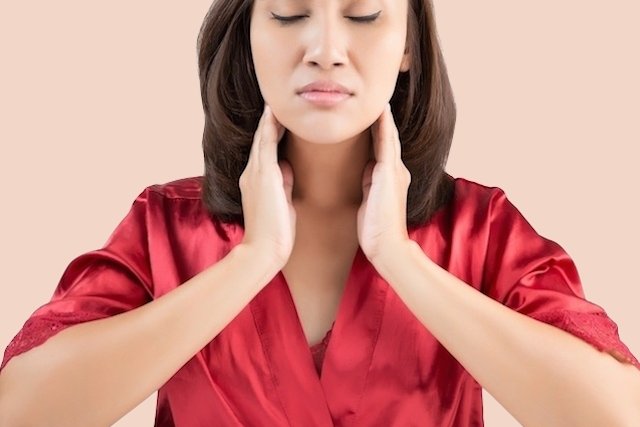
Lumpiness is the enlargement of lymph nodes, or lymph nodes, which usually occurs due to some infection or inflammation close to the region in which it appears, or even due to more serious conditions, such as cancer or autoimmune diseases, resulting in symptoms such as one or more small nodules or lumps under the skin, which may or may not be painful, and usually last between 3 and 30 days.
Swelling, also known as adenopathy or lymphadenopathy, is most common in the neck, groin or armpits, but it can also appear anywhere on the body, as lymph nodes are part of the immune system and act as filters for substances or microorganisms. , helping to fight infections.
Generally, the swelling improves within a few days, however, when it grows a lot, is located in various parts of the body or is accompanied by other symptoms, such as weight loss or night sweats, you should consult your general practitioner for tests to be carried out. The cause was identified and the most appropriate treatment was initiated.
Watch the video below with the main causes of ingua and what you should do:
Language symptoms
The main symptoms of ingua are:
- Lump under the skin, which can measure around 0.5 cm to 1 cm;
- Lump that moves when palpated;
- Increased sensitivity at the tongue site;
- Pain, which usually arises when there is inflammation or infection of the lymph node;
- Lump in the neck or jaw, sore throat or runny or blocked nose, due to infections in the upper respiratory system;
- Lumps in various parts of the body, due to systemic infections or autoimmune diseases.
Furthermore, in cases of cancer, several lumps can generally appear, which increase in size over time, in addition to being hard and accompanied by other symptoms such as night sweats, weight loss, fever or itchy skin.
It is important to consult a general practitioner or infectious disease specialist whenever symptoms of gallbladder appear, if they are multiple, and accompanied by other symptoms, so that their cause can be identified, in order to begin the most appropriate treatment.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of the lump is made by the general practitioner or infectious disease specialist by assessing the location and size of the lump, in addition to palpating the lump, checking whether it is hard or moving, and evaluating the associated symptoms.
In addition, the doctor must evaluate the health history, use of medications, lifestyle habits, and request tests to help identify the cause of the appearance of the tongue, such as complete blood count, metabolic panel, and serology for infectious diseases, such as syphilis, HIV or ganglionic tuberculosis, for example.
Other tests that the doctor may order are X-rays, computed tomography of the chest, abdomen or pelvis, and, in some cases, a biopsy of the affected lymph node. Find out how a biopsy is performed.
Most common locations of tongues
The most common places for tongues to appear are:
- Neck;
- Groin;
- Axillas?
- Jaw;
- Clavicle.
The location of the lump is important to help the doctor identify its cause, such as infections or inflammation close to the lump region. See other causes of lumps in the groin and armpits.
Main causes of language
Lymph nodes are spread across various regions of the body, but are generally noticed as lumps in the skin in more superficial areas, such as the neck, armpits, groin or jaw, for example.
The most common causes of ingua are:
1. Skin inflammation
Any type of inflammation can cause this lump, as the ganglia act as a filter against possible threats to the body. It is common for bumps to appear due to skin irritation due to the use of chemical substances, such as deodorant, or a small wound that occurs after waxing, folliculitis, ingrown hair or cuts that occur on a daily basis, in different places on the body. .
Inflammations that occur in the airways or oral region, such as allergic rhinitis, pharyngitis, gingivitis or inflammation of a tooth, for example, are also important causes of swelling in the neck or jaw. See other causes of swelling in the neck.
2. Infections
Any type of infection causes waterlogging, and some of the most common are colds, flu, otitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis, infectious mononucleosis, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, or any type of virus, such as Zika or dengue, for example, which cause the emergence of lump on the neck, back of the head, jaw or behind the ear. See other causes of a lump on the back of the neck.
Furthermore, COVID-19 infection can also lead to swelling in the neck or back of the head, and in cases of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children, swelling can also appear in the neck, armpits, groin or any other part of the body.
Other types of infection such as pneumonia or bronchitis can also cause lumps in the armpits, and, in addition, infections in the abdominal region, such as gastroenteritis, genital infections, such as HPV, syphilis, candidiasis or vaginosis, and in the legs or feet, due to small injuries, They typically cause lumps in the groin.
3. Autoimmune diseases
Diseases that interfere with immunity can also cause enlarged lymph nodes, and some examples are lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, vasculitis or inflammatory bowel disease.
4. Cancer
Cancer is a rarer cause of lymph nodes, which can appear anywhere in the body and have a more hardened appearance, which do not disappear after 1 or 2 months and do not stop growing.
Any type of cancer can cause swelling, but some of the most common are lymphoma, breast cancer and lung cancer, for example. Know how to identify all the symptoms of lymphoma, breast cancer and lung cancer.
Furthermore, swelling can also appear due to tumor metastases, which occur when cancer spreads to other regions of the body.
5. Vaccination
Some vaccines, such as the BCG vaccine, flu, herpes zoster or the vaccine against COVID-19, for example, can cause swelling in the armpit, as a response from the immune system to the immunization, stimulating the production of antibodies, or as an effect vaccine collateral. Find out how to alleviate the side effects of vaccines.
When should you go to the doctor
The presence of lumps becomes worrying, indicating more serious illnesses, such as cancer, lymphoma or lymph node tuberculosis, for example, when:
- It is located on the arms or around the collarbone;
- It is spread across various parts of the body;
- Measures more than 2.5 cm;
- It is hard and does not move;
- Does not improve after 1 month;
- It is accompanied by fever that does not improve within 1 week, night sweats, weight loss or malaise.
In these situations, you should consult your general practitioner or infectious disease specialist so that blood tests can be carried out to assess infections or inflammation in the body, or the presence of autoimmune diseases or cancer.
How the treatment is carried out
The treatment of swelling should be guided by the general practitioner or infectious disease specialist, according to the cause of the swelling.
To treat inflamed tongue, generally, only rest and hydration are recommended, in addition to identifying and eliminating what is causing it, as it is not necessary to take any specific medication to treat it. Furthermore, a good home remedy is to drink eucalyptus tea and use clay compresses, as they help to reduce inflammation and strengthen the body’s defenses. Check out the recipes for home remedies for sore throat.
However, if the swelling causes pain, discomfort or increased local sensitivity, the doctor may recommend the use of analgesic or anti-inflammatory medications, for example.
In cases of infections, the doctor may recommend the use of antibiotics, antifungals or antivirals, for example, to help fight the infection. If the swelling was caused by cancer, surgical removal of the ganglion or tumor that is causing the swelling may be recommended, in addition to chemotherapy or radiotherapy sessions.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13