Obesity is a chronic disease that can increase the risk of developing diseases, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, heart attack, some types of cancer or osteoarthritis of the bones, in addition to psychological changes, such as depression and anxiety.
Obesity can be caused by several factors, such as excessive food consumption, lack of physical activity, but it can also be related to psychological issues, genetic predisposition and hormonal changes.
Read too: 10 main causes of obesity (and what to do)
Therefore, if obesity is suspected, it is important to consult an endocrinologist, general practitioner or pediatrician, so that a complete assessment can be carried out and appropriate treatment can be indicated, which can be done by changing eating habits, physical activity practices, use of medications and bariatric surgery.
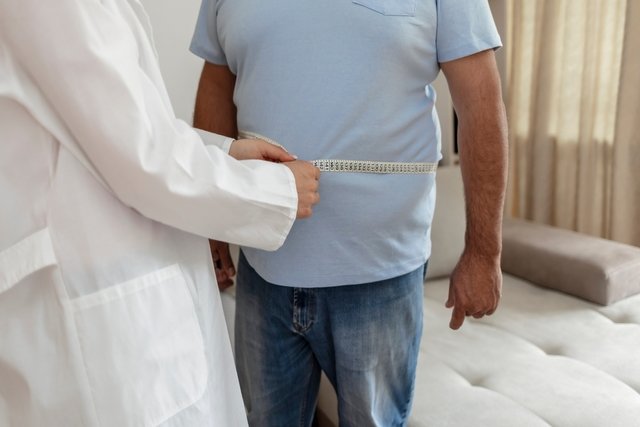
Symptoms of obesity
A person with obesity may not present symptoms, especially if it is classified as grade 1, or mild.
However, some parameters can be used to assess obesity, such as body mass index (BMI), which is a calculation that allows you to assess whether a person is within the weight considered ideal for their height.
Furthermore, another parameter is the excessive distribution of body fat, which can be checked by measuring waist circumference.
How to calculate BMI
To calculate BMI, enter your data into the calculator:
It is important to note that BMI estimates, but does not directly measure, body fat. Thus, people with a lot of muscle mass, such as athletes, for example, may have a BMI in the overweight range, even if they do not have excess body fat.
Degrees of obesity
According to BMI, obesity is classified into different degrees:
- Grade 1 obesity or mild obesity: BMI between 30.0 – 34.9 kg/m2;
- Grade 2 obesity or moderate obesity: BMI between 35.0 – 39.9 kg/m2;
- Grade 3 obesity or severe or morbid obesity: BMI equal to or greater than 40 kg/m2.
This classification is only recommended for adults, as there are specific calculations for children and adolescents.
Read too: Morbid obesity (grade 3): what it is, symptoms, causes and treatment
Types of obesity
There are two types of obesity, depending on the distribution of fat throughout the body: peripheral obesity, or gynoid, where body fat accumulates in the hip and thigh region, where the hips are almost rounded and the buttocks are larger compared to other people.
In abdominal obesity, or android obesity, fat is deposited mainly in the abdomen and waist, and may also appear in other parts of the body, such as the trunk, neck, neck and shoulders. This type of obesity is linked to a higher risk of diseases such as type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome and heart disease.
Child obesity
Childhood obesity is excessive weight gain during childhood, which can cause low self-esteem and complications such as type 2 diabetes, knee pain, sleep apnea and easy tiredness.
Generally, childhood obesity is caused by unhealthy eating habits and an inactive lifestyle, but it can also arise due to hormonal imbalances or specific genetic syndromes, in some cases.
Read too: Childhood obesity: what it is, causes, treatment and how to avoid it
Obesity in adolescence
Thus, like childhood obesity, obesity in adolescence can also cause low self-esteem, in addition to causing health problems, such as diabetes, fatty liver and depression.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of obesity can be made by an endocrinologist, pediatrician or general practitioner, by evaluating the signs and symptoms presented, and the person’s health history, in addition to weight, height and BMI calculation.
If you think you may be obese, make an appointment with the specialist closest to you:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor also assesses the percentage of body fat, using tools such as bioimpedance, abdominal circumference, waist-hip ratio and blood tests, such as TSH, free T4, cholesterol, glucose and cortisol.
