Otitis media is an inflammation of the ear that can occur due to the presence of viruses or bacteria, being common after a cold or sinusitis attack, for example. But otitis media can also appear as a result of trauma or allergies, for example.
Due to inflammation in the ear, it is possible to notice symptoms such as ear pain, the presence of yellow or whitish discharge in the ear canal, fever and irritability.
In the presence of signs and symptoms indicative of otitis, it is important to consult a pediatrician, in the case of children, or an otorhinolaryngologist, in the case of adults, to confirm the diagnosis and initiate the most appropriate treatment, which can be done with medication to alleviate symptoms. or antibiotics.
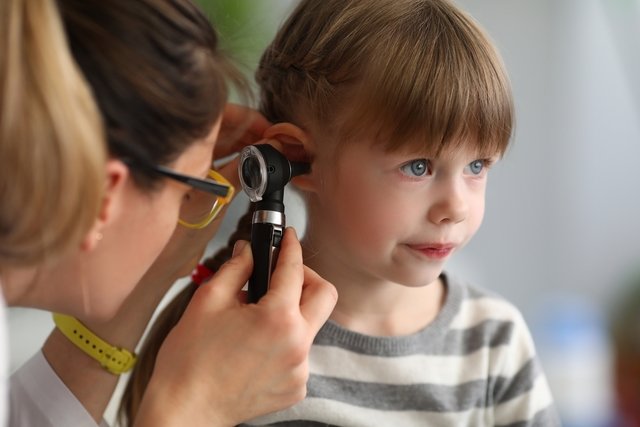

Symptoms of otitis media
The main symptoms of otitis media are:
- Secretion or accumulation of fluid in the ear;
- Decreased hearing;
- Ear pain;
- Fever;
- Irritability;
- Redness;
- Perforation of the eardrum, in some cases, with the presence of pus noted;
In the case of a baby, it can be suspected that he has otitis when the baby often puts his hand on his ear, becomes more irritable, cries a lot and has difficulty sleeping, for example, and it is important that the pediatrician is consulted.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis is made by evaluating the signs and symptoms and carrying out a physical examination, which consists of observing the ear with equipment called an otoscope. This way, it is possible to observe any changes in the ear and recommend the most appropriate treatment to combat inflammation and promote symptom relief.
When to make an appointment
It is advisable to make an appointment with an otorhinolaryngologist when there are symptoms suggestive of otitis, especially if they are very intense or accompanied by a fever. In the case of a child, you can also consult your pediatrician.
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
Types of otitis media
Otitis media can also be divided into different types according to the signs and symptoms present, duration of symptoms and frequency with which they occur:
- Acute otitis media: is the most common form, with the rapid onset of signs and symptoms, such as ear pain and fever, caused by acute middle ear infection;
- Recurrent acute otitis media: is acute otitis media that repeats for more than 3 episodes in 6 months or 4 episodes in 12 months, generally due to the same microorganism that proliferates again or due to new infections;
- Serous otitis media: also called otitis media with effusion, is the presence of fluid in the middle ear, which can remain for several weeks to months, without causing signs or symptoms of infection;
- Chronic suppurative otitis media: is characterized by the presence of persistent or recurrent purulent secretion, together with perforation of the tympanic membrane.
To differentiate between these types of otitis, the doctor usually carries out a clinical evaluation, with a physical examination, observation of the ear with an otoscope, in addition to evaluating the signs and symptoms.
Find out more about the main types of otitis.
Possible causes
Otitis media usually occurs as a result of the flu, cold or sinusitis and is therefore mainly caused by viruses and bacteria. The main viruses related to otitis media are Influenza, respiratory syncytial virus and rhinovirus, while the most common bacteria are Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae e Moraxella catarrhalis.
However, this type of otitis can also be triggered by other situations, such as allergies, reflux, fungal infection or anatomical changes in the ear, but these causes are rarer.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for otitis media may vary depending on the symptoms presented and the cause. Typically, the doctor recommends the use of medicines to relieve symptoms, such as dipyrone and ibuprofen, for example.
If otitis media is associated with the flu, cold or allergy, the doctor may also prescribe decongestants and antihistamines.
If the presence of an infection is verified, the use of antibiotics for 5 to 10 days may be recommended, such as Amoxicillin, for example, which is generally used when symptoms persist even after starting treatment with other medicines, if there are changes when examining the tympanic membrane, if the eardrum is perforated or if the symptoms are very intense.
Read too: 8 remedies for otitis (and how to use them)
Depending on the type and severity of otitis, treatment may also involve surgery to drain fluid from the ear, or tympanoplasty, in the case of perforation of the eardrum.
Home Treatment Options
During the treatment indicated by the doctor, and never replacing it, some measures can be taken at home to speed up recovery and alleviate symptoms, such as:
- Drink plenty of fluidsstaying hydrated throughout the day;
- Stay homeavoiding exercise or exhausting activities;
- Eat a healthy and balanced dietwith a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, grains and seeds, as they are rich in omega-3 and other nutrients that help to better recover from inflammation;
- Make a warm compress in the outer region of the ear, it can help relieve pain.
Furthermore, you should never drip any product into the ear, except those recommended by your doctor, as this can worsen inflammation and harm recovery.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13