and nausea, for example.
Due to the obstruction, there may also be a proliferation of bacteria, also characterizing an infectious condition that, if not treated correctly, can develop into sepsis. Understand what sepsis is.
If appendicitis is suspected, it is important to go to the hospital as quickly as possible, as the appendix may perforate, characterizing suppurative appendicitis, which can put the patient at risk. Learn more about appendicitis.
Main symptoms
The main symptoms of acute appendicitis are:
- Abdominal pain on the right side and around the navel;
- Abdominal distension;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Colic;
- Low fever, up to 38ºC, unless there is a perforation of the appendix, in which case there is a high fever;
- Loss of appetite.
In the presence of signs and symptoms indicative of acute appendicitis, it is important to consult a gastroenterologist or general practitioner so that the diagnosis can be made and the most appropriate treatment can be initiated. See more about the symptoms of appendicitis.
Symptom Test
Select your symptoms from the test below and see your risk of having appendicitis:
How the diagnosis is made
The diagnosis of acute appendicitis is made by the surgeon or general practitioner, initially carrying out an assessment of the signs and symptoms presented by the person and a physical examination. In addition, the doctor may recommend carrying out laboratory tests, such as a blood count and urine test.
To confirm appendicitis, the doctor may recommend computed tomography and abdominal ultrasound to evaluate the structure of the appendix and identify inflammatory signs.
Possible causes
Acute appendicitis is mainly caused by obstruction of the appendix by very dry stools. But it can also happen due to the presence of intestinal parasites, gallstones, enlarged lymph nodes in the region and traumatic injuries to the abdomen, for example. Furthermore, acute appendicitis can occur due to genetic factors related to the position of the appendix. See more causes of appendicitis.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for acute appendicitis usually involves surgical removal of the appendix in order to avoid complications and possible infections. The length of stay is 1 to 2 days, with the patient being released to practice physical exercises and other daily activities 3 months after surgery. Find out how surgery for appendicitis is performed.
The doctor also often recommends the use of anti-inflammatories and antibiotics before and after surgery.
Complications of acute appendicitis
If acute appendicitis is not identified quickly or treatment is not carried out correctly, there may be some complications, such as:
- Abscess, which is excess pus accumulated around the appendix;
- Peritonitis, which is inflammation of the abdominal cavity;
- Hemorrhage;
- Bowel obstruction;
- Fistula, in which an abnormal connection occurs between an abdominal organ and the surface of the skin;
- Sepsis, which is a serious infection of the entire body.
These complications usually occur when the appendix is not removed in time and ruptures.
Bibliography
- BLEARS, E. E.; et al. Review of Operative vs. Non-Operative Management of Appendicitis in Pregnancy. Surgery Curr Res. 7. 2, 2017
- GLASS, C. C.; RANGEL, S. J. Overview and diagnosis of acute appendicitis in children. Semin Pediatr Surg. 25. 4; 198-203, 2016
- MORIS, D.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Acute Appendicitis in Adults: A Review. JAMA. 326. 22; 2299-2311, 2021
- APTILON DUQUE, G.; MOHNEY, S. IN: STATPEARLS (INTERNET). TREASURE ISLAND (FL): STATPEARLS PUBLISHING. Appendicitis in Pregnancy. 2021. Available at: <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551642/>. Accessed on May 17, 2022
- BHANGU, A.; et al. Acute appendicitis: modern understanding of pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. Lancet. 386. 10000; 1278-128, 2015
- SWENSON, D. W.; et al. Practical Imaging Strategies for Acute Appendicitis in Children. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 211. 4; 901–909, 2018
- JONES, M. W.; LOPEZ, R. A.; DEPPEN, J. G. IN: STATPEARLS (INTERNET). TREASURE ISLAND (FL): STATPEARLS PUBLISHING. Appendicitis. 2021. Available at: <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493193/>. Accessed on May 17, 2022
- NHS. Appendicitis. Available at: <https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/appendicitis/>. Accessed on March 5, 2019

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13