Read too: Waist-hip ratio (WHR): what it is and how to calculate it
Is obesity a disease?
Although it is considered, by some people, as a lack of willpower, obesity is a chronic disease caused by several factors and which can be associated with or cause other diseases, therefore requiring medical treatment.
Main causes
The main causes of obesity are:
- Bad eating habits;
- Lack of physical exercise;
- Psychological problems, such as anxiety and stress;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Hormonal changes
Furthermore, the use of some medications, such as corticosteroids, anticonvulsants and antipsychotics, can also, as a side effect, increase the risk of obesity. Learn more about the causes of obesity.
How the treatment is carried out
Obesity treatment is carried out by a multidisciplinary team, with an endocrinologist, nutritionist, psychiatrist and/or psychologist, and includes the use of medication, physical exercise, psychotherapy, diet and bariatric surgery.
1. Medicines
Some medications, such as sibutramine, orlistat, naltrexone with bupropion, liraglutide, semaglutide and tirzepatide may be recommended by your doctor to help with weight loss.
Read too: 16 weight loss remedies: pharmacy and natural
2. Healthy eating
The diet to treat obesity must be healthy and guided by a nutritionist, prioritizing natural foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, lean proteins and tubers. See how to eat healthy.
Furthermore, it is also important to reduce the intake of foods rich in fats and sugars, such as cookies, ice cream, ready-made sauces and meals like fast food, because they are generally rich in sugar and fat, increasing the calories in the diet.
3. Physical exercises
Practicing physical exercise, guided by a physical trainer, is essential to treat obesity, because it helps to increase daily caloric expenditure, in addition to maintaining health and preventing the emergence of other diseases.
Therefore, it is recommended to do 150 minutes of moderate intensity activities per week, which is equivalent to around 30 minutes 5 times a week, including cycling, swimming, dancing and weight training, for example.
Read too: 16 benefits of physical activity (and how to start)
4. Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, such as cognitive behavioral therapy, can help change the way a person thinks about food and eating and also help them recognize when and why they eat. Learn more about cognitive behavioral therapy.
5. Bariatric surgery
In the most serious cases, the doctor may recommend bariatric surgery, a type of stomach reduction surgery, which reduces the amount of food tolerated by the stomach or modifies the natural digestion process, reducing the amount of calories absorbed, making it easier. thus, weight loss.
However, as it is a procedure that, in most cases, is quite invasive, bariatric surgery is generally indicated as a treatment only when other forms of treatment have already been tried and the expected results have not been obtained, or when excess weight puts a person’s life at risk.
Read too: Bariatric surgery: types, when to do it, advantages and risks
Consequences of obesity
The possible health consequences of obesity are:
- Cardiovascular diseases, such as high blood pressure, heart attack, stroke and thrombosis;
- metabolic diseases, such as type 2 diabetes and high cholesterol;
- Liver diseases, such as fatty liver and cirrhosis;
- Increased risk of some types of cancer, such as breast, intestine, liver and pancreas;
- Dermatitis and fungal infectionsdue to the accumulation of sweat and dirt in the folds of the body;
- Greater tendency to varicose veins and venous ulcersdue to changes in vessels and blood circulation.
- Impotence and infertilitydue to hormonal changes and difficulties in blood flow in the vessels;
- Acantose nigricans, which are dark spots on the neck, armpits and groin, a reaction caused by insulin resistance, or pre-diabetes;
- Nighttime snoring and sleep apneadue to the accumulation of fat in the neck and respiratory tract;
Furthermore, obesity can also cause lymphedema, body pain, especially in the back, legs, knees and shoulders, difficulty exerting effort or walking, anxiety and depression, due to dissatisfaction with body image and binge eating.
How to avoid obesity
Some tips to avoid obesity are: maintaining a healthy diet, reducing your intake of ultra-processed foods, exercising regularly, balancing stress and getting a good night’s sleep.
How to avoid childhood obesity
To avoid childhood obesity, it is recommended that parents or guardians encourage the practice of physical activities and active games in groups, for example, which help with socialization, energy expenditure and emotional balance.
Furthermore, it is also recommended to limit the intake of unhealthy foods, such as sweets and meals like fast-food and time spent using screens such as cell phones, televisions or tablets.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13