Leukemia is a cancer that affects white blood cells, or leukocytes, which are the body’s defense cells, causing their uncontrolled production by the body and symptoms such as fever, night sweats, weight loss, purple spots on the skin and tiredness.
Although the cause of leukemia is not completely known, the risk is higher especially in people with a genetic predisposition and a history of exposure to radiation or benzene.
If leukemia is suspected, it is important to consult a hematologist or oncologist. Treatment may involve chemotherapy, radiation therapy or a bone marrow transplant, for example, depending on the type of leukemia and the person’s health history.
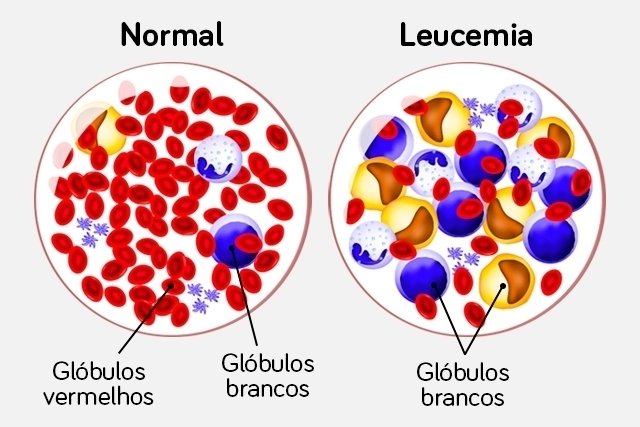
Types of Leukemia
There are more than 12 types of leukemia, but the main ones are:
1. Acute myeloid leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia is the most aggressive type and, although it is the most common acute leukemia in adults, the chance of a cure is greater, especially in younger people. Check out the symptoms of acute myeloid leukemia.
2. Acute lymphocytic leukemia
Acute lymphocytic leukemia is the most common type of leukemia in children, although it can also develop in adults. Furthermore, the chance of a cure is greater in children and adolescents, especially when it is identified and treated early. Understand better what acute lymphocytic leukemia is.
3. Chronic myeloid leukemia
It is more common in adults and develops slowly, causing no or few symptoms at first. Treatment can be carried out with the use of specific medications for life. Find out how chronic myeloid leukemia is treated.
4. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
It is a type of leukemia in which symptoms develop slowly and is more common in older people, especially men between 60 and 70 years of age. See the symptoms of chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
5. T or NK granular lymphocytic leukemia
This type of leukemia is slow-growing, but a small number can be more aggressive and difficult to treat.
6. Aggressive NK cell leukemia
It can be caused by the Epstein-Barr virus, affects adolescents and young adults, and is aggressive. Treatment is with chemotherapy.
7. Adult T-cell leukemia
It is caused by the virus (HTLV-1), a retrovirus similar to HIV, and is very serious. The treatment is not very effective but is carried out with chemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation.
8. Hairy cell leukemia
It is a type of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, which affects cells that appear to have hair, affects men more, and is not found in children.
Leukemia symptoms
The main symptoms of leukemia are:
- Fever;
- Night sweats;
- Weight loss without apparent cause;
- Frequent infections, such as colds and oral candidiasis;
- Pain in bones and joints;
- Purple spots on the skin;
- Bleeding from the nose or gums, for example;
- Discomfort or feeling of bloating in the abdomen;
- Excessive tiredness;
- Somnolence;
- Pallor;
- Waters in the body.
These symptoms are more common in types of acute leukemia, with chronic leukemias usually discovered in a routine exam, such as a complete blood count, as they cause few or no symptoms at the beginning. Check out the main symptoms of leukemia.
Symptoms of childhood leukemia
The most common symptoms of childhood leukemia are tiredness, paleness, fever, purple spots on the skin and swelling on the body. Especially in children, leukemia can affect the bones and joints, causing pain and difficulty walking. Find out more symptoms of childhood cancer.
Symptom Test for Leukemia
To find out the chances of having leukemia, please select the symptoms you present in the test below:
The symptom test is only a guidance tool and does not serve as a diagnosis or replace consultation with a pulmonologist, allergist or general practitioner.
What causes leukemia
The cause of leukemia is not fully known. However, leukemia is more common in people with a genetic predisposition, smokers, a history of exposure to radiation or benzene, viral infections and genetic syndromes such as Down Syndrome.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of leukemia is made by a hematologist or oncologist taking into account the symptoms present and test results, such as blood count, platelet count and blood smear analysis.
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
Especially in cases of suspected acute leukemia, it is common for the doctor to also recommend a bone marrow biopsy and/or myelogram to confirm the diagnosis. Understand what a myelogram is and what it is for.
Could high platelets be leukemia?
High platelets are not typically indicative of leukemia. Although platelet numbers may be high in some blood disorders, such as lymphoma or essential thrombocythemia, leukemia often causes low platelets. Check out other causes of high platelets.
Leukemia treatment
Treatment for leukemia depends mainly on the type of leukemia identified and the person’s health history, and can be done with:
1. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is one of the main treatments recommended for leukemia, being done by injecting specific cancer drugs directly into a vein or in pill form, to eliminate cancer cells.
During treatment, it may be necessary to stay in the hospital for a few days and use different medications in combination. In addition, chemotherapy may also need to be repeated every few weeks or months. See how chemotherapy is done.
2. Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy consists of the use of medications that strengthen the immune system with antibodies, which bind to cancer cells in the blood and bone marrow, allowing them to be eliminated by the body. Find out how immunotherapy works.
3. Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy uses drugs that specifically affect cancer cells while causing little or no harm to normal cells.
It may be indicated especially for chronic myeloid leukemia, in which there is a specific enzyme that causes cells to proliferate uncontrollably and is the target of some medications used in this treatment.
4. Radiotherapy
Although less used in treatment, radiotherapy for leukemia may be indicated in some cases to eliminate cancer cells from the body, especially before performing a bone marrow transplant, for example. Understand better what radiotherapy is.
5. Bone marrow transplant
Bone marrow transplantation in the treatment of leukemia consists of removing a part of the bone marrow from a healthy person and injecting it into the sick person, after undergoing chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy, to produce healthy blood cells. Find out when a bone marrow transplant is indicated.
Is leukemia curable?
Leukemia is curable in some cases, especially when it is identified early and treatment is started quickly. However, the chances of a cure also depend on the type of leukemia and the person’s health history, being higher especially in younger people.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13